Solving Charles' Law for V₂ we get: V₂ = V₁ • T₂ ÷ T₁ V₂ = 1,300 in³ • 549.67 R ÷ 537.67 R = 1,329 in³ Using the calculator: We want to solve for V2 so we click that button. Looking at the previous paragraph, we need to convert both of the Fahrenheit temperatures to Rankine.
Can you solve Charles'law with a calculator?
This calculator can solve for any one of the four variables of Charles' Law. You can input any type of units but you must be consistent. For example, you can't use cubic inches for volume 1 and liters for volume 2. Do you want to solve for:
How do you write Charles’ law equation?
Based on the definition of Charles’ law, we can write the Charles’ law equation in the following way: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ , where V₁ and T₁ are initial volume and temperature, respectively. Similarly, V₂ and T₂ are the final values of these gas parameters.
How do you find the final volume in Charles'law?
Let's say we want to find the final volume, then the Charles' law formula yields: V₂ = V₁ / T₁ * T₂. If you prefer to set the final volume and want to estimate the resulting temperature, then the equation of Charles' law changes to: T₂ = T₁ / V₁ * V₂. In advanced mode, you can also define the pressure and see how many moles ...
How do you calculate T1 and T2 in Charles law?
V1 = 100 liters T1 = 427° C + 273 ° K = 700 ° K (temperatures used in Charles Law must be in Absolute Scale) V2 = 73 liters T2 = ? Click to see full answer. Similarly one may ask, what is the formula used in Charles Law? You calculate Kelvin temperature by adding 273 to the Celsius temperature.

What is the formula for v2 in Charles Law?
V₂ = V₁ / T₁ * T₂ . If you prefer to set the final volume and want to estimate the resulting temperature, then the equation of Charles' law changes to: T₂ = T₁ / V₁ * V₂ .
How do you solve the v2?
2:187:32Rearranging the Combined Gas Equation - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipTimes v1 times t2 equals the cross multiplication of this equals t1 times p2 times v2 now we want toMoreTimes v1 times t2 equals the cross multiplication of this equals t1 times p2 times v2 now we want to get v2 by itself.
How do you find v1 with v2?
1:222:48Kinematics Given V1, V2, A... find D. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFirst so d equals v2 squared minus v1 squared all over 2a.MoreFirst so d equals v2 squared minus v1 squared all over 2a.
How do you find v2 in Boyle's law?
We have to rewrite the Boyle's law equation: V₂ = p₁ * V₁ / p₂ = 2.5 atm * 6 l / 0.2 atm = 75 l . You can always use our Boyle's law calculator to check if your evaluations are correct!
How do you calculate V2 in chemistry?
You can solve for the concentration or volume of the concentrated or dilute solution using the equation: M1V1 = M2V2, where M1 is the concentration in molarity (moles/Liters) of the concentrated solution, V2 is the volume of the concentrated solution, M2 is the concentration in molarity of the dilute solution (after ...
How do you find V2 in c1v1 c2v2?
0:395:27The C1V1 = C2V2 Equation Explained - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipYou would then divide by V one so the starting concentration would therefore equal the finalMoreYou would then divide by V one so the starting concentration would therefore equal the final concentration multiplied by the final volume divided by the starting volume.
How do you find v1 and v2 in a series circuit?
7:5910:10How to Solve a Series Circuit (Easy) - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipAnd so to show you this so v1 is gonna equal our 1.5 amps times our 17 ohms and that's going to giveMoreAnd so to show you this so v1 is gonna equal our 1.5 amps times our 17 ohms and that's going to give us a total voltage of 25. Point 5 volts. Now for our second voltage drop.
What does a v2 v1 t mean?
(change in displacement over time) a = v2 – v1 / t. (a = Δv /t) (change in velocity over time)
How do you find the v2 in P1V1 t1 P2V2 t2?
0:255:021.3 Solve problems on T, P and V for a fixed mass of an ideal gas [SL IB ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipNo matter how you mess with P V and T as long as the ratio P times V divided by T is unchangedMoreNo matter how you mess with P V and T as long as the ratio P times V divided by T is unchanged everything's gonna be dandy. So the equation that you're gonna need is p1 v1 over t1 is p2 v2 over t2.
What is v1 n1 v2 n2?
Avogadro's Law: V1n1=V2n2. Avogadro's Law also explains how when the temperature and pressure are constant, volume is directly proportional to gas amount (in moles), which means that as the volume increases, so does the amount of gas. Avogadro's Law also states that: Vn=k, where k is the proportionality constant.
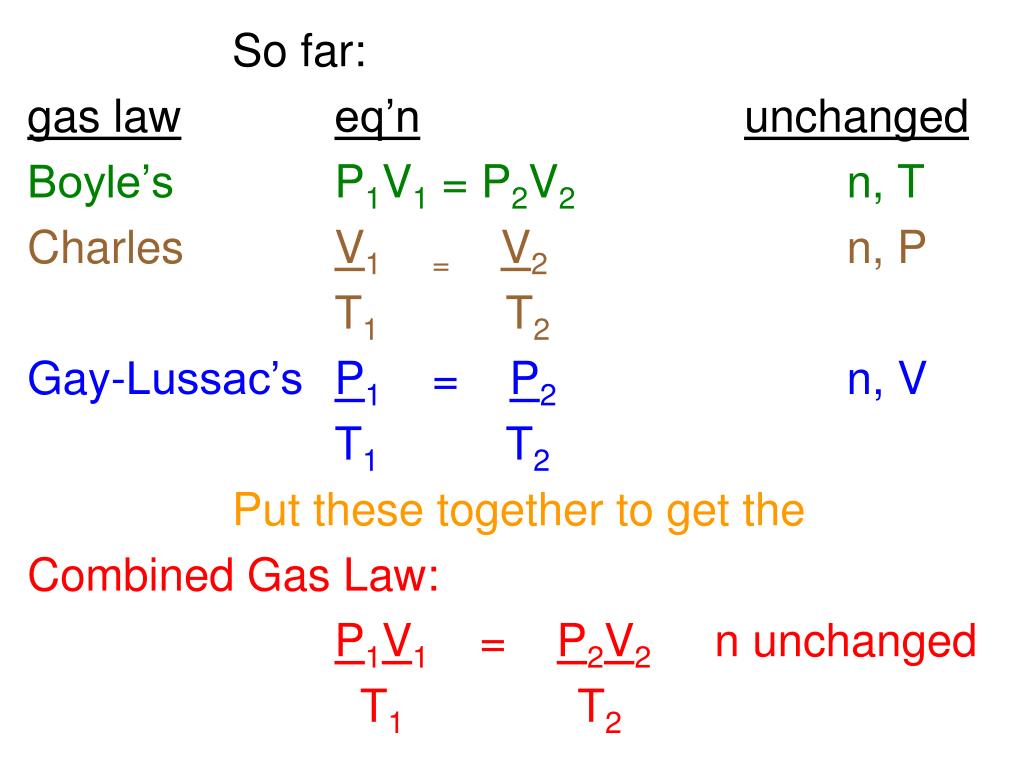
What is p1 v1 p2 v2?
pressure when temperature and amount of substance is constant. P1V1 = P2V2. Charle's law - The volume of a gas is directly proportional to the. temperature when pressure and amount of substance is constant.
How do you verify Charles’s law?
Afterwards, the gas is cooled in a water bath by maintaining the amount of the air in the flask constant. By measuring/determining the initial and final temperature and volume, we verify Charles’s law.
What is the constant in Charles Law?
Pressure is the constant in Charles’ law. If the pressure is constant, then this law upholds as being true. Per the law, if the volume of a gas…
What does Charles law state?
The physical principle known as Charles’ law states that the volume of a gas equals a constant value multiplied by its temperature as measured on the Kelvin scale (zero Kelvin corresponds to -273.15 degrees Celsius).
What is p1v1 p2v2?
According to Boyle’s Law, an inverse relationship exists between pressure and volume. … The relationship for Boyle’s Law can be expressed as follows: P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume values, and P2 and V2 are the values of the pressure and volume of the gas after change.
What does Boyles law mean?
This empirical relation, formulated by the physicist Robert Boyle in 1662, states that the pressure (p) of a given quantity of gas varies inversely with its volume (v) at constant temperature; i.e., in equation form, pv = k, a constant. …
What is Charles' law calculator?
The Charles' law calculator is a simple tool which describes the basic parameters of an ideal gas in an isobaric process. In the text, you can find the answer to the question "What is Charles' law?", learn what the Charles' law formula looks like, and read how to solve thermodynamic problems with some Charles' law examples.
What is Charles' law application in real life?
There are actually various areas where we can use Charles' law. Here is a list of a few of the most popular and most interesting examples:
What is Charles' law?
Charles' law definition. Charles' law (sometimes referred to the law of volumes) describes the relationship between the volume of a gas and its temperature when the pressure and the mass of the gas is constant. It states that the volume is proportional to the absolute temperature. There are a few other ways we can write the Charles' law definition, ...
What is the formula for the volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure?
The above formula is Charles' Law, named after the French experimenter Jacques Charles (1746-1823). It states that the volume of a fixed mass of gas at a constant pressure is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
Can you use cubic inches for volume 1?
You can input any type of units but you must be consistent. For example, you can't use cubic inches for volume 1 and liters for volume 2. Do you want to solve for: Similar to Boyle's Law, every Charles' Law word problem always gives you three of the four variables you will need.
What is Charles' law?
Charles’s law states Definition: Charles’s law (also known as the law of volumes) is an experimental gas law that describes how gases tend to expand when heated. A modern statement of Charles’s law is: When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be directly related.
Does K cancel in units?
The temperature units of K will cancel. x is a symbol for an unknown and, technically, does not carry units. So do not write x L for x liters.
How do you convert to Charles Law?
Based on the definition of Charles’ law, we can write the Charles’ law equation in the following way: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂ , where V₁ and T₁ are initial volume and temperature, respectively. Similarly, V₂ and T₂ are the final values of these gas parameters.
What is a good example of Charles Law?
One easy example of Charles’ Law is a helium balloon. If you fill a helium balloon in a warm or hot room, and then take it into a cold room, it shrinks up and looks like it has lost some of the air inside. But if you take it back to a warm or hot place, it fills back up and seems to be full again.
What is Lussac’s law formula?
The pressure of a gas is directly proportional to its temperature while the volume is kept constant. P / T = constant or Pi / Ti = Pf / Tf are the standard calculations for Gay-Lussac ‘s law.
What is p1v1 p2v2?
According to Boyle’s Law, an inverse relationship exists between pressure and volume. … The relationship for Boyle’s Law can be expressed as follows: P1V1 = P2V2, where P1 and V1 are the initial pressure and volume values, and P2 and V2 are the values of the pressure and volume of the gas after change.
What does p1v1 t1 p2v2 t2 mean?
The general gas equation , namely: i. P1V1/T1 = P2V2/T2. ii. Note: the temperature (T) is expressed in degrees absolute.
What is Charles' law?
Charles’ law is one of the gas laws which explains the relationship between volume and temperature of a gas. It states that when pressure is held constant, the volume of a fixed amount of dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. When two measurements are in direct proportion then any change made in one ...
Which law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional?
Charles’ Law states that at constant pressure, the volume of a fixed mass of a dry gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. We can represent this using the following equation:
What is the initial volume of a gas at 150 K?
The initial volume of a gas at 150 K is 9 litres.
Who discovered that gas varies with temperature?
Jacques Charles, a French scientist, in 1787, discovered that keeping the pressure constant, the volume of a gas varies on changing its temperature. Later, Joseph Gay-Lussac, in 1802, modified and generalized the concept as Charles’s law. At very high temperatures and low pressures, gases obey Charles’ law.