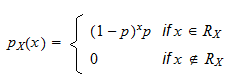
The formula for geometric distribution is derived by using the following steps:
- Firstly, determine the probability of success of the event, and it is denoted by ‘p’.
- Next, therefore the probability of failure can be calculated as (1 – p).
- Next, determine the number of trials at which the first instance of success is recorded, or the probability of success equals one. ...
What is the formula for geometric distribution?
Geometric Distribution Formula. In probability and statistics, geometric distribution defines the probability that first success occurs after k number of trials. If p is the probability of success or failure of each trial, then the probability that success occurs on the \(k^{th}\) trial is given by the formula \(Pr (X = k) = (1-p)^{k-1}p\) Examples
What is the importance of geometric distribution?
In fact, the geometric distribution helps in the determination of the probability of the first occurrence of success after a certain number of trials given the success probability.
What is the geometric distribution of success probability?
The geometric distribution gives the probability that the first occurrence of success requires k independent trials, each with success probability p . If the probability of success on each trial is p, then the probability that the k th trial (out of k trials) is the first success is
How do you find the probability of a hypergeometric distribution?
Finally, the formula for the probability of a hypergeometric distribution is derived using a number of items in the population (step 1), number of items in the sample (step 2), number of successes in the population (step 3) and number of successes in the sample (step 4) as shown below.

What is the formula for the mean of a geometric distribution?
= 1 − p pGeometric Distribution Mean and Variance The geometric distribution is discrete, existing only on the nonnegative integers. The mean of the geometric distribution is mean = 1 − p p , and the variance of the geometric distribution is var = 1 − p p 2 , where p is the probability of success.
How do you find the geometric distribution on a calculator?
1:295:03Geometric Distribution Probabilities on the TI-84 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThrough the probability x is equal to eight.MoreThrough the probability x is equal to eight.
What is the formula for calculating geometric probability?
0:414:27What Is The Geometric Probability Distribution Formula Examples ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe formula for the geometric distribution. Is probability of N equals P times the quantity 1 minusMoreThe formula for the geometric distribution. Is probability of N equals P times the quantity 1 minus P raised to the N minus 1.
What does a geometric distribution look like?
0:3210:47An Introduction to the Geometric Distribution - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd each trial results in one of two possible mutually exclusive outcomes and we're going to labelMoreAnd each trial results in one of two possible mutually exclusive outcomes and we're going to label those outcomes as success. And failure on any individual trial the probability of success is P.
What is the shape of a geometric distribution?
Shape: The heavily right-skewed shape is characteristic of any geometric distribution.
Which of the options is an example of geometric distribution?
For example, suppose an ordinary die is thrown repeatedly until the first time a "1" appears. The probability distribution of the number of times it is thrown is supported on the infinite set { 1, 2, 3, ... } and is a geometric distribution with p = 1/6.
How do you do geometric distribution on Desmos?
1:405:38Statistics: Poisson Distribution Probabilities Using Desmos.comYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipLet's first click show keypad in the lower left hand corner click functions click the distributionMoreLet's first click show keypad in the lower left hand corner click functions click the distribution tab click the sawn distribution.
What is the CDF of a geometric distribution?
The CDF function for the geometric distribution returns the probability that an observation from a geometric distribution, with the parameter p, is less than or equal to m. Note: There are no location or scale parameters for this distribution.
What does Binomcdf mean?
binomial cumulative probabilityBinomcdf stands for binomial cumulative probability. The key sequence for using the binomcdf function is as follows: If you used the data from the problem above, you would find the following: You can see how using the binomcdf function is a lot easier than actually calculating 6 probabilities and adding them up.
How do you calculate uniform distribution?
How do I calculate the expected value of uniform distribution? The expected value of the uniform distribution U(a,b) is the same as its mean and is given by the following formula: μ = (a + b) / 2 .
Solved Examples Using Geometric Distribution Formula
In a school competition, a student is entitled to a prize if he/she throws a ring on a peg from a certain distance. It is observed that only 40% of the students can do this. If someone has already missed 4 chances from 5 chances, what is the probability of that student winning the prize?
Example 1
In a school competition, a student is entitled to a prize if he/she throws a ring on a peg from a certain distance. It is observed that only 40% of the students can do this. If someone has already missed 4 chances from 5 chances, what is the probability of that student winning the prize?
Geometric Distribution Definition
A geometric distribution is defined as a discrete probability distribution of a random variable “x” which satisfies some of the conditions. The geometric distribution conditions are
Geometric Distribution Formula
In probability and statistics, geometric distribution defines the probability that first success occurs after k number of trials. If p is the probability of success or failure of each trial, then the probability that success occurs on the kth k t h trial is given by the formula
Examples
Consider a couple who are planning to have a child and they will continue to babies until it is a girl. What is the probability that they have zero boys, one boy and two boys and so on until a girl is born?
What is geometric distribution?
A geometric distribution is the probability distribution for the number of identical and independent Bernoulli trials that are done until the first success occurs. In order to use the geometric distribution to find probabilities, we use the following formulas, where each one corresponds to the given specific circumstance. ...
What is the mean of a probability distribution?
Each probability distribution has its own unique formula for mean and variance of the random variable Y. The mean or expected value of Y tells us the weighted average of all potential values for Y. For a geometric distribution mean (E ( Y) or μ) is given by the following formula.
What is the sum of all possible probabilities of an event?
No matter how complicated, the total sum for all possible probabilities of an event always comes out to 1. The manner in which these probabilities all add up to 1 is called their probability distribution.
How to know the probability of an event?
If you want to know the probability that an outcome of an event will occur, what you're looking for is the likelihood that this outcome happens over all other possible outcomes. The probability of an outcome occurring could be a simple binary 50/50 choice, like whether a tossed coin will land heads or tails up, or it could be much more complicated.
Can geometric distributions be used to find probability?
There are multiple situations in which the geometric distribution can be used to find a probability, and the formula for each is given in the following table.
Can you solve probability with a sum?
The P ( Y > y) and P ( Y > y) probabilities can't be solved directly with a sum like the formulas with less than signs because the range of y extends infinitely. Summing this directly would mean you need to sum from some value to infinity. We can get around this because we know the sum of all probabilities P ( Y ≥ 1) must equal 1, and P ( Y ≥ 1) can be split into two halves added together that sum over the full range of y.
What is the geometric distribution in a sequence of trials?
The probability of success is assumed to be the same for each trial. In such a sequence of trials, the geometric distribution is useful to model the number of failures before the first success.
What is the geometric random variable Y?
If these conditions are true, then the geometric random variable Y is the count of the number of failures before the first success. The possible number of failures before the first success is 0, 1, 2, 3, and so on. In the graphs above, this formulation is shown on the right.
What is the function of dgeom in R?
The R function dgeom (k, prob) calculates the probability that there are k failures before the first success, where the argument "prob" is the probability of success on each trial.
What are decimal digits in a random variable?
The decimal digits of the geometrically distributed random variable Y are a sequence of independent (and not identically distributed) random variables. For example, the hundreds digit D has this probability distribution:
How to estimate parameter p?
For both variants of the geometric distribution, the parameter p can be estimated by equating the expected value with the sample mean. This is the method of moments, which in this case happens to yield maximum likelihood estimates of p.
What is the expected value of the alternative formulation?
For the alternative formulation, where X is the number of trials up to and including the first success, the expected value is E ( X) = 1/ p = 1/0.1 = 10.
Is geometric distribution memoryless?
The die one throws or the coin one tosses does not have a "memory" of these failures. The geometric distribution is the only memoryless discrete distribution.
What is geometric distribution?
The Geometric distribution is a probability distribution that is used to model the probability of experiencing a certain amount of failures before experiencing the first success in a series of Bernoulli trials.
What is the probability of a network failure in a given week?
Suppose it’s known that the probability that a a certain company experiences a network failure in a given week is 10%. Suppose the CEO of the company would like to know the probability that the company can go 5 weeks or longer without experiencing a network failure.
Explanation
Firstly, determine the total number of items in the population, which is denoted by N. For example, the number of playing cards in a deck is 52.
Examples of Hypergeometric Distribution (with Excel Template)
Let us take the example of an ordinary deck of playing cards form where 6 cards are drawn randomly without replacement. Determine the probability of drawing exactly 4 red suites cards, i.e., diamonds or hearts.
Relevance and Uses
The concept of hypergeometric distribution is important because it provides an accurate way of determining the probabilities when the number of trials is not a very large number and that samples are taken from a finite population without replacement.
Recommended Articles
This article has been a guide to Hypergeometric Distribution Formula. Here we discuss how to calculate the probability of hypergeometric distribution in excel with examples and a downloadable excel template. You can learn more about excel modeling from the following articles-
What is geometric distribution?
The geometric distribution describes the probability of experiencing a certain amount of failures before experiencing the first success in a series of binomial experiments.
What is the outcome of the experiments in both distributions?
The outcome of the experiments in both distributions can be classified as “success” or “failure.”
What are the two most commonly used distributions in statistics?
Two commonly used distributions in statistics are the binomial distribution and the geometric distribution.
Why does X follow a binomial distribution?
Answer: X follows a binomial distribution because there is a fixed number of trials (10 attempts), the probability of “success” on each trial is the same, and each trial is independent.
