The method used to solve truss problems is to:
- Find the forces at the supports by using force and moment equations with given external forces.
- Calculate the internal forces of beams connected to a support, keeping in mind which are in compression and which are in tension.
- Find the other internal forces by moving across the beam using the forces of the beams obtained in other steps and the relevant external forces.
How to solve a truss using the joint method?
To perform a 2D truss analysis using the method of joints, follow these steps:
- Check that the truss is determinate and stable using the methods from Chapter 2.
- If possible, reduce the number of unknown forces by identifying any zero force members in the truss.
- Calculate the support reactions for the truss using equilibrium methods as discussed in Section 3.4
How to repair a truss SAG?
- You’ll need a steel “L” channel to get your rafter or truss back into shape.
- Drill four holes in each side of the L.
- Remove any pieces of wood (broken scraps) that could get in your way using a chisel.
- Starting at the end that’s the most difficult to access, mount the steel “L” channel onto the rafter or truss.
How to create a scissor truss?
To create scissor trusses
- Select Build> Framing> Roof Truss from the menu.
- Click and drag to draw a roof truss perpendicular to the ridge line of the roof and ceiling planes.
- Click on the truss to select it and move it so that the exterior edge of the truss is aligned with the exterior edge of the framing layer of the ...
What is the use of triangles in a truss?
Truss bridges often use equilateral and isosceles triangles to distribute weight because the equal angles allow forces to spread evenly across the bridge. Triangles are one of the best shapes for distributing weight because they take force from a single point and distribute it across a wide base.

How do you solve a truss step by step?
0:0114:52Truss analysis by method of joints: worked example #1 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo the first thing that we need to do for using method of joints is to draw a Freebody diagram ofMoreSo the first thing that we need to do for using method of joints is to draw a Freebody diagram of the entire structure. And now we can find the reaction forces.
How do you calculate truss?
How do I calculate roof trusses? The simplest form of this equation is to take the length of your roof and divide it by 2. For example, if your roof is 40-feet long, it will need a total of 20 trusses.
How do you solve a section of truss method?
0:165:52Truss analysis by method of sections: worked example #1 - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we have our two applied external forces here and then we have a horizontal reaction at our hinge.MoreSo we have our two applied external forces here and then we have a horizontal reaction at our hinge. And a vertical reaction for a and we also have our other vertical reaction over here at the roller.
How many methods are there to solve a truss?
Methods of analysis of trusses: The two common methods of analysis of trusses are the method of joint and the method of section (or moment). Method of joint: This method involves isolating each joint of the truss and considering the equilibrium of the joint when determining the member axial force.
What is a truss example?
Thrust is defined as to quickly push with force. An example of thrust is to move forward as a crowd entering a stadium. An example of thrust is to force one's self into a conversation.
How do you read a truss calculator?
Just remember the acronym: FIS. This stands for Feet, Inches, Sixteenths. So, for example, a dimension string that reads; 4-7-12 would be the dimension 4'-7 12/16” or 4'-7 3/4”.
What is a truss system?
A truss is essentially a triangulated system of straight interconnected structural elements. The most common use of trusses is in buildings, where support to roofs, the floors and internal loading such as services and suspended ceilings, are readily provided.
What is a simple truss?
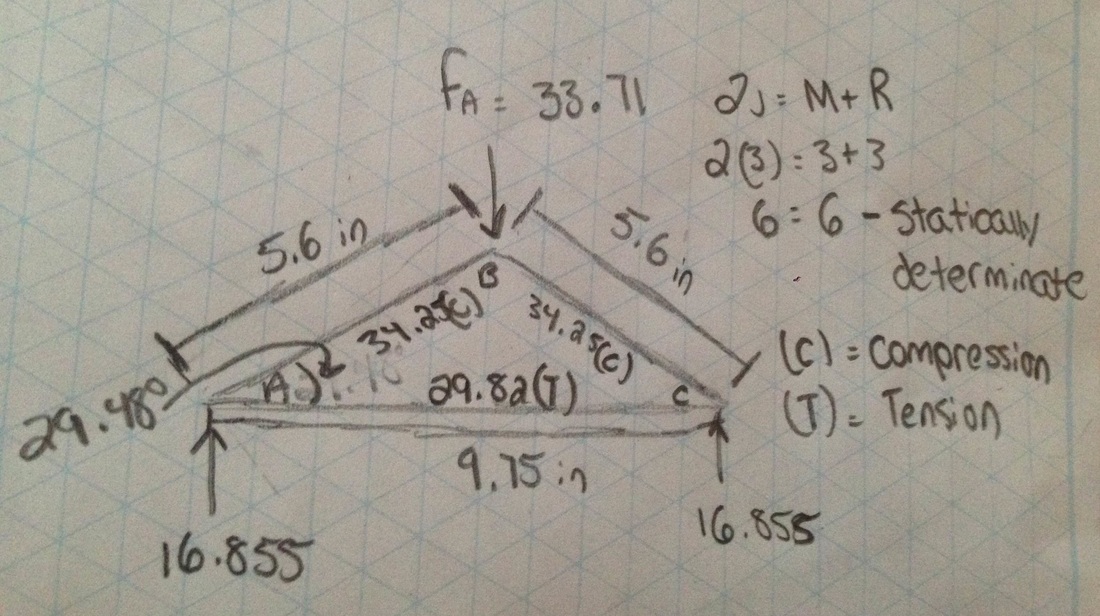
SIMPLE TRUSSES A simple truss is a planar truss which begins A simple truss is a planar truss which begins with a triangular element and can be expanded by adding two members and a joint. For these trusses, the number of members (M) and the number of joints (J) are related by the equation M = 2 J – 3.
How do you solve a truss method of sections the number of unknowns at a section should not be?
Because we can only solve up to three unknowns, it is important not to cut more than three members of the truss. Depending on the type of truss and which members to solve, one may have to repeat Method of Sections more than once to determine all the desired forces.
How is truss slope calculated?
0:301:56How to determine the slope of a roof - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhich is the distance from the Attic joist to the ridge. And divided by the run and the run is halfMoreWhich is the distance from the Attic joist to the ridge. And divided by the run and the run is half of the distance between the front and back of the walls of the house.
How far can 2x4 trusses span?
A 2×4 can span a maximum of 6' 7” when spaced 16” apart and used as a floor or deck joist. When used as a ceiling joist or a roof rafter, a 2×4 can span up to 7' 3” spaced at 16”, and 6' 4” when spaced 24” apart. Due to the small spans of 2x4s, they often are not used in horizontal load-bearing capacities.
How do you calculate truss rise?
Considering the entire truss as a pair of back-to-back, right-angled triangles allows you to base the calculations on the Pythagorean theorem, which tells you that a2 + b2 = c2, where a is the span, b is the rise and c is the rafter length.
How many rafters do I need for a 20 foot span?
As per general rules and guideline, for 10 -12 foot span, generally you need 2″×6″ size of rafter, for 15 -16 foot span, you need 2″×8″ rafter, for 18 – 20 foot span, you need 2″×10″ rafter & for 24 foot span, you need 2″×6″ size of rafter placed at 16″ apart from centre.
What does it mean when you are securing the answers for forces FAF and FAB positive?
If we are securing the answers for forces FAF and FAB positive, it indicates that we have assumed the correct direction for forces.
What does FFE in negative sign mean?
We have secured the value for the force FFE in negative sign and it will indicate that our assumption for the direction for this force FFE is wrong and its direction must be reversed.
What are forces in truss members?
Forces in the truss members are required to calculate for the selection of appropriate size, structural shapes and material to withstand the forces.
What does force away from the joint represent?
Force away from the joint will represent the tension in the member of truss. Therefore, member AB will be in tension.
How many transverse forces are there in 2 KN?
There are two transverse forces of 2 KN are acting on the members of the given truss as displayed here in above figure.
Can a given truss be solved?
If above equation is satisfied then only, we can say that given truss problem could be solved or determined by using the equations of equilibrium.
Do we consider the equilibrium of each joint separately?
We will consider the equilibrium of each joint separately and we will also satisfy the condition of equilibrium.
What is the next step in solving for reactionary force?
After solving for the reactionary force, the next step is to locate a joint in the truss that connects only two members, or that has only 2 unknown forces. Based on the simple truss used in the last step, this joint would be either A or B. The choice of this joint is up to you, as long as it only connects two members.
What is a truss in engineering?
A truss is one of the major types of engineering structures and is especially used in the design of bridges and buildings. Trusses are designed to support loads, such as the weight of people, and are stationary. A truss is exclusively made of long, straight members connected by joints at the end of each member.
How does the method of joints work?
Method of joints. The method of joints analyzes the force in each member of a truss by breaking the truss down and calculating the forces at each individual joint. Newton's Third Law indicates that the forces of action and reaction between a member and a pin are equal and opposite.
How to find forces on a truss?
To calculate forces on a truss you will need to use trigonometry of a right triangle. A right triangle is a triangle in which one angle is equal to 90 degrees. If the angle is 90 degrees, the two sides of the triangle enclosing the angle will form an "L" shape.
How to keep a truss stationary?
In order for the truss to remain stationary, the forces on each joint from every direction must cancel each other out. If a force is directed at an angle, like in the case of some members of a truss, the force can be broken into a vertical and a horizontal component.
What are trusses used for?
Step 1: Examples of Trusses. Trusses are used in the construction of nearly every road bridge you will encounter in your city's highway system. The 3 main types of trusses used in bridge design are Pratt, Warren and Howe. Truss type differs only by the manner and angle in which the members are connected at joints.
What are the forces that a truss absorbs?
In the case of a stationary truss, the acceleration taken into account is that of gravity. Therefore, the forces that a truss absorbs are the weight (equal to mass multiplied by gravity) of its members and additional outside forces, such as a car or person passing over a bridge.
Geometry and basic principles
A truss represents a structural system whose elements are two-force members arranged in a planar triangular pattern and each member is either in tension or compression. The stability of a truss relates to its triangular shape. By definition, trusses have pinned joints and concurrent straight members and have to be loaded through their joints.
Stability and determinacy in trusses
The first step in designing a truss is the analysis of its stability, its internal and external determinacy or indeterminacy. Stability in trusses refers to their ability to maintain their configuration while resisting loads applied to their joints.
Zero-force members
There are members in trusses that are designed for moving loads. Thus, depending on the position of the external load, they may carry no load. These members are often referred to as zero-force members.
3D Trusses – Space frames
Space frames are three-dimensional trusses where members are in tension and compression only. By definition, true trusses should have pinned connections while frames have rigid joints. Space frames may have both pinned and rigid connections.
Rule of thumb to determine the proportions of structural components
The economic depth-to-span ratio for steel trusses is 1:10 to 1:20, and for timber trusses is 1:6 to 1:10. The spacing of trusses in roof structures should be 20 to 30 ft for steel structures and 12 to 27 ft for timber trusses. The economic spans of different trusses are shown in the following table.
Topics for critical thinking
The best way to understand how tensegrity structures work is to make a physical model. Let’s get started by watching the following instructional video (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=DQxNPhR20r0) on making a tensegrity model!
Why is the third one useless?
The third one is useless in this case because one assumption of the truss is that the connections are hinges; meaning , it cannot experience moment. This further tells us that the method of joints only works on joints with two unknown bar forces.
How to solve bar forces?
Usually, this is the strategy for solving bar forces – find the point where two or more forces will meet and apply ΣM = 0 at the intersection point to find the unknown bar force.
What is the final step in truss design?
As a final step, it is best to summarise all results in a table as shown. For ease in reference, categorise truss members as top chords, bottom chords, or web members. This table serves as a basis for the design phase.
How to tell if bar force is compression or tension?
Another way of determining whether the bar force is tension or compression is to look at the direction of the force at the joint. The bar force is tension if it points away from the joint and compression if it points towards it. Based from this, bar force AB is in compression while AC is in tension.
How many bar forces have been solved?
Congratulations! You have solved all 11 bar forces. You can double-check your results by considering joints C and E (unused joints in the solution) and check if the computed values satisfy the equilibrium equations.
What is the first part of the reaction analysis?
The first part of our analysis is to find the reactions : Av, Ah, and RE. We assume their directions and apply the equilibrium equations to the whole structure to get these components. In case one of the answers are negative, it means we have a wrong assumed direction and the correct is the opposite. Starting with Ah:
How many members are in a truss?
For this truss example, there are 11 members, 3 reaction components (hinge at A and roller at E), and 7 joints:
