- The Symptoms of Corneal Erosion. The cornea is a dome-shaped surface which, much like our skin, protects and covers the front of the eye.
- Treating Corneal Erosions. Treating a corneal erosion is often straightforward and varies from lubricating drops, topical ointment, and using a therapeutic contact lens (TCL) which reduces the pain and encourages ...
- Laser Eye Surgery: A Solution to Corneal Erosions. Other than the treatments outlined above, as it is a minimally invasive and considered one of the only effective therapies over the ...
- ointments like sodium chloride 5%
- placing a bandage lens and starting topical antibiotics.
- surgery (superficial keratectomy) or laser treatment to remove corneal tissue.
- surgery called anterior stromal puncture. Your ophthalmologist will make tiny holes on the surface of your cornea.
Can a corneal abrasion heal on its own?
Most corneal abrasions aren’t serious and will heal on their own within a day or two. But if the abrasion becomes infected, it can lead to a serious eye problem called a corneal ulcer. In other cases, the abrasion can cause inflammation inside the eye called iritis. Symptoms of corneal abrasion Symptoms of corneal abrasion include:
How will I recover from a corneal abrasion?
If the corneal abrasion is small, it will be healed in a couple of days with the help of eye drops or ointment. When the abrasion is large, bandage contact lenses may be advised to place in the eye to support your comfy level and healing.
How do you treat a corneal abrasion at home?
What is the fastest way to heal a scratched eye?
- DO rinse your eye with saline solution or clean water. …
- DO blink. …
- DO pull your upper eyelid over your lower eyelid. …
- DO wear sunglasses. …
- DON’T rub your eye. …
- DON’T touch your eye with anything. …
- DON’T wear your contact lenses. …
- DON’T use redness-relieving eye drops.
What are good home remedies for corneal abrasion?
Home Remedies To Treat A Scratched Cornea Tea Bags, For minor corneal abrasions, It causes discomfort to the eyes, Flush The Eye With Saline Dreamstime, When individuals flush the eye with saline, To complete this, several treatments options are available but one of the best natural treatments you can try is to wear sunglass during the healing ...
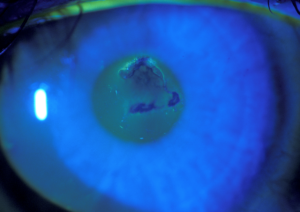
Can corneal erosion be cured?
The good news about recurrent corneal erosion is that, unless there is an ongoing underlying corneal disease, most patients will ultimately heal completely and not have any more episodes. However, it may take years for this to happen.
What causes corneal erosions?
Corneal erosion is caused by a loose attachment of the epithelium to the underlying tissue. This often happens at the site of an earlier abrasion. Some patients have an underlying condition called “map-dot-fingerprint dystrophy” that predisposes them to having recurrent corneal erosions.
How long does a corneal erosion take to heal?
A corneal erosion or abrasion typically heals quickly, often within a few days to a week. It is important not to rub your eye during the healing process as the new epithelial cells are fragile and can easily be rubbed off. Sometimes your ophthalmologist may choose to patch your eye tightly.
What is the best treatment for recurrent corneal erosion?
Recurrent corneal erosion is relatively common, and may not be adequately managed with medications. Surgical intervention may enhance outcomes and reduce recurrences. Epithelial debridement with diamond burr polishing is a safe, effective procedure for the treatment of this condition.
Can dry eye cause corneal erosion?
Damage to the surface of your eyes. If left untreated, severe dry eyes may lead to eye inflammation, abrasion of the corneal surface, corneal ulcers and vision loss.
How painful is corneal erosion?
The most common symptom of corneal erosion is mild to severe pain. The pain may be particularly uncomfortable in the morning upon awakening because the eyes naturally get dry at night, and the eyelid can stick slightly to the epithelium.
Do eye drops help corneal abrasion?
Use lubricating eye drops to keep your eye moist. These over the counter drops won't fix the abrasion but they will keep your eye comfortable during the healing process. Try to rest your eyes as much as possible for a few days. Don't do anything that can cause eye strain like reading or staring at a computer screen.
Can you watch TV with a corneal abrasion?
MEASURES YOU SHOULD TAKE TO HELP TREAT YOUR CORNEAL ABRASION: 1. Rest your eyes as much as possible. Watching television, reading, or any task requiring concentrated vision can be irritating.
Does sleep help corneal abrasion?
Most of the time, a scratched cornea is a minor injury that will heal by itself. Due to the high density of nerve endings in your cornea, even a small injury can be painful. To minimize pain while sleeping, it's a good idea to avoid sleeping on the side of your injured eye.
Can an optometrist treat corneal erosion?
There is a new treatment protocol that a primary care optometrist can employ to treat recurrent corneal erosions in office, involving corneal debridement and amniotic tissue transplantation.
Why is my corneal abrasion not healing?
Several conditions can lead to the corneal healing process failing, forming persistent epithelial defects (PED) and possibly underlying ulceration. Neurotrophic keratitis (NK), for example, compromises corneal healing by reducing nerve function.
Why does my corneal abrasion keep coming back?
A recurrent corneal erosion is typically caused by a previous injury to the cornea and Bowman's layer. 1 If you injure your eye with a sharp instrument or fingernail or suffer a paper cut to the eye resulting in corneal abrasion, you are at risk of later developing a recurrent corneal erosion.
How do you get corneal abrasion?
A corneal abrasion is a superficial scratch on the clear, protective "window" at the front of your eye (cornea). Your cornea can be scratched by contact with dust, dirt, sand, wood shavings, metal particles, contact lenses or even the edge of a piece of paper.
Can a damaged cornea repair itself?
The cornea can recover from minor injuries on its own. If it is scratched, healthy cells slide over quickly and patch the injury before it causes infection or affects vision. But if a scratch causes a deep injury to the cornea, it will take longer to heal.
How can I stop my cornea from scarring?
Prevention is always the easiest and most efficient way to prevent scarring. Conditions that notoriously lead to scarring (corneal infection or ulcer) may be treated with immune-suppressing steroid eye drops after the infection is resolved to minimize or prevent scar formation.
How long does a BCL last?
Patients who are unresponsive to lubrication or have large erosions may benefit from an extended-wear bandage soft contact lens (BCL), such as Focus Night & Day or Kontur, in the affected eye for two to eight weeks, with a prophylactic topical antibiotic, such as ofloxacin, applied twice a day. 3 This intervention is particularly useful for patients in whom meibomian gland dysfunction and ocular rosacea are not significant contributing factors. In a small retrospective study, 75 percent of patients who underwent BCL placement had no recurrence of RCES symptoms for one year after treatment. 3
What is PTK in keratectomy?
Phototherapeutic ke ratectomy. This may be considered for patients for whom all other treatments have failed. PTK is also indicated in patients with macroerosions, which are often associated with nondystrophic RCES following ocular trauma. In PTK, an excimer laser is used to ablate 5 to 10 µm of Bowman’s layer after mechanical debridement of the overlying corneal epithelium. Like superficial keratectomy, this allows the cornea to re-epithelialize with stronger adhesion to the basement membrane. We recommend placement of a BCL and administration of topical antibiotics and corticosteroids, such as fluorometholone acetate 1 percent, two to four times daily after ablation. In a retrospective study of 76 eyes, PTK was used to treat RCES, with a recurrence rate of 11 percent. 5
What is corneal erosion syndrome?
Recurrent corneal erosion syndrome (RCES) is a common clinical disorder involving the corneal epithelium and epithelial basement membrane. Characterized by the repeated breakdown of epithelium, RCES can cause moderate to severe eye pain, photophobia, lacrimation, and corneal scarring leading to visual changes. Patients are often debilitated by the resulting pain and visual deficits and frustrated by the condition’s lack of response to treatment.
How deep should a BCL be placed after keratectomy?
The depth of the keratectomy should reach the anterior portion of Bowman’s layer. After surgery, a BCL should be placed until re-epithelialization has been achieved, with topical antibiotics applied up to four times daily.
What percentage of RCES cases are trauma?
In a study of 104 RCES cases, trauma contributed to 45 percent , epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) contributed to 29 percent, and a combination of trauma and EMBD contributed to 17 percent of cases. 1
What is the best ointment for RCES?
For patients with chronic RCES, we recommend the nighttime application of a prophylactic bland ointment, such as Refresh PM or Lacri-Lube, or hypertonic saline, such as Muro 128. For recovering patients whose epithelium is healing, we recommend bland ointment to prevent surface aggravation.
Why does EBMD not adhere to the basement membrane?
Patients with EBMD, a congenital condition, have an anterior epithelium that does not adhere well to the basement membrane due to morphological changes in the epithelial cells or basement membrane matrix. 1 This creates a loose epithelial layer prone to shifting and tearing when damaged. Adhesions between the palpebral conjunctiva ...
Who is most likely to get a recurrent corneal erosion?
Unfortunately, some people are predisposed to having RCE’s based on their corneal anatomy. On the other hand, others end up getting them if they have a history of injury to the eye, like a scratched cornea.
What does it mean when your eye hurts when you wake up?
Have you ever woken up with extreme eye pain, where it felt like you scratched your eye? Did the pain gradually subside as the day went on? If so, you may have had a recurrent corneal erosion (or RCE).
What happens when the top layer of the cornea doesn't adhere well to the second layer of the cornea?
An RCE happens when the top layer of the cornea doesn’t adhere well to the second layer of the cornea. If your cornea dries out at night, when you open your eye in the morning, your eyelid can essentially rip the top layer away from the second layer.
What is the most common symptom of RCE?
Unfortunately, the most common symptom of an RCE is intense eye pain upon waking (ouch). Other symptoms include light sensitivity, irritation, and watering.
What to do if eye drops don't help?
However, if these drops do not help your symptoms there are a few other treatment options your eye doctor can recommend. For example, stromal micropuncture or amniotic membranes are both advanced options. With the help of your eye doctor, you can determine if either of these measures are right for you.
Why is my eye sore?
All of these nerve endings are the reason your eye will become sore or tender when there is irritation on the cornea.
What to do if you have corneal erosion?
If you’ve had a recurrent corneal erosion, it’s a great idea to have your eyes checked regularly to treat any underlying dryness that may exacerbate this condition. Talk to your eye care provider to discuss the best treatment options for you.
What Is a Corneal Abrasion?
A corneal abrasion is a scratch, scrape on the surface of your cornea. Fingernails, makeup brushes and tree branches are common culprits of corneal abrasions. Some other causes of corneal abrasion are rubbing your eye and having very dry eyes.
Why Do Corneal Abrasions and Corneal Erosions Hurt So Much?
The cornea has many nerve cells. Cells called pain receptors transmit pain to tell us about possible damage to the eye’s surface. In fact, there are hundreds of times more pain receptors in our cornea than there are in our skin.
How long does it take for a corneal abrasion to heal?
If your corneal abrasion is small, it probably will heal in 1–2 days. A larger corneal abrasion may take about a week to heal. If playback doesn't begin shortly, try restarting your device. Videos you watch may be added to the TV's watch history and influence TV recommendations.
How do you know if you have corneal erosion?
Corneal erosion pain may start suddenly, often when you first wake in the morning. Your eyes get dry while you sleep, and your eyelid might stick to the cornea. If the epithelium is not firmly attached, opening your eyelids might peel the epithelium off.
What is the name of the dye that is used to look at the cornea?
Corneal Abrasion Diagnosis. Your ophthalmologist will put dye called fluorescein on your eye’s surface. Then they will look at your cornea with an instrument called a slit lamp. The dye will highlight a cut or scratch on the cornea.
Why does my eyelid stick to my cornea?
Corneal erosion is when the layer of cells on the surface of the cornea, called epithelium, loosens from the layer underneath. This is painful and makes your vision blurry or hazy. Cor neal erosion pain may start suddenly, often when you first wake in the morning. Your eyes get dry while you sleep, and your eyelid might stick to the cornea.
What is the treatment for corneal erosion?
If you get corneal erosion two or more times, your ophthalmologist may recommend other treatment. This could include: surgery called anterior stromal puncture. Your ophthalmologist will make tiny holes on the surface of your cornea. The scar tissue from these holes binds the epithelium to the layer underneath.
How to remove a loose epithelium?
Mechanical debridement of loosely adhered or nonadherent epithelium provides a smooth basement membrane to which healthy epithelium may re-adhere. 1 This is a safe and relatively noninvasive procedure that is typically performed at the slit lamp under topical anesthesia. 1,8 The patient is prepared by instilling topical anesthetic in both eyes. 2 Topical prophylactic antibiotics may be used, and an eyelid speculum is often helpful. 2 Depending upon practitioner preference, various instruments may be used to remove loose epithelium. 8 A methylcellulose spear-shaped surgical sponge (i.e., Weck-cel) is a safe and effective option. 1,8,14 A Kimura spatula may also be used since its blunt edges make it unlikely to damage Bowman’s membrane. 2,8 Occasionally, sharper instruments such as a scalpel blade are sometimes advocated; other authors contend that sharp instruments are inappropriate for this. 1,2 Remove any loose epithelial debris with jeweler’s forceps or a cellulose surgical sponge. 8
What is RCE in medical terms?
RCE is commonly associated with prior corneal trauma or underlying corneal disease. The most common underlying etiologies are trauma (45% to 69%) and epithelial basement membrane dystrophy (EBMD) (20% to 30%). 1 Causative trauma is typically a shallow corneal injury such as an abrasion from a fingernail, piece of paper, or tree branch.
How long does microform erosion last?
Microform erosions consist of minor episodes lasting as little as 30 minutes and typically have an intact corneal epithelium upon examination. 2,4 Macroform erosions are more severe episodes with epithelial defects or areas of edematous, poorly adherent epithelium. These may last for days and are associated with severe pain, eyelid edema, ...
How to protect the epithelium from the shearing force of the lids?
Bandage contact lenses are often used to protect the epithelium from the shearing force of the lids. 1,12 When using a bandage lens, the clinician should take care to avoid tight lens syndrome. 1 This condition involves acute tightening of the contact lens, which leads to decreased lens movement, inflammatory debris beneath the lens, increased inflammation and pain. 1 The use of a relatively flat base curve and topical NSAIDs can help avoid tight lens syndrome. 1 Nonpreserved artificial tears help to flush inflammatory debris and improve comfort. Topical prophylactic antibiotics should be used to decrease the risk of microbial keratitis, which may be caused by extended use of bandage soft lenses. 1,11 Patients may wear bandage contact lenses continuously for six to 12 weeks to allow for restoration of tight epithelial basement membrane adhesions. 13 The lens must be replaced as appropriate. 1,2
What are the effects of RCE on the cornea?
Patients with RCE have increased activity of matrix metalloproteinases (MMP)-2 and -9. These enzymes can adversely affect the basement membrane and anchoring fibrils, thereby causing dysfunctional adhesion complexes. 1,3 Further, there are high rates of meibomian gland dysfunction (MGD) and ocular rosacea in eyes with non-traumatic corneal erosion. 3 Diseases with high colonization of Staphylococcus epidermidis tend to have higher levels of bacterial lipases, which act upon meibum to produce toxic free fatty acids. Investigators believe these fatty acids interfere with the epithelial healing process and predispose patients to erosions. 3 Therefore, many medical treatments are aimed at decreasing MMP activity, or managing MGD, or both.
What is corneal erosion?
Recurrent corneal erosion (RCE) is a clinical syndrome characterized by inadequate epithelial basement membrane adhesions, resulting in repeat episodes of corneal epithelial defects . 1 These episodes are typically acute and may involve symptoms ranging from mild irritation to significant pain. 1-3 The average age of onset is the fourth or fifth decade, with a slight female predominance. 1,3
How far away from the limbus should the epithelium be?
11 Aggressive removal of the epithelium near the limbus can damage stem cells; therefore, a protective band of epithelium should be maintained 1mm to 2mm from the limbus. 3,8 Bowman’s layer is lightly debrided to remove the epithelial basement membrane. 2 Cyclopentolate is instilled. 11
What is the treatment for recurrent erosion?
Recurrent erosions generally respond to medical treatment with antibiotics and lubricants or a bandage soft contact lens. If unsuccessful, a variety of surgeries can be effective ranging from anterior stromal micropuncture, removal of the epithelium with or without diamond burr polishing of the stroma (see “Surgical Procedures” page), to excimer laser resurfacing (phototherapeutic keratectomy or PTK) (see “Surgical Procedures” page).
How long does corneal abrasion last?
The pain may be fleeting or can last for hours or days, depending on how much of the surface layer separates and whether a corneal abrasion occurs.
What type of trauma is a fingernail?
Shearing type trauma to the eye (e.g. fingernail, paper or tree branch injury) or an underlying corneal dystrophy, most likely epithelial basement membrane dystrophy or less commonly other dystrophies such as Reis-Bucklers or lattice corneal dystrophies.
How long does eye pain last?
Mild to severe eye pain that typically develops during the night or upon awakening, The pain may be fleeting or can last for hours or days, depending on how much of the surface layer separates and whether a corneal abrasion occurs.
Can corneal erosion cause scarring?
Corneal erosions can predispose to corneal infection s which can cause corneal scarring and poor vison.
How long does it take for corneal erosion to heal?
The good news about recurrent corneal erosion is that, unless there is an ongoing underlying corneal disease, most patients will ultimately heal completely and not have any more episodes. However, it may take years for this to happen.
What is recurrent corneal erosion?
Recurrent corneal erosion is the recurrent breakdown of the outermost layer (epithelium) of the cornea. In recurrent corneal erosions, the outermost layer of the cornea fails to glue in tightly to its underlying membrane (basement membrane), making it possible for the epithelium to break off too easily with little effort.
How many times does abrasion recur?
It is more than once that the abrasion has recurred.
When to seek medical advice for corneal erosion?
Just as noted with corneal abrasions, you should seek medical advice for recurrent corneal erosions when: The pain is persisting beyond the first day, or the pain is increasing despite self-care. There is no improvement with self-care after 24 hours. There is progressive vision loss.
What causes squinting in the eye?
Spasm of the muscles surrounding the eye resulting in squinting
Can you see corneal abrasion with the naked eye?
Just as it is nearly impossible to see a corneal abrasion with the naked eye, the same is true for recurrent corneal erosion. What is most important is the time course. In recurrent corneal erosion, the patient can remember having had a corneal abrasion relatively recently (usually within the past 3–10 days) and then, most often when first opening the eye in the morning, feels a sudden burst of pain accompanied by symptoms of a corneal abrasion, which are:
Who is at risk of corneal erosion?
Who's at risk? The most likely victim of recurrent corneal erosion is the person who has had a previous corneal abrasion that was very sharp, clean, and linear, like that from a paper cut. Because the cut is so sharp, without ragged edges, it is less likely to stick down tightly to the underlying basement membrane.
