
Explore
How do you test for stiff person syndrome? A diagnosis of stiff person syndrome (SPS) is typically made based on symptoms, a detailed medical history, and various tests used to support the diagnosis or rule out other diseases with overlapping symptoms. One commonly used test is a blood test to detect the presence of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies.
What is the prognosis for stiff person syndrome?
Tests for diagnosing stiff person syndrome may include the following: serum anti-GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase) 65 antibody serum amphiphysin antibody several other serum autoantibodies, hemoglobin A1c and vitamin levels lumbar puncture MRI of the brain and spine neurophysiological studies ...
What causes stiff person syndrome?
Apr 09, 2020 · A diagnosis of stiff person syndrome (SPS) is typically made based on symptoms, a detailed medical history, and various tests used to support the diagnosis or rule out other diseases with overlapping symptoms. [4] [8] One commonly used test is a blood test to detect the presence of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies.
What is the treatment for stiff person syndrome?
Dec 10, 2019 · Reaching a diagnosis for Stiff Person Syndrome can be difficult. Generally, SPS is suspected based on characteristic symptoms. A comprehensive medical history and examination, along with additional investigations, including blood …
What are the symptoms of stiff man syndrome?
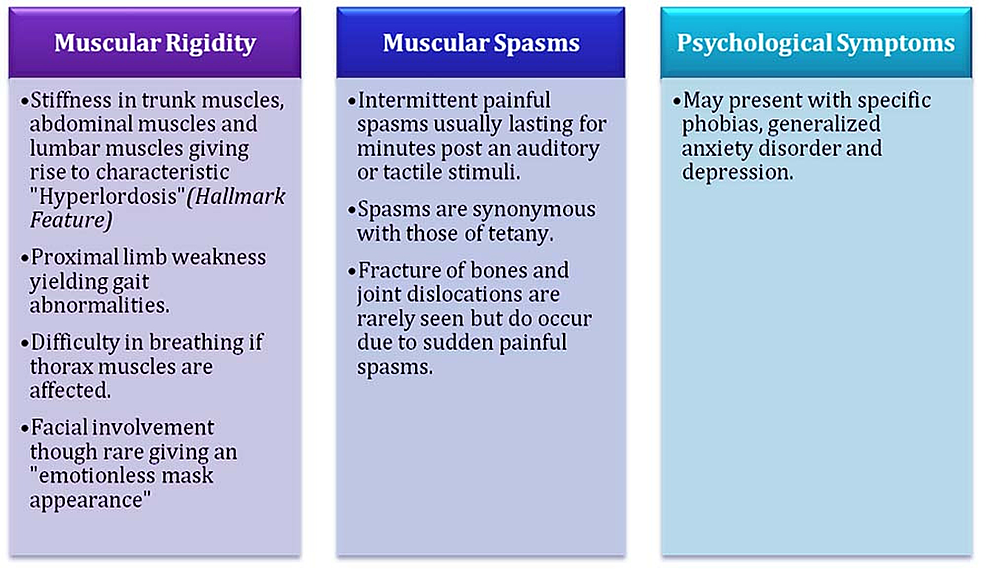
WHAT IS STIFF PERSON SYNDROME? Stiff person syndrome (SPS) is a rare autoimmune neurological disease that most often causes muscle stiffness and intermittent painful spasms. SPS can also cause unsteadiness and double vision along with other symptoms. Symptoms can worsen with quick movement, cold temperature, stress, and/or unexpected loud noises.
What is the protein that is involved in making gamma-aminobutyric acid?
Most people with stiff person syndrome have antibodies that are made to attack glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD). GAD is a protein in some neurons that are involved in making a substance called gamma-aminobutyric acid (GABA), which is responsible for controlling muscle movement.
What is the purpose of the Autoimmune Registry?
The Autoimmune Registry supports research for Stiff person syndrome by collecting information about patients with this and other autoimmune diseases. You can join the registry to share your information with researchers and receive updates about participating in new research studies. Learn more about registries.
What is the treatment for SPS?
Treatment aims to control symptoms and improve mobility and function. While some people on treatment for SPS may maintain reasonable levels of activity, the majority become increasingly disabled over time. Treatment options depend on the symptoms and severity in each person and may include: [2] [3]
What causes SPS?
SPS is caused by increased muscle activity due to decreased inhibition of the central nervous system. It is thought to have an autoimmune component and is often associated with diabetes, as well as other autoimmune diseases such as thyroiditis, vitiligo, and pernicious anemia.
What is the HPO database?
People with the same disease may not have all the symptoms listed. This information comes from a database called the Human Phenotype Ontology (HPO) . The HPO collects information on symptoms that have been described in medical resources.
How does stiff person syndrome affect the body?
For some people with this syndrome, symptoms resolve with treatment, or symptoms only affect a particular area of the body . For other people, symptoms may progress to include the muscles of the face, and some of the muscles in the body may be constantly rigid. Progression of the symptoms related to SPS can lead to frequent falls, which can become dangerous. [3] [4]
What is PubMed or Orphanet?
Orphanet is a European reference portal for information on rare diseases and orphan drugs. Access to this database is free of charge. PubMed is a searchable database of medical literature and lists journal articles that discuss Stiff person syndrome. Click on the link to view a sample search on this topic.
What is the name of the disorder that makes your muscles rebel against you?
But, though it’s rare, those muscles can sometimes rebel against us. Stiff Person Syndrome (SPS) is an autoimmune and neurological disorder with no known cause that can make the muscles in the torso and limbs alternate between ...
What are the symptoms of stiff person syndrome?
What are the symptoms associated with Stiff Person Syndrome? The main symptoms of Stiff Person Syndrome are muscle stiffening in the torso and limbs, along with episodes of violent muscle spasms. These can be triggered by environmental stimuli (like loud noises) or emotional stress.
What percentage of people with stiff person syndrome have anti-GAD antibodies?
About 60-80 percent of Stiff Person Syndrome patients have anti-GAD antibodies in their blood and cerebrospinal fluid (a water-like substance surrounding the brain). Many patients with SPS also have another autoimmune disease, such as type 1 diabetes, vitiligo, and pernicious anemia.
Can stiff person syndrome cause depression?
These symptoms can lead to difficulty walking and, over time, even greater disability. People with Stiff Person Syndrome are also more likely to have symptoms of depression and anxiety.
Is there a cure for stiff person syndrome?
There is no cure for Stiff Person Syndrome. When doctors treat patients with this condition, they focus on relieving symptoms with medications such as diazepam (a sedative that helps relieve muscle stiffness), baclofen (a muscle relaxant), and steroids (drugs to help suppress the immune response).
Is SPS more common in cancer?
SPS is also more common in people with certain kinds of cancer, including breast cancer, lung cancer, kidney cancer, thyroid cancer, colon cancer, and lymphomas. However, the reason for these links is still unknown.
Can SPS be confirmed by blood test?
Generally, SPS is suspected based on characteristic symptoms. A comprehensive medical history and examination, along with additional investigations, including blood tests and spinal fluid analysis, can confirm the diagnosis. When conducting those tests, your doctor is looking for elevated levels of GAD antibodies.
What is the name of the condition where the body is stiff?
Stiff person syndrome is a rare autoimmune movement disorder that affects the central nervous system (the brain and spinal cord). People with this condition first experience a stiffening of the muscles of their trunk followed, over time, by the development of stiffness and rigidity in the legs and other muscles in the body.
Why do my legs get stiff?
Over time, leg muscles become stiff and more muscles throughout your body become stiff including the arms and even the face. As stiffness increases, some people developed a hunched posture. In severe cases, this stiffness can make it hard to walk or move. Painful muscle spasms also occur.
What protein decreases Gaba?
It is thought that the immune system in people with stiff person syndrome mistakenly attacks GAD enzyme, which decreases the amount of GABA in the body. Antibodies to another protein called amphiphysin is a less common finding in people with this syndrome.
How long does it take for stiff person syndrome to develop?
Symptoms of stiff person syndrome can take several months to a few years to develop. Some patients remain stable for years; other slowly worsen. In most people with stiff person syndrome, the trunk and abdomen muscles are the first to become stiff and enlarged. Symptoms include pain, muscle stiffness and aching discomfort.
What to do if you have muscle spasms in your legs?
Contact your healthcare provider if you experience muscle spasms or stiffening of the muscles in your trunk, arms or legs. If you have any of the risk factors, especially an autoimmune condition, ask your doctor specifically about stiff person syndrome.
What test is used to diagnose stiff person syndrome?
If your healthcare provider suspects stiff person syndrome, tests to confirm the diagnosis may include: Blood test: Your blood is checked for the presence of antibodies to GAD or amphiphysin and for other signs that might indicate or rule out other diseases.
How rare is stiff person syndrome?
Stiff person syndrome is extremely rare. Only about one out of every one million people have been diagnosed this syndrome. Twice as many women have stiff person syndrome as men. Symptoms can occur at any age but usually develop between ages 30 and 60.
What is the test for GAD?
GAD antibodies may also be measured in the cerebral spinal fluid from a lumbar puncture. A doctor may also recommend electromyography (EMG), which records electrical activity in skeletal muscles. The EMG of a person with SPS typically shows continuous motor activity in the skeletal muscles.
Why is lumbar puncture not available?
Genetic testing currently is not available because the underlying genetic cause of stiff person syndrome has not been established.
What is stiff person syndrome?
stiff person syndrome (SPS) is typically done based on symptoms, a detailed medical history, and various tests used to support the diagnosis or rule out other diseases with overlapping symptoms. One commonly used test is a blood test to detect the presence of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies. About 60-80% of people with SPS have ...
What is SPS treatment?
TREATMENT. aims to control symptoms and improve mobility and function. While some people on treatment for SPS may maintain reasonable levels of activity, the majority become increasingly disabled over time. Treatment options depend on the symptoms and severity in each person.
Is a stiff person syndrome drug FDA approved?
It had never been tried for Stiff Person Syndrome before but had been successful with other autoimmune diseases. It was not FDA approved and was quite difficult to get. This Oncologist was the only one in the country willing to go through the numerous levels of medical appeals needed to get the drug.
How many people with SPS test positive for GAD?
Around 60 to 80% of people with SPS test positive for GAD antibodies. 4. Stiff-person syndrome treatment varies depending on a patient’s symptoms. There’s no cure, so treatment for stiff-person syndrome aims to control symptoms and improve a person’s mobility.
What is the test for SPS?
One common tool used to diagnose SPS is a blood test to detect the presence of glutamic acid decarboxylase (GAD) antibodies, a type of protein in your immune system designed to attack foreign objects. GAD is a protein contained in some of your neurons responsible for making a substance that helps control your movements.
What is stiff person syndrome?
Stiff-person syndrome does show patterns that resemble an autoimmune condition, where an overactive immune system attacks healthy parts of your body. Stiff-person syndrome has been associated with diabetes and other autoimmune conditions, including thyroiditis and vitiligo. 2. Almost all people with stiff-person syndrome experience anxiety.
What is the best treatment for SPS?
Standard therapies for managing SPS include taking a medication like a benzodiazepine (often used to treat acute anxiety), taking a muscle relaxant like baclofen or receiving immune-modulating therapies.
Why do people with SPS have stress?
However, many people with SPS also experience stress as the result of trying to cope with the disease and worry about having unexpected spasms. 3. A diagnosis for stiff-person syndrome is often made by ruling out other diseases.
What causes SPS symptoms?
Experts know SPS symptoms are caused by issues in your nervous system, especially the brain and spinal cord, areas associated with movement control. What, exactly, causes these central nervous system issues isn’t quite as clear.
What test is used to diagnose SPS?
Tests could include a hemoglobin A1C test to rule out diabetes, a complete blood count to rule out pernicious anemia, or a thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) test to rule out thyroiditis. Electromyography, a test that records muscles at rest and during contraction, may also be used to diagnose people with SPS.
Overview
Symptoms
- Stiff person syndrome (SPS) is characterized by episodes of muscle stiffness in the trunk and limbs. This muscle rigidity may cause abnormal postures such as being stiffened and hunched over. During episodes of muscle stiffness, affected individuals may also have muscle spasms. The spasms and muscle rigidity may cause people to fall when they are walking or standing. Th…
Causes
- Scientists dont yet understand the complete picture of what causes stiff person syndrome, but research indicates that it is the result of an abnormal autoimmune response in the brain and spinal cord. Autoimmune responses occur when the immune system mistakenly attacks the body. Most people with stiff person syndrome have antibodies that are made to attack glutamic acid d…
Genetics
- Some individuals with stiff person syndrome will have antibodies to amphiphysin, a protein involved in the transmission of signals from one neuron to another. Individuals with these antibodies have a higher risk for developing breast, lung, or colon cancer.
Diagnosis
- A diagnosis of stiff person syndrome (SPS) is typically made based on the presence of the characteristic symptoms, a detailed medical history and clinical exam, and various tests. Specific tests are used to support or confirm the diagnosis, and to rule out conditions with overlapping symptoms. One commonly used diagnostic tool is a blood test to de...
Treatment
- Treatment of stiff person syndrome (SPS) focuses on the specific symptoms present in each person. Benzodiazepines, diazepam, or baclofen may be used to treat muscle stiffness and spasms. Anti-seizure medications and pain medications may also be effective for some people. Recently, studies have shown that intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) or plasmapheresis may b…
Prognosis
- The long-term outlook for people affected by stiff person syndrome (SPS) can vary widely depending on the symptoms of each person. For some people with this syndrome, symptoms resolve with treatment, or symptoms only affect a particular area of the body. For other people, symptoms may progress to include the muscles of the face, and some of the muscles in the bod…