These include:
- Bending forward and placing your palms on the ground with your legs straight
- Bending your thumbs backwards
- Bending your little fingers backwards
Full Answer
How is ligamentous laxity measured?
Jan 14, 2020 · How do you test for ligament laxity? ACL LAXITY TESTS The most frequently used tests for assessing ACL laxity are the anterior drawer test , Lachman test , Maclntosh test , jerk test , flexion rotation drawer test , Slocum test , and Losee test .
How do you test for ligaments in the knee?
Nov 10, 2021 · Knee ligamentous laxity can be diagnosed using a knee arthrometer such as the DYNEELAX, the GNRB or the KT-1000 or doing some physical tests like the Lachman test or the anterior drawer test. Using an arthrometer is advised …
How do you test for medial collateral ligament stress?
Nov 06, 2021 · Knee ligamentous laxity can be diagnosed using a knee arthrometer such as the DYNEELAX, the GNRB or the KT-1000 or doing some physical tests like the Lachman test or the anterior drawer test. Using an arthrometer is advised as the results are objective and reproducible. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device.
What tests are used to assess lateral instability of the ankle?
Feb 17, 2022 · How do you perform the thumb ulnar collateral ligament laxity test? The patient is sitting position for the test. While the examiner stabilizes the patient’s hand with the help of one hand. While holding the thumb in extension position, the examiner applies valgus stress to the metacarpophalangeal ...
What is ligament laxity?
What is Ligamentous Laxity? Ligamentous Laxity or ligament laxity is nothing, but loose ligaments which lead to chronic body pains. If this condition affects all the joints of the body then this condition is known as generalized joint hypermobility.
How to diagnose laxity?
There is a simple test to diagnose Ligamentous Laxity which is done by bending the index finger backwards. If the patient is able to bend their index finger backward by 90 degrees without any discomfort, then it means that the patient has Ligamentous Laxity or loose ligaments.
What is joint hypermobility?
Joint hypermobility occurs when the ligaments, which hold the joints together, are extremely loose. Weak muscles surrounding the joint also can contribute to joint hypermobility. The common joints which are affected are shoulders, knees, wrists, elbows and fingers. Ligamentous Laxity is quite a common condition, particularly in children, ...
What causes laxity in the body?
Such ligamentous laxity is known as benign hypermobility syndrome. The only symptom of ligamentous laxity is hypermobile joints, the causes of which include: The structure and shape of the bone. The structure of the muscle, such as the strength ...
What is conservative treatment for ankle sprain?
Conservative treatment for ligament injury or an ankle sprain comprises of R.I.C.E. (Rest, Ice, Compression, Elevation), to prevent and relieve any swelling. After the pain and swelling has subsided, then further examination will show which ligaments are affected and the severity of the injury.
What is a Beighton score?
Beighton score is a tool, which is used for measuring loose ligaments or Ligamentous Laxity. Getting a score of 5 or more is a positive test; however, the patient may still have Ligamentous Laxity even if the test result is negative.
How is a non-test leg flexed?
The foot should be flat on the floor. The non-test leg is flexed at the knee to prevent the foot on the non-test leg from contacting with the ground. The examiner supports the patient by the outstretched hand or hands to provide balance.
What is a positive test for medial collateral ligament?
Increased laxity compared to the unaffected side is considered a positive test for medial collateral ligament (MCL) injury.
How is the McMurray test performed?
The McMurray test is performed with the patient supine and the examiner grasping the medial aspect of the affected knee with one hand and the patient’s heel with the other hand. A valgus force is generated and the tibia internally rotated as the knee is moved from a fully flexed position to full extension. The test is repeated while externally rotating the tibia. Any “popping” or pain along the joint line is considered a positive test.
Is anterior drawer test positive?
The first is the opposite of the anterior drawer test. Absence of a discrete endpoint with posterior force applied to the tibia is considered positive. The second approach is positive if anterior force applied to the tibia corrects a posterior subluxation or “sag” of the affected knee.
What is the function of the Deltoid ligament?
The deltoid ligament as a whole has a dual function of providing stability to the talotibial joint as well as transferring forces between the tibia and tarsus. It fixates the tibia above the talus and restricts the talus from shifting into a valgus postion, translating antero-laterally or rotating externally.
What is the sensitivity of anterior drawer?
1. Sensitivity values for the Anterior Drawer test have been shown to be between 32% to 80% while specificity value has been reported as 80%. 2. A positive drawer test done 5 days after the injury, has been shown to be more sensitive and specific than the test done withing the 24-48 hours. 3.
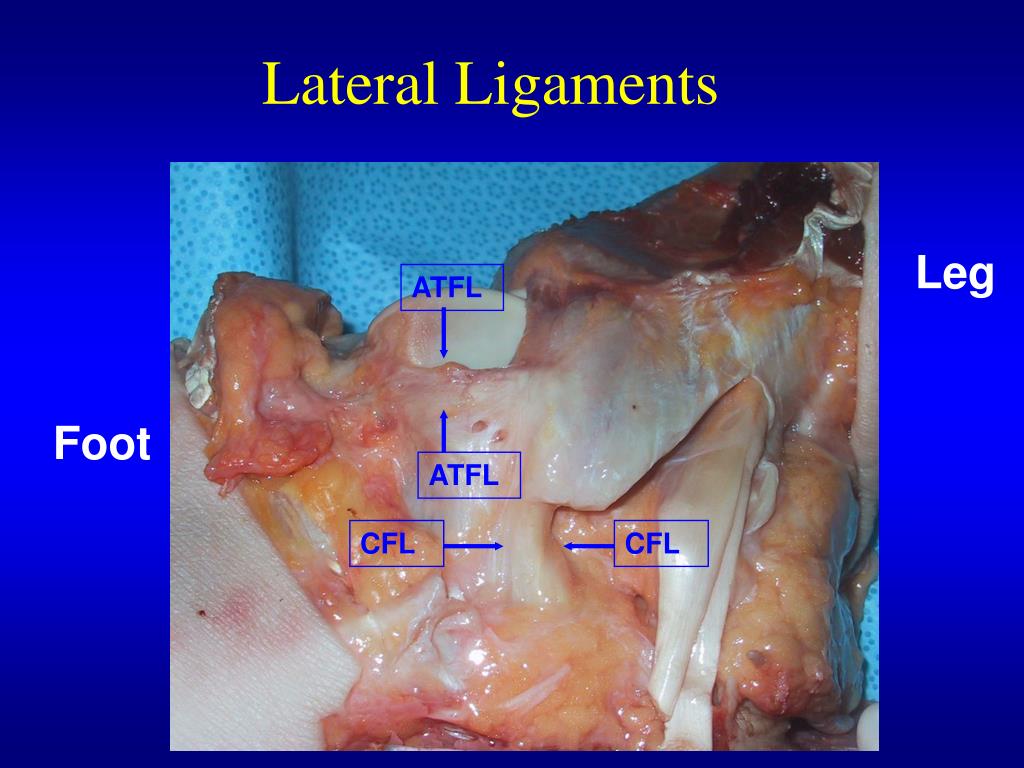
What is the PTFL?
The PTFL resists posterior movement of the talus. It is the strongest and least injured part of the complex. Injuries to PTFL usually occur in severe ankle sprains which also involve the ATFL and CFL. Lateral Ankle Ligaments.