
To solve problems using the Charles law first one defines the values he knows, like for example initial and final volumes of the gas and and initial temperature . Then one writes the Charles law in the form and from this relation one finds the value of the unknown variable (final temperature in this example)
What are some real life examples of Charles law?
Top 6 Charles Law Examples in Real Life
- Hot Air Balloon
- Bursting Of A Deodorant
- Bakery Products
- Turkey Pop Up Timer
- Opening Of A Soda Can
- Helium Balloon On Cold Day
How to calculate Charles law?
The procedure to use the Charles law calculator is as follows:
- Enter the volume, temperature, and x for the unknown in the input field
- Now click the button “Calculate x” to get the volume of gas
- Finally, the result will be displayed in the output field
Which formula represents Charles's law?
Charles Law Formula Definition of Charles Law Formula is, “When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and therefore the volume is going to be in direct proportion.” The equation of the law is PV = k.
What relationship does Charles law explain?
The relationship between the volume and temperature of a gas was first put forward by the French scientist Jacques-Alexandre-César Charles at around 1787 and is known as Charles’ Law. Charles’ law states: "For a fixed mass of gas, at a constant pressure, the volume (V) is directly proportional to the absolute temperature (T)."
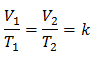
How do you solve for final volume in Charles Law?
0:172:05Charles's Law - Solving for Final Volume - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe first thing I'm going to do here is write up my formula. V1 over t1 is equal to v2 over t2 theMoreThe first thing I'm going to do here is write up my formula. V1 over t1 is equal to v2 over t2 the second thing I'm going to do is convert my Celsius temperatures into Kelvin. So 10 degrees Celsius
How do you solve Charles law problems for v2?
1:115:25Charles' Law - Volume and Temperature - V1/T1=V2/T2YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTo get your temperature in Kelvin you add 273.15 I'm going to be lazy here just do 273. That givesMoreTo get your temperature in Kelvin you add 273.15 I'm going to be lazy here just do 273. That gives me 313. Must be in Kelvin cannot stress that enough. I'm looking for my final volume my v2.
What is Charles's law example?
Here are several examples of situations in which Charles' Law is at play: If you take a basketball outside on a cold day, the ball shrinks a bit as the temperature is decreased. This is also the case with any inflated object and explains why it's a good idea to check your car's tire pressure when the temperature drops.
What is Charles's law as an equation?
Charles' Law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. We can represent this using the following equation: V α T. Since V and T vary directly, we can equate them by making use of a constant k. V T = c o n s t a n t = k.
What is the formula for V1 in Charles Law?
If V1 and P1 are the initial volume and pressure, and V2 and P2 are the final volumes and pressure, then V1 x P1 = V2 x P2. Charles' Law – the volume of a given mass of gas at constant pressure increases by 1/273 of its volume for every 1°C rise in temperature.
What is Charles Law easy?
The physical principle known as Charles' law states that the volume of a gas equals a constant value multiplied by its temperature as measured on the Kelvin scale (zero Kelvin corresponds to -273.15 degrees Celsius).
How do you solve v1 t1 v2 t2?
0:457:35Charles' Law Practice Problems & Examples Explained: V1/T1 = V2/T2YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipSo we just do 132 plus 273. And I'll be 405 degrees Kelvin then to solve for v2 we just crossMoreSo we just do 132 plus 273. And I'll be 405 degrees Kelvin then to solve for v2 we just cross multiply. So notice will be 900.
How is a ping pong ball An example of Charles Law?
In this image we can see how volume increases when temperature increases. You can use Charles law on crushed ping pong balls too. When you put the crushed ping pong ball in hot water, the air molecules inside expand making the ping pong round again. Charles law can also be used in architecture.
What is 2nd Charles Law?
Alternate titles: Gay-Lussac's law, second gas law. By The Editors of Encyclopaedia Britannica • Edit History. Table of Contents. Charles's law, a statement that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature, if the pressure remains constant.
How do you rearrange Charles Law to find t2?
2:315:44Rearranging Charles', Gay-Lussac's, and Avogadro's Laws - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clip1 V 1 over V 1 that cancels out and I get t2 equals t1 times v2 divided by V 1. So that's crossMore1 V 1 over V 1 that cancels out and I get t2 equals t1 times v2 divided by V 1. So that's cross multiplication. And it's a good technique to know it can save you a little bit of time.
What formula is v1 t1 V2 t2?
Charles's law states that temperature and pressure are directly proportional. This means if temperature increases, then pressure will also increase. On the other hand, if temperature decreases, then pressure will also decrease. The equation for comparing two samples of a gas using this law is V1T1=V2T2.
What are the 2 constants in Charles Law?
Charles law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. The law also states that the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion when the pressure exerted on a sample of a dry gas is held constant.
Why do we use Charles' law?
Because of this proportionality, we can use Charle’s law to see how a system would react to a change in temperature, or how a system would react to a change in volume (both with constant pressure). As temperature increases, volume increases, and vice versa.
Who discovered the relation between temperature and volume?
French physicist Jacques Charles also noticed this phenomenon, and discovered the relation between temperature and volume. This is what is know as Charle’s Law, and can be written as: .
What is Charles' law?
Charles’ law is one of the gas laws which explains the relationship between volume and temperature of a gas. It states that when pressure is held constant, the volume of a fixed amount of dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. When two measurements are in direct proportion then any change made in one ...
Which law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional?
Charles’ Law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. We can represent this using the following equation:
Who discovered that gas varies with temperature?
Jacques Charles, a French scientist, in 1787, discovered that keeping the pressure constant, the volume of a gas varies on changing its temperature. Later, Joseph Gay-Lussac, in 1802, modified and generalized the concept as Charles’s law. At very high temperatures and low pressures, gases obey Charles’ law.
What is Charles Law?
Charles’ Law, also sometimes referred to as the law of volumes, gives a detailed account of how gas expands when the temperature is increased. Conversely, when there is a decrease in temperature it will lead to a decrease in volume.
Who created the law of physics?
This law was formulated in the year 1780 by French physicist Jacques Charles. This law was described extensively in his unpublished work.
What is the law of volume?
Charles law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. The law also states that the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion when the pressure exerted on a sample of a dry gas is held constant. This law was formulated in the year 1780 by French physicist ...
How to equate V and T?
Since V and T are varying directly, we can equate them by making use of the constant k.
Is the volume of the fixed amount of dry gas directly proportional to absolute temperature?
As we are aware of the fact that, at constant pressure, the volume of the fixed amount of the dry gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature according to Charle’s law. We can represent the statement in the following manner.
What is Charles' law calculator?
The Charles' law calculator is a simple tool which describes the basic parameters of an ideal gas in an isobaric process. In the text, you can find the answer to the question "What is Charles' law?", learn what the Charles' law formula looks like, and read how to solve thermodynamic problems with some Charles' law examples.
What is Charles' law?
Charles' law definition. Charles' law (sometimes referred to the law of volumes) describes the relationship between the volume of a gas and its temperature when the pressure and the mass of the gas is constant. It states that the volume is proportional to the absolute temperature. There are a few other ways we can write the Charles' law definition, ...
What is Charles' law application in real life?
There are actually various areas where we can use Charles' law. Here is a list of a few of the most popular and most interesting examples:
