
- Break big chunks of information into small, bite-sized pieces. ...
- Use checklists for tasks with multiple steps. ...
- Develop routines. ...
- Practice working memory skills. ...
- Experiment with various ways of remembering information. ...
- Reduce multitasking.
How can I improve my working memory capacity?
Although there’s no consensus on whether you can improve working memory capacity significantly through training, scientists agree that you can train your brain to use working memory resources better. The most effective option is to keep your memory sharp over the years by training your brain to retain information and be able to recall it at will.
How does information reach your working memory?
Information only reaches your working memory if it is given attention. If you make an effort to actively maintain the information, through repetition, evaluation, or other means, it will make its way into your working memory and maybe into your long-term memory.
Can you train your brain to improve memory?
Other research has shown that brain training delivers significant improvements in working memory if you commit to sticking with it. The first step to better working memory is to understand how memory works and to accept your limitations. That doesn’t mean saying, “Oh, I forgot,” to excuse yourself.
What are the functions of working or operative memory?
Thanks to working or operative memory, we are able to: 1 Integrate two or more things that took place close together. For example, remembering and responding to the information that was said during a conversation. 2 Associate a new concept with previous ideas. It allows us to learn 3 Retain information while we pay attention to something else. ...
What are working memory exercises?
What activities can improve working memory capacity?Write tasks down.Say it aloud.Throw a ball back and forth whilst discussing what to do.Draw the task.Use pictures to support verbal information.Demonstrate the task.
What is working memory and how do you improve it?
15 ways to better yourselfMake time for rest. Before you learn how to be better, it's important to start with the basics. ... Read more books. ... Start a gratitude practice. ... Learn a new language. ... Try meditation. ... Write in a journal. ... Nourish yourself with healthy foods. ... Add more movement to your life.More items...•
How much can working memory be improved?
Psychologists Bopp and Verhaeghen, for example, found that the working memory capacity of participants subjected to memory training tasks over a five-day period had expanded their working memory capacity from one to four items. These findings suggest that there isn't a set limit to the capacity of working memory.
What is an example of using your working memory?
Examples of using our working memory in our daily life include remembering someone's email address, asking for directions and remembering them until we reach our destination, learning the name of someone new and keeping it in mind throughout the conversation.
What causes poor working memory?
Developmental and intellectual disabilities like ADHD, autism, Down syndrome, Rett syndrome, and developmental language disorder commonly cause memory problems. Though some of these conditions may affect long-term and visual memory, they most often disrupt working memory.
Can you improve poor working memory?
Rather than there being a set limitation, working-memory capacity could improve through practice--suggesting that those with working-memory problems could improve their capacities through repetition.
Can reading improve working memory?
Well, the key to it all is in a well-trained memory, and training your memory begins with reading. Reading can improve your memory. It is a brain-stimulating activity that needs constant recall of words and meaning. It can improve short-term as well as your long-term memory as you take notes or discuss what you read.
How can students improve their working memory?
How to Improve Working MemoryBreak big chunks of information into small, bite-sized pieces. ... Use checklists for tasks with multiple steps. ... Develop routines. ... Practice working memory skills. ... Experiment with various ways of remembering information. ... Reduce multitasking.More items...•
Which of your everyday tasks require the most working memory?
Examples of everyday tasks that require working memory include:Listening to, remembering, and following directions that contain multiple steps.Remembering a question long enough to think about it and formulate an answer.Carrying out the steps to a recipe when no longer looking at the recipe.More items...
How can you improve working memory in the classroom?
Use visual reminders of the steps needed to complete a task. Provide opportunities to repeat the task. Encourage practice to increase the amount of information encoded into memory. Teach students to practice in short sessions, repeatedly throughout the day.
How is attention related to working memory?
The Relationship between Working Memory and Attention. Attention and working memory aren’t the same, but they’re closely linked. And both are key to learning and reasoning. Attention allows you to focus on information-processing relevant to your goals, and ignore distractions.
Why is working memory important in childhood?
During childhood, the capacity of working memory is a strong indicator of cognitive function development. It can even predict the future reasoning abilities of children. The slower processing ability during old age allows more time for the contents of working memory to decay. This can reduce your working memory ability.
What is the working memory of a person who recalls 5 items?
If you recall five items, your working memory capacity is five. This is a memory span measure and is also called working memory span . Daneman and Carpenter invented the reading span test wherein you read a paragraph and recall the last word of each sentence you read.
Why is working memory more susceptible to shocks?
Working memory skills are associated with a temporary activation of your neuron network, while long-term memory is connected to physical neuronal changes. That’s why your working memory is more susceptible to shocks and interruptions.
How to know if your child has poor working memory?
First, you need to determine if your child or relative has poor working memory skills or an attentional problem. Here’s how you can investigate: Do a complete evaluation. If working memory problems are found, you should check for other problems related to executive functions like ADHD.
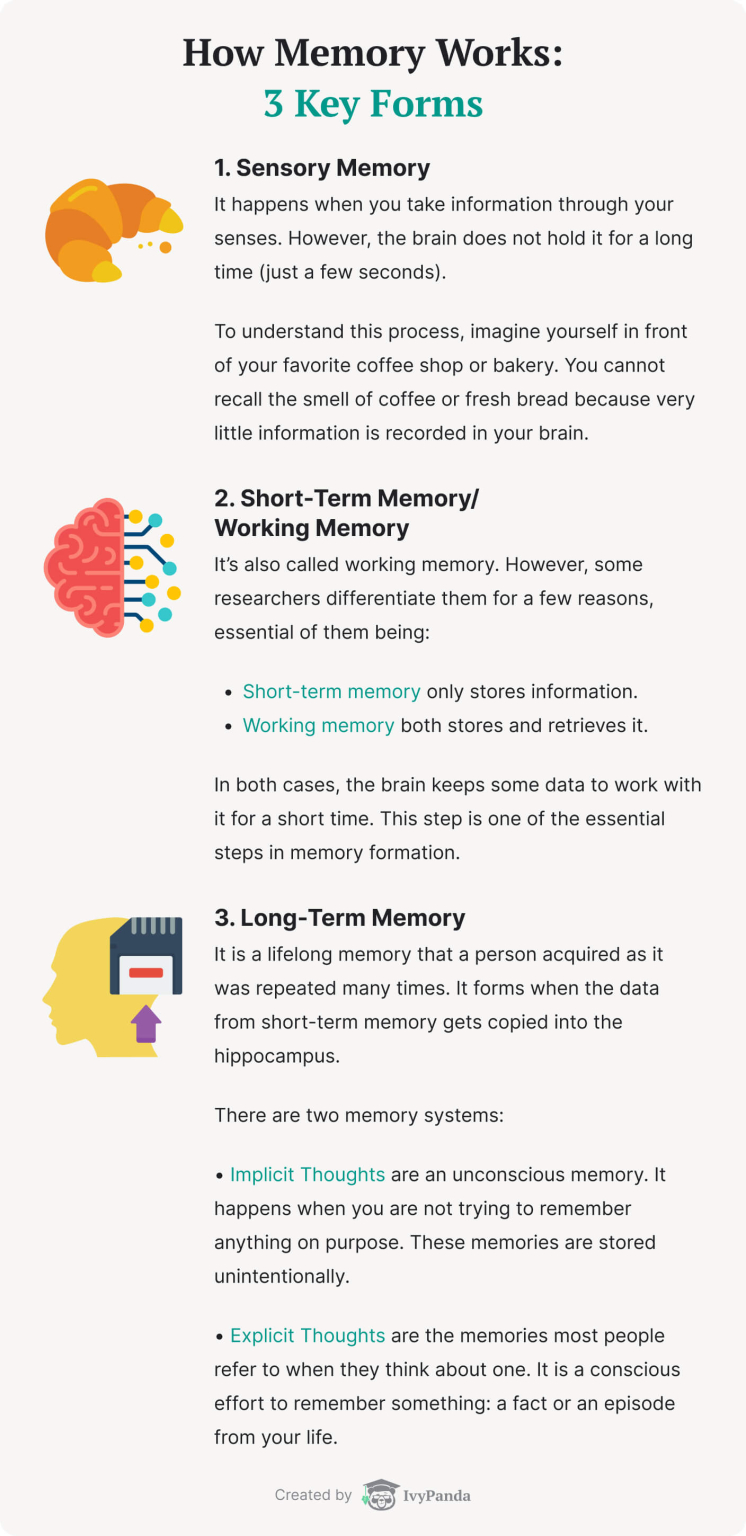
What are the three types of memory?
In 1968, Atkinson and Shiffrin proposed a multi-store model suggesting that human memory is made up of: 1 A sensory register 2 A short-term store (working memory or short-term memory), and 3 A long-term store (long-term memory).
What is long term working memory?
According to Anders Ericsson and Walter Kintsch, long-term working memory is made up of retrieval structures that seamlessly retrieve information for any daily task. In 2010, Cowan suggested that working memory representations are a subset of representations in long-term memory.
What are some strategies to improve memory?
If you’re working on memory skills with your clients, you may be training internal memory strategies such as verbal rehearsal, chunking/grouping, associations, visualization, or remembering the total number of items in a list.
How to improve memory in a clinic?
If there is a discrepancy in scores, perhaps the memory strategies need to be revisited in the clinic. Let’s take a look at these 5 memory exercises. 1. Match pictures. Targeting visual memory skills, the client will tap on the cards to match pairs of pictured objects. 2. Match faces. Targeting visual memory skills, ...
How many levels are there in matching tasks?
All matching tasks have five levels. As the levels increase, more items are added to the grid. Levels are as follows. Level 1: 6 items in a grid. Level 2: 12 items in a grid. Level 3: 20 items in a grid. Level 4: 24 items in a grid. Level 5: 30 items in a grid.
Where is verbal information stored?
Verbal information is stored in an area of working memory called the phonological loop , and visual information is stored in an area called the visuospatial sketchpad. After a stroke, traumatic b rain injury, or other neurological impairment, often this mental clipboard may hold less information.
Can you forget how much information you keep in your head?
With a smartphone always handy, it’s easy to forget how much information we keep in our heads on a regular basis. If you have to add up how many dinner plates you need for a party you’re hosting, do you grab your calculator to figure out an answer? Most likely, no, because you can keep and access small chunks of information—your working memory is what allows you to access and manipulate that info.
Why are working memory exercises so popular?
In the last several years, working memory exercises have gained popularity. This is due in part to their claims to benefit students. They are often sold as help for poor academic performance, ADHD, dyslexia, language disorders, and other issues. Some even claim to boost people’s IQs. Memory exercises are increasingly found online, ...
Why is working memory important?
These skills are rare and important. Working memory enables people to recycle information for short periods of time. One example of a working memory exercise is to be given a series of numbers one at a time on a computer screen. The computer shows a new digit and erases the last one.
Why is it important to focus on a game?
In playing games, it helps to focus, critical thinking, and problem solving – important elments in learning a new skill or simply doing a math problem. Even in a basketball game, your focus on making sure the ball will go into the loop, you might lose the game, but in reality you had just learned to concentrate! Reply.
Do memory exercises transfer to new situations?
The problem that any gains made on the memory exercises don’t transfer to new situations is a common one in cognitive science. This is what makes mind building different and harder than body building. Some cognitive skills do transfer, such as memory retrieval practice. These skills are rare and important.
Do memory exercises help?
According to Melby-Lervåg, the belief that memory exercises help is often based on the idea that you can train your brain in much the same way as you can lift weights to build muscle. Her review of the research shows memory exercises do not improve memory outside of the tasks presented within these tests. The problem that any gains made on the ...
Who led the study on memory?
The study was led by Monica Melby-Lervåg of the University of Oslo. Her team found that memory exercises appear to have limited effect on healthy adults and children looking to do better in school or improve their cognitive skills.
Does working memory improve cognitive ability?
However, the memory exercises did not improve other cognitive skills such as verbal skills, attention, reading or arithmetic. The findings cast strong doubt on claims that working memory exercises improve cognitive ability and scholastic attainment.
What is working memory?
Working memory refers to the memory you can consciously hold in your mind at any one instant—such as a phone number you just looked up. Most people can only hold about four totally independent items in their working memory. Working memory relates to intelligence.
How does playing games help your memory?
Some games that are fun to play may also help working memory. The most obvious example is chess. To play chess well, you have to learn to expand working memory capacity to hold a plan for several offensive moves while at the same time holding a memory of how the opponent could respond to each of the moves.
What are the four memory training programs?
At the moment, there are four dominant memory training programs: MindSparke, Lumosity, Jungle Memory , and Cogmed.
How long did children train for IQ?
While they were at it, they tested for any effect on IQ. Children ages 6-8 were trained 10 minutes a day each day for two months. The training task to expand working memory capacity consisted of presenting a digit or a word item for a second, with one-second intervals between items.
Does working memory improve IQ?
The investigators found working memory training improved scores on the IQ test. Moreover, the effect was dose-dependent, in that intelligence scores increased in a steady straight-line fashion as the number of training sessions increased from 8 to 12 to 17 to 19.
What are the characteristics of working memory?
Characteristics of working memory: 1 Its capacity is limited We are only able to store 5-9 elements at a time. 2 It is active. It doesn't only store information, it also manipulates and transforms it. 3 Its content is permanently being updated. 4 It is modulated by the dorsolateral frontal cortex.
What are the problems associated with working memory?
This is why its alteration can be seen in dysexecutive syndromes and many learning disorders like ADHD and dyslexia. Other problems like schizophrenia and dementias tend to be associated with working memory.
How many times a week should I do cognitive stimulation?
A correct cognitive stimulation requires at least 15 minutes a day, two or three times a week. The CogniFit brain training program is available online, from anywhere in the world and is made up of fun and interactive brain games that can be played on computers or mobile devices.
Why is working memory important?
Instead, it’s about holding together the present in your mind so you can learn, make decisions and solve problems. Working memory is essentially your mental bandwidth. If you have a good working memory, or can use yours more effectively, you can think and learn better.
What is working memory?
Working memory enables you to generate new thoughts, change them, combine them, search them, apply different rules and strategies to them, or do anything else that helps you navigate your life. By enabling all of these functions, working memory underpins your thinking, planning, learning and decision-making.
What is cognitive load?
[ 72] Cognitive load is defined as the effort used by the working memory system to process information.
What is a phonological loop?
Phonological loop is the first kind of short-term memory storage which stores sounds. Being able to have a conversation, listen to music and understand a lecture all depend on your phonological loop.
Is working memory a storage?
It’s a workspace – the carpenter uses it to combine different materials to create new products. Similarly, working memory is not just a simple storage.
Does music help with memory?
Secondly, music could drown out even more disrupting external noise, which might actually help to protect working memory. Interestingly, although white noise seems to worsen the performance of students with normal attention, it can actually improve the performance of students with attention problems.
How does information reach your working memory?
Information only reaches your working memory if it is given attention. If you make an effort to actively maintain the information, through repetition, evaluation, or other means, it will make its way into your working memory and maybe into your long-term memory. Without attention, the information begins to decay.
Why is working memory important?
A good working memory allows someone to remember information while recalling other pieces of information or performing other functions. And while more research still has to be done, many experts say that working memory is a good predictor of general intelligence.
What is central executive memory?
Psychologists know the basics of what Central Executive Memory does, but the process in which it is done isn’t so clear. Much more is known about the areas of the brain where the CEM delegates the processing of information. These areas include the Phonological Loop, Episodic Buffer, and VisuoSpatial Sketchpad.
Why does stress make us work faster?
The release of cortisol (the stress hormone) puts us into “survival mode.”. Studies have known that due to high stress levels, working memory works faster. Humans need a faster reaction time in moments when they have to choose between fight or flight.
What is the function of short term memory that processes language and perception data in the brain?
Working Memory is the function of short term memory that processes language and perception data in the brain. This memory allows us to manipulate objects, items, and numbers to perform complex tasks. Intelligence and working memory are very closely related.
How does working memory affect intelligence?
According to Peter Doolittle, people with good working memory tend to be good storytellers and score higher on standardized tests.
What are the parts of working memory?
He describes the four parts of working memory: 1 Temporarily storing immediate experience into short-term memory storage 2 Reaching back into long-term memory 3 Mixing and processing the experience and memories together 4 Applying the meaning discovered from this process to the task at hand
How does working memory work?
Virtually everyone seems to put working memory to work throughout the day, but the performance of this memory system (or “working memory capacity”) is strong er in some individuals than in others—with implications for a person’s ability to learn and function.
What is working memory?
Working memory is a form of memory that allows a person to temporarily hold a limited amount of information at the ready for immediate mental use. It is considered essential for learning, problem-solving, and other mental processes.
Why is it important to retain information?
It allows one to retain multiple pieces of information for use in the moment, which is essential to activities from reading or having a conversation to learning new concepts to making decisions between different options.
Which part of the brain is responsible for visual representation?
The representation of different kinds of information (such as visual or or verbal details) in working memory seems to depend on parts of the cerebral cortex that are involved in the perception and long-term memory of those kinds of information. The prefrontal cortex, a part of the brain linked to cognitive control, ...
Which part of the brain is responsible for managing the current contents of working memory?
The prefrontal cortex , a part of the brain linked to cognitive control, is thought to play a key role in managing the current contents of working memory, regardless of type.
Is long term memory limited?
While long-term memory can store a huge amount of information, the amount of details contained for ready usage in working memory is thought to be relatively limited. There are differing models of the working memory system. Some have argued that it includes multiple components that handle different kinds of information and are distinct ...
Is working memory a part of long term memory?
Others propose that working memory represents a part of long-term memory that is especially activated and a smaller part that is the focus of attention.
