- Medications. If you have ventricular tachycardia, you may be given medications called anti-arrhythmics by mouth or IV to slow the fast heart rate.
- Cardioversion. This medical procedure is generally used when emergency care is needed for a rapid heart rate, such as that seen with sustained ventricular tachycardia.
- Surgery or other procedures. An ICD works to control the heartbeat by delivering shocks to the heart when the device detects an irregular heartbeat.
How do you treat V tach?
VTACH + VFIB | A Nurse’s Guide to Ventricular Arrhythmias
- Check for a Pulse / Breathing. If you see a ventricular arrhythmia on the monitor, you should immediately assess your patient first.
- Call an RRT or Code Blue. If the patient is pulseless, call for help and call a CODE BLUE. ...
- Start CPR if Needed. ...
- Give Life-Saving Treatment. ...
- Reverse any known causes (Hs & Ts) In ACLS you are taught all about Hs and Ts. ...
What is the prognosis of ventricular tachycardia (VT)?
What is the prognosis of ventricular tachycardia (VT)? , the prevalence of sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) is low; therefore, it is considered a medical emergency as ppl often but not always become unconscious, cardiac arrest, as stated by AFIB Matters.
What medications cause ventricular tachycardia?
- Anagrelide
- Aspirin and Oxycodone
- Chlordiazepoxide and Clidinium Bromide
- Dothiepin
- Ephedrine
- Epinephrine
- Epoprostenol
- Glyceryl Trinitrate
- Moclobemide
- Nalmefene
What is the treatment for ventricular tachycardia?
- Pulseless VT is a medical emergency that requires immediate defibrillation.
- The energy of 150-200 J on biphasic and 360 J on monophasic defibrillator should be used.
- Delaying defibrillation of pulseless VT dramatically decreases the survival rate.
- Critical interventions in the post-arrest phase are coronary angiography and PCI.

What is the recommended treatment for stable VT with a pulse?
Those with VT storm, having pulse and are hemodynamically unstable should receive synchronized cardioversion. Patients who have poor systolic function or rapid VT might require multiple electrical cardioversions or defibrillations [11].
Can V tach be stable?
Background—Sustained ventricular tachycardia (VT) can be unstable, can be associated with serious symptoms, or can be stable and relatively free of symptoms. Patients with unstable VT are at high risk for sudden death and are best treated with an implantable defibrillator.
Do you Cardiovert stable Vtach?
For stable Vtach, IV antiarrhythmic drugs or elective cardioversion is recommended. Lidocaine has been found to be less effective than amiodarone, sotalol or procainamide.
What is the initial treatment for V tach?
Anti-arrhythmic medications are the first-line therapy in emergency departments and CCUs, as discussed earlier. Amiodarone is most commonly used, along with lidocaine, and in some cases procainamide.
What is the most common cause of V-tach?
Ventricular tachycardia most often occurs when the heart muscle has been damaged and scar tissue creates abnormal electrical pathways in the ventricles. Causes include: Heart attack. Cardiomyopathy or heart failure.
How many beats of V-tach is concerning?
Ventricular tachycardia (VT) is a fast, abnormal heart rhythm (arrhythmia). It starts in your heart's lower chambers, called the ventricles. VT is defined as 3 or more heartbeats in a row, at a rate of more than 100 beats a minute. If VT lasts for more than a few seconds at a time, it can become life-threatening.
What rhythms require synchronized cardioversion?
Synchronized cardioversion is used to treat other arrhythmias, including atrial fibrillation (AF), atrial flutter, and stable ventricular tachycardia when medications have failed to convert the rhythm, or when the patient is becoming unstable and the rhythm must be immediately terminated.
Do you Cardiovert v tach with a pulse?
Unlike defibrillation, which is used in cardiac arrest patients, synchronized cardioversion is performed on patients that still have a pulse but are hemodynamically unstable. It is used to treat both hemodynamically unstable ventricular and supraventricular rhythms.
Which rhythms do you Cardiovert?
Rhythms that can be cardioverted are atrial fibrillation/flutter (AF), supraventricular tachycardias (SVT), ventricular tachycardia or ventricular fibrillation. Synchronized cardioversion is appropriate for all of these rhythms except ventricular fibrillation or unstable ventricular tachycardia.
What is stable v tach?
Summary. – Stable, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is defined by a rate faster than 120 beats/min with QRS greater than 120 ms. – Hemodynamically unstable VT requires immediate synchronized direct current cardioversion. – Medical management of hemodynamically stable monomorphic VT is controversial.
Do you give epinephrine in V tach?
Currently, the ACLS protocol for v fib and pulseless v tach recommends that epinephrine be given after the second defibrillation. Many hospitals and EMS systems, however, have been giving it earlier.
Is V tach always pulseless?
Ventricular tachycardia is not always pulseless. In ventricular tachycardia, the heart rate usually exceeds 100 beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What is stable v tach?
Summary. – Stable, monomorphic ventricular tachycardia is defined by a rate faster than 120 beats/min with QRS greater than 120 ms. – Hemodynamically unstable VT requires immediate synchronized direct current cardioversion. – Medical management of hemodynamically stable monomorphic VT is controversial.
What is unstable v tach?
Ventricular tachycardia is unstable any time a patient is in dysrhythmia and hemodynamic compromise. This is most often associated with mental status changes or a loss of consciousness.
What is stable tachycardia?
Tachycardia is classified as stable or unstable. Heart rates greater than or equal to 150 beats per minute usually cause symptoms. Unstable tachycardia always requires prompt attention. Stable tachycardia can become unstable.
How long can v tach last?
Ventricular tachycardia may go away on its own within 30 seconds (nonsustained V-tach ) or last more than 30 seconds (sustained V-tach or VT ). Brief episodes may not cause any symptoms. But sustained VT can cause serious problems, including: Fainting.
What Is Stable Ventricular Tachycardia?
Many conditions, diseases and even medications can cause ventricular tachycardia, but not all episodes of tachycardia may be immediately serious. For example, a certain medication may simply need to be stopped, or the root cause of a disease may need to be addressed to get the heart back to functioning correctly. When V-tach is described as being stable, it occurs with very few if any symptoms. The patient will still be able to talk and generally function and may even have mostly normal vital signs other than heart rate.
How Should Stable V-Tach Be Treated?
Stable V-tach should certainly be addressed to prevent the rhythm from becoming more erratic and to prevent the patient from becoming symptomatic. Anti-arhythmic medications, such as adenosine, are usually given. Synchronized cardioversion is typically recommended as well for patients who have either narrow or regular QRS complexes.
What is the rate of heartbeat in a patient with ventricular tachycardia?
Tachycardia usually refers to any heart rhythm over 120 beats per minute, but emergency treatments are usually considered when the heart rate gets to 150 beats per minute or more.
How to manage tachycardia?
Prior to this point, the tachycardia can usually be managed by attending physicians or by family physicians through medication changes. If you’re caring for a patient in your hospital or clinic who has a fast heart rhythm, you must first determine what the EKG is showing and whether your patient is stable or unstable.
What is Project Heartbeat?
At Project Heartbeat, we offer several classes and certifications that can help you understand these subjects better. Our Basic ECG Interpretation and Pharmacology Course will give you the basics for heart rhythm interpretation, and our Advanced 12 Lead EKG Interpretation Certification will take you a step further. This advanced class is particularly important if you’re working specifically with cardiovascular patients or if you’re on your agency’s code response team.
What are the symptoms of unstable V-tach?
In unstable V-tach, the patient will present with symptoms. Mental symptoms, such as confusion or loss of consciousness, may be the first changes noted. Without quick treatment, complete hemodynamic collapse is possible, which could lead to the need for CPR and emergency treatments.
Is V-tach stable?
When V-tach is described as being stable, it occurs with very few if any symptoms. The patient will still be able to talk and generally function and may even have mostly normal vital signs other than heart rate.
How to tell if you have ventricular tachycardia?
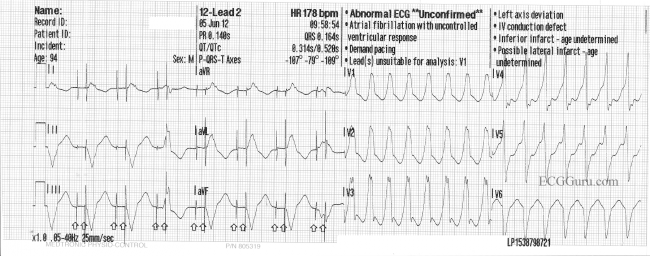
The most common test used to diagnose ventricular tachycardia is an electrocardiogram (ECG/EKG). An EKG records your heart’s electrical activity. Electrodes (small sticky patches) are placed on your chest and arms to record the heart’s rhythm, and the pattern prints on graph paper. Your doctor may also want to track your heart rhythm at home. If so, you will wear a Holter monitor at home for 24 to 48 hours.
What is radiofrequency ablation?
Radiofrequency catheter ablation is a procedure performed by a cardiac electrophysiologist, which is a cardiologist who specializes in treating patients with heart rhythm disorders. In the first part of the procedure, the doctor uses electrophysiology techniques to pinpoint the location in the heart where the abnormal rhythm begins. In the second step, the doctor uses a catheter with a special tip that emits a high-frequency form of electrical current. The current is used to destroy a tiny amount of tissue in the area of the ventricle where the abnormal rhythm begins. This is called an ablation procedure.
What is an ICD device?
Implantable Cardioverter Defibrillator. An ICD is a device that is implanted under the skin. It monitors and controls the heart’s rhythm. If it detects an episode of ventricular tachycardia, it acts quickly to get your heart back to a normal rhythm.
What causes tachycardia in the heart?
When something goes wrong and signals are sent too quickly, it can cause tachycardia. Most patients with ventricular tachycardia have another heart problem, such as coronary artery disease, high blood pressure, an enlarged heart (cardiomyopathy) or heart valve disease.
What is the second step of a cardiac ablation procedure?
In the second step, the doctor uses a catheter with a special tip that emits a high-frequency form of electrical current. The current is used to destroy a tiny amount of tissue in the area of the ventricle where the abnormal rhythm begins. This is called an ablation procedure.
How long do you have to wear a Holter monitor?
Your doctor may also want to track your heart rhythm at home. If so, you will wear a Holter monitor at home for 24 to 48 hours. Normal Heart Rhythm recorded on EKG. Ventricular Tachycardia recorded on EKG. Your doctor may refer you to a specialist to electrophysiology testing.
What is the normal heart rate for tachycardia?
The ventricles are the heart’s two lower chambers. Blood flows from the top chambers of the heart (atria) into the ventricles, then it moves to the lungs and through the aorta to be circulated throughout the body. Tachycardia is a heart rate higher than 100 beats per minute. A normal resting heart rate is 60 to 100 beats per minute.
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Your heart rate is regulated by electrical signals sent to your heart muscle. Certain conditions can interfere with normal electrical signals and cause ventricular tachycardia:
What are the signs and symptoms of ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia goes away on its own in 30 seconds. However, sustained ventricular tachycardia can last more than 30 seconds and requires emergency treatment.
How is ventricular tachycardia diagnosed?
Your doctor will ask you about your symptoms and take a complete medical history. They may order tests that include:
What can you do to prevent ventricular tachycardia?
Following your doctor’s treatment recommendations can help you prevent or manage episodes of the disease. In some cases, the causative factor (cardiovascular disorder, tumor, drugs, electrolyte imbalance, etc.) may need to be addressed and treated. It is also advised to adopt a healthy lifestyle that includes:
Top Best Treatment of Ventricular Tachycardia Related Articles
This procedure is used to treat abnormal heart rhythms. Depending on the type of arrhythmia and the presence of other heart disease, a nonsurgical ablation or a surgical ablation, may be performed. During a catheter ablation, catheters are advanced to the heart via blood vessels in the groin, neck, and arm.
How long does ventricular tachycardia last?
Ventricular tachycardia may last for only a few seconds, or it can last for much longer. You may feel dizzy or short of breath, or have chest pain. Sometimes, ventricular tachycardia can cause your heart to stop (sudden cardiac arrest), which is a life-threatening medical emergency.
What is the dangerous condition of ventricular tachycardia?
A dangerous condition related to ventricular tachycardia is ventricular fibrillation (V-fib). In V-fib, your lower heart chambers contract in a very rapid and uncoordinated manner. This abnormal rhythm happens most often in people with heart disease or a prior heart attack.
What causes ventricular tachycardia?
Causes. Ventricular tachycardia is caused by a disruption in the normal electrical impulses that control the rate of your heart's pumping action. Many things can cause or contribute to problems with the heart's electrical system.
What causes a heart to beat faster?
In ventricular tachycardia, an abnormal electrical impulse originating in the lower chambers of the heart (ventricles) causes the heart to beat faster. The problem may involve either a small cluster of cells or a large area of scar tissue.
How many times does the heart beat in a minute?
A healthy heart normally beats about 60 to 100 times a minute at rest. In ventricular tachycardia, the heart beats faster than normal, usually 100 or more beats a minute. The chaotic heartbeats prevent the heart chambers from properly filling with blood. As a result, your heart may not be able to pump enough blood to your body and lungs.
How to live a healthy life?
Live a heart-healthy lifestyle by exercising regularly and eating a healthy, low-fat diet that's rich in fruits, vegetables and whole grains.
What causes scarring in the heart?
Abnormalities of the heart that result in scarring of heart tissue (sometimes called "structural heart disease"), the most common cause is a prior heart attack. Poor blood flow to the heart muscle due to coronary artery disease. Congenital heart conditions, including long QT syndrome.
What causes the most sudden cardiac death?
Ventricular tachycardia and ventricular fibrillation cause most cases of sudden cardiac death with an estimated rate of 300,000 deaths each year in the United States. [5][6] This accounts for approximately half of the deaths related to cardiac causes.[6] Risk factors for ventricular tachycardia are hypertension, previous myocardial infarction, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and ST-segment changes at presentation.[7] Patients presenting with acute myocardial infarction have ventricular fibrillation or ventricular tachycardia at a rate of 5% to 10%. [1][8] Ventricular tachycardia 48 hours after hospital presentation is associated with an increased risk of death compared to ventricular tachycardia occurring within the first 48 hours of hospital presentation. [9]
What is ventricular tachycardia?
Ventricular tachycardia is characterized as a wide complex (QRS duration greater than 120 milliseconds) tachyarrhythmia at a heart rate greater than 100 beats per minute. It is classified by duration as non-sustained or sustained. Non-sustained ventricular tachycardia is defined as more than 3 beats of ventricular origin at a rate greater than 100 beats per minute that lasts less than 30 seconds in duration.[1] When the rhythm lasts longer than 30 seconds or hemodynamic instability occurs in less than 30 seconds, it is considered sustained ventricular tachycardia.[1]
What is the first step in the evaluation of presumed ventricular tachycardia?
The first step in the evaluation of presumed ventricular tachycardia is a 12-lead electrocardiogram (ECG). [12][13] Patients with ventricular tachycardia symptoms associated with exertion, ischemic heart disease, or catecholaminergic polymorphic ventricular tachycardia should undergo further testing with a treadmill stress test.[14] Patients having syncope, presyncope or palpitations with no arrhythmia detected on a single 12-lead ECG should undergo further evaluation with ambulatory ECG monitoring.[15] In patients with ventricular tachycardia and possible structural heart disease, .an echocardiogram is recommended. [16][17] Patients who undergo an episode of unexplained sudden cardiac arrest secondary to a ventricular tachyarrhythmia, CT, or coronary angiography can be used to confirm the presence or absence of ischemic heart disease. [18][19]
What is the best medication for SMVT?
Hemodynamically stable patients should be pharmacologically cardioverted using an anti-arrhythmic medication. Intravenous amiodarone or procainamide can be used for this purpose. Procainamide will terminate between 50% and 80% of ventricular tachycardias, and it will slow the conduction of those that it does not terminate. [23][24]Amiodarone will convert about 30% of patients to sinus rhythm but is very effective in reducing the reversion rate of refractory SMVT. [25][26][27]
What is the mechanism of ventricular tachyarrhythmia?
The mechanism for ventricular tachyarrhythmias includes enhancement of normal automaticity or abnormal automaticity, activity triggered by early or late afterdepolarizations, and reentry.[10] In acute myocardial infarction, the transient ischemia results in an increased concentration of extracellular potassium, which causes partial depolarization of the resting membrane potential.[10] This creates injury currents between the infarcted tissue and healthy myocardium that may trigger spontaneous activity.
What is the prognosis of VT?
The prognosis of VT depends on the cause and cardiac status. Patients who develop VT can suffer from hemodynamic failure and the mortality can exceed 30% if no treatment is provided. In the setting of percutaneous coronary intervention, VT occurring prior to revascularization is associated with very high mortality. The prognosis does not correlate with ejection fraction. Patients with hypertrophic cardiomyopathy, long QT syndrome and right ventricular dysplasia often have normal heart function but yet are a high risk for sudden death.
What does the findings of cannon A waves and variable intensity of the S1 heart sound suggest?
The physical examination findings of cannon A waves and variable intensity of the S1 heart sound suggest AV dissociation, a criterion favoring the diagnosis of ventricular tachycardia. [11]
What is PVC in a ventricular beat?
A PVC is recognized as a premature ventricular beat and must not be preceded by a P wave that may have been conducted with aberrancy (distortion of the QRS). PVCs can be uniform or multiform. They can occur singly or in short runs. The origin of the PVC could be identified by the morphology (RBBB or LBBB) in lead V1. The axis (leads 1, AVF) will determine the site such as the apex or outflow tract. If there is a need to quantify the PVC count, a Holter recording is justified.
How many consecutive PVCs are in NSVT?
NSVT is defined as 3 consecutive PVCs, but <30 seconds.
Why are Torsades self limiting?
Torsades is often self-limiting, the reason being that the tachycardia itself will lead to termination.
What are the symptoms of ventricular arrhythmias?
The patient may complain of palpitations, dizziness, or syncope.
What is the pattern of PVCs in ECG?
Those originating from the LV will show a right bundle branch block pattern, and those from the right ventricle will show a left bundle branch block pattern.
Where does Verapamil sensitive VT originate?
Verapamil sensitive VT. This VT originates from the lower left ventricular septum with the electrocardiogram (ECG) showing a right bundle block and superior axis. The QRS is narrower than other forms of VT.
What electrolytes are good for torsades?
Electrolytes are often very helpful. Check the potassium and magnesium. Hypokalemia and hypomagnesemia can be risks for torsades.
How Fast Is Too Fast?
Tachycardia is generally defined as anything faster than 100 beats per minute (bpm) when resting, but not all tachycardias are clinically significant. Without an ECG monitor, a good rule of thumb is to be concerned if the patient has a pulse rate greater than 150 bpm, or if a radial pulse is irregular, weak, or absent. 1
Why is the QRS narrow?
This is the normal conduction pathway, and the only way the QRS can be narrow is if the impulse travels through it properly. Because the impulse has to start above the ventricles in a narrow-complex tachycardia, it's also known as supraventricular tachycardia (SVT).
Why isn't a 12-lead ECG available?
One reason not to treat tachycardia unless it's hemodynamically unstable is because of the possibility of treating a wide-complex tachycardia as ventricular tachycardia when it is not. Taking that chance when the patient is in significant danger of cardiac arrest is acceptable. ...
What does a QRS complex mean?
A QRS complex wider than 120 milliseconds is usually associated with ventricular tachycardia (VT)—meaning the impulse originates in the ventricles, below the atrioventricular node. That's not always the case, however. If it's narrow, it has to be SVT. If it's wide, it could be VT, or it could be that an impulse originating above the ventricles is not being conducted through the AV node. It's off the course and charting its own path, which makes it slower. This is often referred to as a heart block, an AV block, or a bundle branch block, depending on where the block occurs. 4
How fast does tachycardia get?
Below, we will discuss narrow-complex versus wide-complex tachycardia, but for now, just know that a wide-complex tachycardia gets worrisome once it's faster than 150 bpm. 2 A narrow-complex tachycardia can be a little faster, but consider it concerning if it is over 160 bpm. 3
What is considered a tachycardia?
Tachycardia is generally defined as anything faster than 100 beats per minute (bpm) when resting, but not all tachycardias are clinically significant. Without an ECG monitor, a good rule of thumb is to be concerned if the patient has a pulse rate greater than 150 bpm, or if a radial pulse is irregular, weak, or absent. 1
What is the primary factor to consider when considering tachycardia?
Outside of a hospital, the primary factor to consider is hemodynamic stability —that is, the stability of blood flow from the heart to the brain. When there is hemodynamically unstable tachycardia, the chambers of the heart do not have enough time to fill with blood between contractions.
What Are Unstable Ventricular Tachycardias?
Unstable ventricular tachycardias occur when an anomalous ventricular circuit is activated, reducing cardiac muscle activity, leading to inadequate cardiac output.
What is the term for a reduction in cardiac output?
The reduction in cardiac output resulting can cause symptoms ranging from decreased level of consciousness to a total lack of cardiac output, known as a pulseless ventricular tachycardia.
What is the best course of action for an arrhythmia?
If the patient is having short episodes of the arrhythmia, followed by spontaneous conversion out of it and returned stability, pharmacologic therapy may be the best course of action, rather than cardioversion.
What is the difference between VT and AF?
This may provide information which could reduce the range of options for treatment to more appropriate solutions, (i.e. VT tends to respond to lower levels of therapeutic electrical therapy, whereas AF often requires higher levels to convert the arrhythmia).
Does epinephrine cause tachycardia?
Additionally, if conversion occurs, the epinephrine could induce a significant tachycardia resulting in further damage to the myocardium. If the goal of the use of epinephrine is enhancement of coronary perfusion pressure, the use of a pure alpha agonist seems more appropriate.
Is an antiarrhythmic pharmacologic agent refractory?
In the uncommon situation that the arrhythmia is totally refractory to any level of energy, antiarrhythmic pharmacologic agents can be considered
Can you administer epinephrine to a patient with atrial fibrillation?
If the arrhythmia fails to convert with a lower level of energy, increase the delivered energy for the next shock (most common with broad QRS atrial fibrillation) DO NOT administer epinephrine to a patient who is refractory to a shock.
Diagnosis
Clinical Trials
- Explore Mayo Clinic studiestesting new treatments, interventions and tests as a means to prevent, detect, treat or manage this condition.
Coping and Support
- If you have a plan in place to deal with an episode of a fast heartbeat, you may feel calmer and more in control when one occurs. Talk to your doctor about: 1. How to take your pulse and what a normal pulse rate is for you 2. When and how to use a variety of maneuvers or take additional medications if they are appropriate for you 3. When to call your doctor 4. When to seek emergen…
Preparing For Your Appointment
- Whether you first see your family doctor or get emergency care, you'll likely be referred to a doctor trained in heart conditions (cardiologist) for one or more appointments for a complete evaluation. If possible, bring along a family member or friend who can give some moral support and help you keep track of new information. Because there may be a lot to discuss, it will be helpful to prepar…
Overview
Symptoms
- When the heart beats too fast, it may not pump enough blood to the rest of the body. So the organs and tissues may not get enough oxygen. Signs and symptoms that occur during an episode of ventricular tachycardia are due to a lack of oxygen and may include: 1. Chest pain (angina) 2. Dizziness 3. Pounding heartbeat (palpitations) 4. Lightheadedness 5. Shortness of br…
Causes
- Ventricular tachycardia is caused by faulty heart signaling that triggers a fast heart rate in the lower heart chambers (ventricles). The fast heart rate doesn't allow the ventricles to fill and squeeze (contract) to pump enough blood to the body. Many things can cause or contribute to problems with heart signaling and lead to ventricular tachycardia. These include: 1. Prior heart a…
Risk Factors
- Any condition that puts a strain on the heart or damages heart tissue can increase the risk of ventricular tachycardia. Lifestyle changes or proper medical treatment for the following conditions and events may lower the risk: 1. Heart disease 2. Medication side effects 3. Severe electrolyte imbalances 4. Use of stimulant drugs such as cocaine or methamphetamine A famil…
Complications
- Complications of ventricular tachycardia depend on: 1. How fast the heart is beating 2. How long the rapid heart rate lasts 3. Whether there are other heart conditions Possible complications of ventricular tachycardia include: 1. Frequent fainting spells or unconsciousness 2. Heart failure 3. Sudden death caused by cardiac arrest
Prevention
- The best ways to prevent tachycardia are to maintain a healthy heart and prevent heart disease. If you already have heart disease, monitor it and follow your treatment plan. Be sure you understand your treatment plan, and take all medications as prescribed. Take the following steps to keep the heart healthy: 1. Eat a balanced, nutritious diet.A die...