
Drugs used to treat some of the most common causes of chest pain include:
- Artery relaxers. Nitroglycerin — usually taken as a tablet under the tongue — relaxes heart arteries, so blood can flow more easily through the narrowed spaces. ...
- Aspirin. If health care providers think that your chest pain is related to your heart, you'll likely be given aspirin.
- Thrombolytic drugs. ...
- Blood thinners. ...
- Acid-suppressing medications. ...
- Antidepressants. ...
What are common non-cardiac causes of chest pain?
Some less-common problems that can cause non-cardiac chest pain include:
- Muscle or bone problems in the chest, chest wall, or spine (back)
- Lung conditions or diseases, including diseases of the pleura, the tissue that covers the lungs
- Stomach problems, such as ulcers
- Stress, anxiety, or depression
What causes chest pain other than the heart?
In most people, non-cardiac chest pain is related to a problem with the esophagus, such as gastroesophageal reflux disease. Other causes include muscle or bone problems, lung conditions or diseases, stomach problems, stress, anxiety, and depression. What is non-cardiac chest pain?
Is chest pain a symptom of heart disease?
The NHS says the most common symptoms of coronary heart disease are chest pain, known as angina, and breathlessness. The Mayo Clinic says angina is caused by reduced blood flow to the heart muscle. Blood carries oxygen, which the heart muscle needs to survive. It adds there are different types of angina.
Does Gerd cause chest pain?
Yes, GERD can cause chest pain, and many people have gone to an Emergency Room only to find they have GERD problems and are not experiencing a heart attack. A few weeks ago, I went through a similar experience after eating salsa and chips.
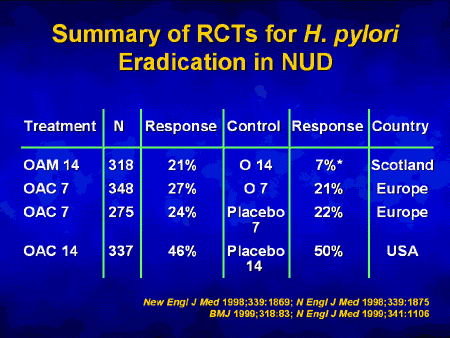
What helps with non-cardiac chest pain?
If your noncardiac chest pain is, like most people's, from GERD, treatment is usually simple and effective. Proton-pump inhibitors (PPI) are the most commonly used medicine to treat GERD. PPIs reduce the amount of stomach acid that your glands secrete, which also allows ulcers and acidic corrosion to heal.
What causes chest pain if it's not your heart?
Common gastrointestinal-related causes include acid reflux or esophageal pain. Additionally, chest pain can result from pain referred from areas outside of the chest, such as the gallbladder, pancreas or the spine. Anxiety or panic attacks may also cause chest pain.
How do you know if chest pain is not heart related?
It can be difficult to distinguish heart-related chest pain from other types of chest pain. However, chest pain that is less likely due to a heart problem is more often associated with: A sour taste or a sensation of food reentering your mouth. Trouble swallowing.
Which treatment is best for chest pain?
TreatmentArtery relaxers. Nitroglycerin — usually taken as a tablet under the tongue — relaxes heart arteries, so blood can flow more easily through the narrowed spaces. ... Aspirin. ... Thrombolytic drugs. ... Blood thinners. ... Acid-suppressing medications. ... Antidepressants.
How do you know if chest pain is muscular or heart?
The pain of a heart attack differs from that of a strained chest muscle. A heart attack may cause a dull pain or an uncomfortable feeling of pressure in the chest. Usually, the pain begins in the center of the chest, and it may radiate outward to one or both arms, the back, neck, jaw, or stomach.
How do I know if chest pain is muscular?
Symptoms of muscle strain in chestpain, which may be sharp and intense pull or chronic pain.swelling.muscle contractions.trouble moving the injured area.pain while breathing.bruising.
What causes pain in middle of chest between breasts?
It can be due to heart attack or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. When a person is obese or have a lax esophageal sphincter there is a chance for stomach juices to get reflexed upto esophagus, causing burning pain or tightness in the middle of the chest.
Will chest pain go away on its own?
Chest pain may arise and subside every few minutes or over several days. The cause may be related to the heart, the muscles, the digestive system, or psychological factors. Underlying causes of chest pain may be mild, as in the case of acid reflux. Or, they may be serious and indicate, for example, a heart attack.
What are 4 common causes of chest pain?
Chest pain may be caused by angina or a heart attack. Other causes of chest pain can include indigestion, reflux, muscle strain, inflammation in the rib joints near the breastbone, and shingles. If in doubt about the cause of your chest pain, call an ambulance.
What blood tests are done for chest pain?
Troponin blood test - troponin is a protein which is released into the blood stream when the heart muscle is damaged. The troponin level provides a quick and accurate measure of any heart muscle damage. It's used to help in the assessment following suspected heart attack.
What are 5 causes of chest pain?
Five Different Common Causes of Chest PainHeart-Related Causes. Heart issues frequently cause chest pain. ... Lung-Related Causes. If you experience lung (pulmonary) pain, it's likely that you'll also feel chest pain. ... Stress-Related Causes. ... Digestion-Related Causes. ... Muscle-Related Causes.
Why can't doctors figure out my chest pain?
Unfortunately, physicians are often unable to make an accurate diagnosis based solely on history because, for example, descriptions of chest pain of cardiac, upper gastrointestinal, or gallbladder origin can be identical.
What causes pain in middle of chest between breasts?
It can be due to heart attack or gastro-oesophageal reflux disease. When a person is obese or have a lax esophageal sphincter there is a chance for stomach juices to get reflexed upto esophagus, causing burning pain or tightness in the middle of the chest.
What causes chest pain in ladies?
In some cases, pain or discomfort may be due to other causes, such as heartburn, reflux, a lung-related issue, or another problem affecting the heart. Although some possible causes of chest pain are less serious, a woman should seek help immediately as this symptom may indicate a medical emergency.
Can chest pain not be serious?
More often than not, chest pain does not signal a heart attack. A study of emergency room visits found that less than 6% of patients arriving with chest pain had a life-threatening heart issue. Here are some examples of chest pain that usually doesn't result in a heart attack diagnosis.
What is noncardiac chest pain?
Purpose of review: Noncardiac chest pain (NCCP) has been defined as recurrent chest pain that is indistinguishable from ischemic heart pain after excluding a cardiac cause. NCCP is a common and highly challenging clinical problem in Gastrointestinal practice that requires targeted diagnostic assessment to identify the underlying cause of the symptoms. Treatment is tailored according to the cause of NCCP: gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), esophageal dysmotility or functional chest pain. The purpose of this review is to discuss the current diagnosis and treatment of NCCP.
Is GERD a cause of NCCP?
Summary: GERD is the most common esophageal cause of NCCP, ...
What is non-cardiac chest pain?
Non-cardiac chest pain (NCCP) is a term used to describe chest pain that resembles heart pain (also called angina) in patients who do not have heart disease. The pain typically is felt behind the breast bone (sternum) and is described as oppressive, squeezing or pressure-like. It may radiate to the neck, left arm or the back (the spine).
What tests are done to determine if a patient has a heart attack?
In fact, many patients present to emergency rooms concerned about a heart attack and commonly undergo cardiac studies (such as EKGs, laboratory tests, stress test and even coronary angiography – where dye is injected into the heart vessels). After these cardiac tests fail to show evidence of heart disease, the patients receive the diagnosis ...
What causes a person to have a nccp?
Non-esophageal sources that can cause NCCP include: Musculo-skeletal conditions of the chest wall or spine, pulmonary (lung) disorders, pleural illness (the layers of tissue that cover the lungs), pericardial conditions (the layer of tissue that protects the heart) and even digestive disorders such as ulcers, gallbladder, pancreatic diseases and rarely tumors (particularly in patients past age 50).
Do you have to have a cardiac evaluation for chest pain?
Patients suffering from chest pain must have thorough cardiac evaluations to ensure they do not have heart disease prior to being labeled as having NCCP. In addition, a variety of other disorders described above, both esophageal and non-esophageal must also be considered since specific treatment for these disorders are available. ...
Is NCPP esophageal or non-esophageal?
The sources of NCPP can be grouped into esophageal and non-esophageal. Several studies have shown that approximately 60% or more of patients with NCCP suffer from acid reflux (mostly due to what is commonly referred to as Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease). Therefore, patients having chest pain who have had a negative cardiac evaluation are ...
What is it?
Non-cardiac chest pain is a feeling of having bothersome pain in your chest that is not a heart attack or coming from the heart. This pain can sometimes feel like a heart attack, so if you experience these symptoms, it is best to seek emergency care. Once it is known that the pain is not from your heart, the pain is called non-cardiac.
What are the symptoms?
The symptoms of non-cardiac chest pain are chest pain that may be associated with difficulty swallowing, pain when swallowing, regurgitation of food, or a sensation of food getting stuck.
How is it treated?
Treatment for non-cardiac chest pain depends on what the underlying cause is. It can vary from medications and lifestyle modification to a variety of other procedure-based therapies.
Why is it important to write a referral letter for chest pain?
It is important that the patient understands that there are numerous causes for chest pain other than heart disease and that the referral letter outlines the history and the need for an explanation for the symptoms.
What causes chest pain and oesophageal reflux?
9 Psychiatric causes include panic, major depression, and health anxiety (hypochondriasis-like and other so called somatoform disorders).
Is chest pain a cardiac condition?
Non-cardiac chest pain: assessment and management. Chest pain is a common reason for patients to attend cardiac clinics, but the cause of pain in more than 50% of these patients is non-cardiac. 1 In a recent study of 660 consecutive referrals to a “one stop” clinic, only 27% had a cardiac cause for their symptoms.
Can acid reflux be treated with proton pump inhibitors?
There is uncertainty about the status of oesophageal abnormalities; however, acid reflux is common in patients with normal coronary a natomy, and as many as a third respond well to H 2 receptor antagonists or proton pump inhibitors. 15 In some cases oesophageal function testing may reveal a motility disorder or acid reflux unresponsive to first line medication. These may require specialist gastroenterological referral.
Is non-cardiac chest pain multifactorial?
The view that the aetiology of non-cardiac symptoms is multifactorial means that the assessment in primary care or outpatient clinics should encompass not only heart disease but other possible physical causes as well as psychological factors, including the patient's beliefs and concerns. This can be done with relatively simple standardised questionnaires. 12 The possibility of a positive diagnosis of non-cardiac chest pain also needs to be considered. 13
Does imipramine help with chest pain?
16-18 The analgesic effect of imipramine was harnessed in a study of patients with chest pain and normal coronary arteries: there was a mean reduction in frequency of chest pain episodes by 50% in the imipramine group, which occurred independently of baseline levels of psychiatric morbidity and oesophageal abnormalities. 16
What to do if your chest hurts when you have a panic attack?
Antidepressants. If you're experiencing panic attacks, your doctor may prescribe antidepressants to help control your symptoms.
What is the best way to check for chest pain?
Stress tests. These measure how your heart and blood vessels respond to exertion, which may indicate if your chest pain is heart-related. There are many kinds of stress tests. You may be asked to walk on a treadmill or pedal a stationary bike while hooked up to an ECG.
What is the procedure for a blockage in the heart?
Angioplasty and stent placement. Chest pain that is caused by a blockage in an artery feeding the heart is typically treated with angioplasty. The doctor inserts a catheter with a balloon on the end into a large blood vessel, usually in the groin, and guides the catheter to the blockage. The doctor inflates the balloon to widen the artery, then deflates it and removes the catheter. A small wire mesh tube (stent) is often placed on the outside of the balloon tip of the catheter. When expanded, the stent locks into place to keep the artery open.
What to do if you have a heart attack?
Aspirin. If doctors suspect that your chest pain is related to your heart, you'll likely be given aspirin. Thrombolytic drugs. If you are having a heart attack, you may receive these clot-busting drugs. These work to dissolve the clot that is blocking blood from reaching your heart muscle. Blood thinners.
What is chest xray?
Chest X-ray. An X-ray of your chest allows doctors to check the condition of your lungs and the size and shape of your heart and major blood vessels. A chest X-ray can also reveal lung problems such as pneumonia or a collapsed lung. Computerized tomography (CT scan). CT scans can spot a blood clot in your lung (pulmonary embolism) ...
What is the procedure to repair a collapsed lung?
Dissection repair. You may need emergency surgery to repair an aortic dissection — a life-threatening condition in which the artery that carries blood from your heart to the rest of your body ruptures. Lung reinflation. If you have a collapsed lung, doctors may insert a tube in your chest to reinflate the lung.
What causes chest pain?
Procedures to treat some of the most dangerous causes of chest pain include: Angioplasty and stent placement. If your chest pain is caused by a blockage in an artery feeding your heart, your doctor will insert a catheter with a balloon on the end into a large blood vessel in your groin, and thread it up to the blockage.
What is chest pain?
Cardiac Chest Pain. Cardiac chest pain in this context is considered as any pain attributed to ischemia – oxygen deprivation to the heart muscle. This must be taken very seriously as it can progress to an infarct (death of heart muscle tissue) without prompt and appropriate treatment. Example : heart attack (myocardial infarction).
What is cardiac pain?
Cardiac. Pain is dull, constricting, choking and/or crushing. Other terms to describe ischemic cardiac chest pain includes squeezing, burning or heavy. Sometimes it may just feel like discomfort which is why the character of cardiac chest pain can be so misleading.
What is a common but inconclusive presentation in cardiac chest pain?
A common but inconclusive presentation in cardiac chest pain is a patient clutching the chest (picture below).
What does "non-cardiac" mean?
Non-Cardiac. Not relieved significantly by rest, if at all. Does not respond to nitrates or there may be a slow response. Pain relived by antacids may be related to gastrointestinal disorders. Pain that improves upon leaning forward may be related to the pericarditis (inflammation of the lining around the heart).
What does it mean when you feel shortness of breath?
Severe shortness of breath – patient may report a feeling of suffocation. Other signs and symptom may be present that is helpful in identifying the cause of the pain. Gastrointestinal – bloating, belching, nausea, vomiting and/or regurgitation. Refer to Gastric Chest Pain.
Can GERD cause ischemic pain?
However, it must be remembered that certain conditions affecting the heart may not always result in ischemia and may therefore not present in a manner resembling ischemic cardiac pain. Example : GERD (heartburn), pleuritis or even pericarditis (inflammation of the lining around the heart).
Where is the pain located in the chest?
Pain may be away from the center of the chest where a patient can clearly identify it as a right-sided or left-sided chest pain. Pain is usually localized – located at only one spot which can be clearly pinpointed by the patient.
Why does my chest hurt?
Chest pain can stem from dozens of conditions besides heart attack, from pancreatitis to pneumonia or panic attack. Millions of Americans with chest pain are seen in hospital emergency departments every year. Only 20% of them are diagnosed with a heart attack or an episode of unstable angina, a warning sign that a heart attack may happen soon.
What test do doctors use to determine if you have a heart attack?
In addition to the description of your symptoms and your heart risk profile, doctors use the results of an electrocardiogram (ECG) and a blood test called cardiac troponin. But sometimes these don't immediately show abnormalities.
What are the symptoms of a heart attack?
The other tricky problem with heart attacks is that different people experience them in different ways. Some have classic chest pain. Others have jaw pain or back pain. Still others become breathless, or extremely fatigued, or nauseated.
Is a stabbing pain a heart attack?
A few seconds of recurrent stabbing pain is less likely to be a heart attack ( see box), while pain centered in the chest that spreads out to the left arm or jaw is more likely to be one.
