
There are 5 main steps in hypothesis testing:
- State your research hypothesis as a null hypothesis and alternate hypothesis (H o) and (H a or H 1 ).
- Collect data in a way designed to test the hypothesis.
- Perform an appropriate statistical test.
- Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis.
- Present the findings in your results and discussion section.
- Step 1: State your null and alternate hypothesis. ...
- Step 2: Collect data. ...
- Step 3: Perform a statistical test. ...
- Step 4: Decide whether to reject or fail to reject your null hypothesis. ...
- Step 5: Present your findings.
How can you verify a hypothesis?
Hypothesis-driven validation can be broken down into seven steps: Identify your assumptions. Reframe assumptions as “hypotheses” Rank them in order of importance. Design appropriate tests. Conduct the tests. Synthesize your learnings. Act.
What are the five steps of a hypothesis?
Five Steps in Hypothesis Testing: Specify the Null Hypothesis. Specify the Alternative Hypothesis. Set the Significance Level (a) Calculate the Test Statistic and Corresponding P-Value. Drawing a Conclusion.
How to write a good hypothesis?
Use the following points as a checklist to evaluate the effectiveness of your research hypothesis:
- Predicts the relationship and outcome
- Simple and concise – avoid wordiness
- Clear with no ambiguity or assumptions about the readers’ knowledge
- Observable and testable results
- Relevant and specific to the research question or problem
What type of experiment is an one way to test a hypothesis?
The most common way to test a hypothesis is to create an experiment. A good experiment uses test subjects or creates conditions where you can see if your hypothesis seems to be true by evaluating a broad range of data (test results).
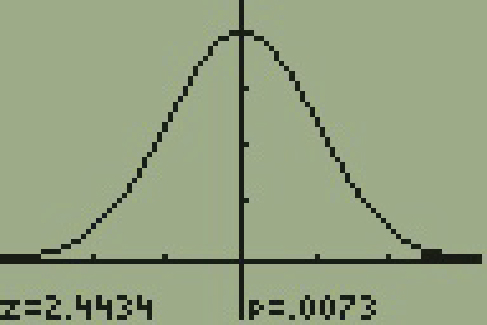
How do you prove or disprove a hypothesis?
The proof lies in being able to disprove A hypothesis or model is called falsifiable if it is possible to conceive of an experimental observation that disproves the idea in question. That is, one of the possible outcomes of the designed experiment must be an answer, that if obtained, would disprove the hypothesis.
How do you prove a hypothesis in a conclusion?
The key to making an appropriate conclusion to a hypothesis test is to identify results that are statistically significant. When results observed from the sample are unlikely under the assumption that the null hypothesis is true, we say the result is statistically significant.
Can you confirm a hypothesis?
A hypothesis can be rejected or modified, but it can never be proved correct 100% of the time. For example, a scientist can form a hypothesis stating that if a certain type of tomato has a gene for red pigment, that type of tomato will be red.
What p value proves a hypothesis?
A p-value less than 0.05 is typically considered to be statistically significant, in which case the null hypothesis should be rejected. A p-value greater than 0.05 means that deviation from the null hypothesis is not statistically significant, and the null hypothesis is not rejected.
What are the 4 steps of hypothesis testing?
Step 1: State the hypotheses. Step 2: Set the criteria for a decision. Step 3: Compute the test statistic. Step 4: Make a decision.
What are the two possible conclusions of a hypothesis test?
There are only two possible outcomes to a hypothesis test: (1) reject the null hypothesis, and (2) fail to reject the null hypothesis.
What do scientists do to confirm a hypothesis?
The scientific methodMake an observation.Ask a question.Form a hypothesis, or testable explanation.Make a prediction based on the hypothesis.Test the prediction.Iterate: use the results to make new hypotheses or predictions.
How do you test a research hypothesis?
Determine the characteristics of the comparison distribution. Determine the cut off sample score on the comparison distribution at which the null hypothesis should be rejected. Determine your sample's score on the comparison distribution. Decide whether to reject the null hypothesis.
Can you confirm null hypothesis?
Technically, no, a null hypothesis cannot be proven. For any fixed, finite sample size, there will always be some small but nonzero effect size for which your statistical test has virtually no power.
Why do we use 0.05 level of significance?
A p-value less than 0.05 (typically ≤ 0.05) is statistically significant. It indicates strong evidence against the null hypothesis, as there is less than a 5% probability the null is correct (and the results are random). Therefore, we reject the null hypothesis, and accept the alternative hypothesis.
What does p-value indicate?
1. What is the P value? The P value means the probability, for a given statistical model that, when the null hypothesis is true, the statistical summary would be equal to or more extreme than the actual observed results [2].
Is p 0.1 statistically significant?
If the p-value is under . 01, results are considered statistically significant and if it's below . 005 they are considered highly statistically significant.
What is the conclusion of hypothesis?
The conclusion is the final decision of the hypothesis test. The conclusion must always be clearly stated, communicating the decision based on the components of the test. It is important to realize that we never prove or accept the null hypothesis.
What is a hypothesis statement examples?
A few examples of simple hypotheses: "Students who eat breakfast will perform better on a math exam than students who do not eat breakfast." Complex hypothesis: "Students who experience test anxiety before an English exam will get lower scores than students who do not experience test anxiety."
How do you conclude the null and alternative hypothesis?
The general procedure for null hypothesis testing is as follows:State the null and alternative hypotheses.Specify α and the sample size.Select an appropriate statistical test.Collect data (note that the previous steps should be done prior to collecting data)Compute the test statistic based on the sample data.More items...
What is the conclusion when the null hypothesis is not rejected?
In testing of hypothesis, one has to give a conclusion to each and every problem about the population parameter. If we have enough evidence to reject any hypothesis then we reject it. If the null hypothesis is not rejected, it means that there is no enough evidence is there to reject that.
What is hypothesis testing?
Hypothesis testing is a formal procedure for investigating our ideas about the world using statistics. It is used by scientists to test specific p...
What is a hypothesis?
A hypothesis states your predictions about what your research will find. It is a tentative answer to your research question that has not yet be...
What are null and alternative hypotheses?
Null and alternative hypotheses are used in statistical hypothesis testing . The null hypothesis of a test always predicts no effect or no rela...
What happens if the test statistic is not in the critical region?
If the test statistic is in our critical region, then we must reject the null hypothesis. The alternative hypothesis stands. If the test statistic is not in our critical region, then we fail to reject the null hypothesis. This does not prove that the null hypothesis is true, but gives a way to quantify how likely it is to be true.
How to prove a hypothesis is false?
The Traditional Method. The traditional method is as follows: Begin by stating the claim or hypothesis that is being tested. Also, form a statement for the case that the hypothesis is false. Express both of the statements from the first step in mathematical symbols.
What is hypothesis testing?
The idea of hypothesis testing is relatively straightforward. In various studies, we observe certain events. We must ask, is the event due to chance alone, or is there some cause that we should be looking for? We need to have a way to differentiate between events that easily occur by chance and those that are highly unlikely to occur randomly. Such a method should be streamlined and well defined so that others can replicate our statistical experiments.
Which statement from the first step makes the statement that a parameter equals a particular value?
The statement from the first step that makes the statement that a parameter equals a particular value is called the null hypothesis, denoted H0.
When to use a one tailed test?
Here we will have to consider if we are conducting a two-tailed test (typically when the alternative hypothesis contains a “is not equal to” symbol, or a one-tailed test (typically used when an inequality is involved in the statement of the alternative hypothesis).
What Is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
Hypothesis Testing is a type of statistical analysis in which you put your assumptions about a population parameter to the test. It is used to estimate the relationship between 2 statistical variables.
What happens if the sample falls within the range of the null hypothesis?
If the sample falls within this range, the alternate hypothesis will be accepted, and the null hypothesis will be rejected.
What is a one-tailed test?
The One-Tailed test, also called a directional test, considers a critical region of data that would result in the null hypothesis being rejected if the test sample falls into it, inevitably meaning the acceptance of the alternate hypothesis.
What is the alpha value in statistics?
The alpha value is a criterion for determining whether a test statistic is statistically significant. In a statistical test, Alpha represents an acceptable probability of a Type I error. Because alpha is a probability, it can be anywhere between 0 and 1. In practice, the most commonly used alpha values are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1, which represent a 1%, 5%, and 10% chance of a Type I error, respectively (i.e. rejecting the null hypothesis when it is in fact correct).
What is composite hypothesis?
Composite Hypothesis: A composite hypothesis specifies a range of values.
What is a null hypothesis?
The Null Hypothesis is the assumption that the event will not occur. A null hypothesis has no bearing on the study's outcome unless it is rejected.
What does a p-value mean?
A p-value is a metric that expresses the likelihood that an observed difference could have occurred by chance. As the p-value decreases the statistical significance of the observed difference increases. If the p-value is too low, you reject the null hypothesis.
What happens if there is insufficient evidence?
If there is insufficient evidence, then the jury does not reject the null hypothesis. We behave as if the defendant is innocent.
What is hypothesis testing?
The general idea of hypothesis testing involves: Making an initial assumption. Collecting evidence (data). Based on the available evidence (data), deciding whether to reject or not reject the initial assumption. Every hypothesis test — regardless of the population parameter involved — requires the above three steps.
What is Table S.3.2?
Table S.3.2 shows how this corresponds to the two types of errors in hypothesis testing.
When do we make assumptions in statistics?
In the practice of statistics, we make our initial assumption when we state our two competing hypotheses -- the null hypothesis ( H0) and the alternative hypothesis ( HA ). Here, our hypotheses are:
How many steps are required for a hypothesis test?
Every hypothesis test — regardless of the population parameter involved — requires the above three steps.
What does "behave as if" mean?
Did you notice the use of the phrase "behave as if" in the previous discussion? We "behave as if" the defendant is guilty; we do not "prove" that the defendant is guilty. And, we "behave as if" the defendant is innocent; we do not "prove" that the defendant is innocent.
What is the average temperature of a sample of 130 adults?
In doing so, he selects a random sample of 130 adults. The average body temperature of the 130 sampled adults is 98.25 degrees.
What is statistical significance testing?
A set of statistical tools that quantifies your confidence about the ‘real’ difference based on the measurements. It is a method of making a statistical decision using experimental data. This is also called as Statistical Significance testing. Hypothesis Testing – key concepts.
What is statistical hypothesis test?
A statistical hypothesis test is a method of making statistical decisions using data. It is sometimes called confirmatory data analysis.
What is the null hypothesis?
In the previous section, we have read that Null hypothesis is about the status quo or no difference. So here also the Null hypothesis will be µA = µB (mean of country A=mean of country B), this means in simple words that there is no significant difference between the average weight of country A and B.
What is the application used to calculate the P value of a hypothesis?
You can use Minitab, SPSS or R. Minitab is a popular application used for applied statistics and when we perform any statistical test, we get P-value as one of the output. Key concepts which will help you to interpret the test output: Minitab will calculate P-value for the Ho hypothesis.
Why do we do hypothesis testing?
Hypothesis Testing is done to help determine if the variation between or among groups of data is due to true variation or if it is the result of sample variation. With the help of sample data we form assumptions about the population, then we have test our assumptions statistically. This is called Hypothesis testing.
What is the difference between population and real difference?
Real Difference – ‘Real’ difference is the difference that will be there if you measure everything , also in the future. This is called ‘population’.
What does "ha" mean in a sentence?
Ha = Alternative Hypothesis. Statement/claim assumed to be true and we are trying to prove it to be true. The burden of proof rests with Ha. Testing a hypothesis is similar to a court trial. The hypothesis is that the defendant is presumed not guilty until proven guilty.
What Is Hypothesis Testing in Statistics?
- Hypothesis Testing is a type of statistical analysisin which you put your assumptions about a population parameter to the test. It is used to estimate the relationship between 2 statistical variables. Let's discuss few examples of statistical hypothesis from real-life - 1. A teacher assumes that 60% of his college's students come from lower-middle-...
Null Hypothesis and Alternate Hypothesis
- The Null Hypothesis is the assumption that the event will not occur. A null hypothesis has no bearing on the study's outcome unless it is rejected. H0 is the symbol for it, and it is pronounced H-naught. The Alternate Hypothesis is the logical opposite of the null hypothesis. The acceptance of the alternative hypothesis follows the rejection of the null hypothesis. H1 is the symbol for it. L…
Simple and Composite Hypothesis Testing
- Depending on the population distribution, you can classify the statistical hypothesis into two types. Simple Hypothesis: A simple hypothesis specifies an exact value for the parameter. Composite Hypothesis: A composite hypothesis specifies a range of values.
One-Tailed and Two-Tailed Hypothesis Testing
- The One-Tailed test, also called a directional test, considers a critical region of data that would result in the null hypothesis being rejected if the test sample falls into it, inevitably meaning the acceptance of the alternate hypothesis. In a one-tailed test, the critical distribution area is one-sided, meaning the test sample is either greater or lesser than a specific value. In two tails, the t…
Type 1 and Type 2 Error
- A hypothesis test can result in two types of errors. Type 1 Error: A Type-I error occurs when sample results reject the null hypothesis despite being true. Type 2 Error: A Type-II error occurs when the null hypothesis is not rejected when it is false, unlike a Type-I error.
Level of Significance
- The alpha value is a criterion for determining whether a test statistic is statistically significant. In a statistical test, Alpha represents an acceptable probability of a Type I error. Because alpha is a probability, it can be anywhere between 0 and 1. In practice, the most commonly used alpha values are 0.01, 0.05, and 0.1, which represent a 1%, 5%, and 10% chance of a Type I error, res…
P-Value
- A p-value is a metric that expresses the likelihood that an observed difference could have occurred by chance. As the p-value decreases the statistical significance of the observed difference increases. If the p-value is too low, you reject the null hypothesis. Here you have taken an example in which you are trying to test whether the new advertising campaign has increased …
Conclusion
- After reading this tutorial, you would have a much better understanding of hypothesis testing, one of the most important concepts in the field of Data Science. The majority of hypotheses are based on speculation about observed behavior, natural phenomena, or established theories. If you are interested in statistics of data science and skills needed for such a career, you ought to explore …