Grasp the slide sheet firmly from the other side and pull it towards you and over the patient until you achieve the side-lying position; and Move to the other side of the bed and now pull the slide-sheet laterally so that you can bring the patient with that lateral manoeuvre into the middle of the bed.
How do you position a stroke patient in bed?
How to Position a Stroke Patient. Ensure the weaker leg is positioned in a neutral position. You can also use pillows to hold the leg in position. If the patient is lying on the strong side: Ensure that the patient is well rolled over onto the side. Keep the head well supported and in good alignment.
How do you turn a patient in bed alone?
How to turn a patient in bed alone. Push gently across the hip and the shoulder so that the patient rolls away from you; Once the patient is in a side-lying position, ensure that the knees and the ankles of the patient do not rest on each other; Place a wedge behind the upper back, support the top leg using a pillow or an appropriate positioning...
How to move a stroke patient?
Moving a stroke patient requires assistace from a caregiver as the stroke may have caused partial paralysis to the patient. Stroke may cause paralysis to one side of the body, making it difficult for a patient to move in bed.
Why is it important to position a stroke patient safely?
Stroke may cause paralysis to one side of the body, making it difficult for a patient to move in bed. Regular changing of positions is important to minimise the patient's risk of skin breakdown, contractures and chest complications. Let us show you how to position a stroke patient safely and comfortably.

How do you put a stroke patient to sleep?
1:224:19After Stroke: 3 Bed Positions You Will Want to Know and Follow. - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBecause what legs in strokes tend to like to do they like to come back and straight and it the hipMoreBecause what legs in strokes tend to like to do they like to come back and straight and it the hip tends to retract on them so we're getting a little bend at the hip a little bend at the knee.
What position do you put a stroke patient in?
HOUSTON -- Keeping the head elevated is the favored head position for acute stroke patients, but some studies have indicated that lying flat may improve recovery. A new, international study suggests it may not matter.
Do you lay someone down if they are having a stroke?
Help the person lie down. A stroke can cause dizziness, difficulty controlling movement, even paralysis. Keep stroke victims on their side with the head slightly elevated to promote blood flow. It may slow the process. “Help them lie down and be comfortable,” says Cramer.
How do you transfer a stroke patient from a wheelchair to bed?
2:103:26Tips for Stroke Survivors: Bed to Wheelchair Transfer - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipI'm gonna back up until your legs touch the chair. Good reach back with your right hand to theMoreI'm gonna back up until your legs touch the chair. Good reach back with your right hand to the armrest. Try not to let them plop.
Why positioning is important in stroke?
Proper positioning post-stroke is essential in order to reduce the risk of shoulder subluxation, contractures and pain. Proper positioning may also enhance motor recovery, range of motion, and oxygen saturation.
How do you calm a stroke patient?
When communicating with a stroke survivor who has communication problems (aphasia), it is helpful to:Be patient.Eliminate distractions. ... Keep the questions simple, so that the survivor may reply using yes or no.Keep commands and directions simple.Speak in a normal voice at normal loudness.More items...•
What a stroke patient should not do?
Three Things Not to Do When Someone Is Having a StrokeDo not let that person go to sleep or talk you out of calling 911. Stroke survivors often complain of suddenly feeling very sleepy when a stroke first happens. ... Do not give them medication, food, or drinks. ... Do not drive yourself or someone else to the emergency room.
What percentage of stroke patients make a full recovery?
Although just 10% of people fully recover from a stroke, 25% have only minor impairments and 40% have moderate impairments that are manageable with some special care.
How likely is a second stroke?
Even after surviving a stroke, you're not out of the woods, since having one makes it a lot more likely that you'll have another. In fact, of the 795,000 Americans who will have a first stroke this year, 23 percent will suffer a second stroke. What can stroke patients do to avoid a recurrence?
How do you transfer a patient who had a stroke?
1:465:43Transfer Techniques For Patients With Stroke (Part 1: Maximal Assistance ...YouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipThe patient up to a sitting position your helper could assist you with the patient's trunk neverMoreThe patient up to a sitting position your helper could assist you with the patient's trunk never lift by putting your hand under the patient's neck.
What are some devices that can help with a bed to chair transfer?
Best Transfer Aids for BedsSammons Preston Rigid Leg Lifter. A leg lifter is a great tool if you just need a little assistance getting into bed. ... SafetySure Transfer Slide. Once in bed, a transfer slide sheet can help with repositioning. ... Sammons Preston Bed Pull. ... Days Bed Assist Handle. ... Days Curved Transfer Board.
How do I transfer an immobile patient?
5:528:35How To Transfer Immobile Patient - by Singapore General HospitalYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipBring the patient to one side cut the opposite buttock backwards. And repeat on the opposite side toMoreBring the patient to one side cut the opposite buttock backwards. And repeat on the opposite side to transfer the patient back to bed. The sling need to be placed behind the patient.
Should stroke patients lay on their affected side?
Conclusion: Patients should preferably be positioned on the paretic side to prevent aspiration, to have the unaffected arm free for movement and to avoid additional hemianopia or visual hemineglect to the paretic side possibly disrupting communication with the helpers.
What is the best position to transport an unresponsive stroke patient?
For the SICK (unstable) and unconscious stroke patient, position in a supine position or in the most appropriate position to control the airway and maintain good ventilation.
Why do stroke patients rotate their beds?
A Stroke may affect the physical independence of an individual by severely damaging brain cells and areas of the brain responsible for body movement and mobility. The Freedom Bed’s programmed rotation provides a true benefit by ensuring unparalleled levels of independence and comfort for users.
What causes a hemmoragic stroke?
Hemorrhagic stroke is caused by the breakage of a cerebral artery that is weakened, damaged, or ruptured.
How does the Freedom Bed work?
The Freedom Bed’s automatic lateral rotation and air-powered kinetic therapy systems smoothly and quietly rotates its users from side to side by mechanically repositioning the body to restore blood flow to compressed tissue. It is built from the highest quality materials to provide users with powerful assistance in lessening mobility issues associated with the effects of stroke. The Freedom Bed ensures that users can enjoy deep and uninterrupted sleep with little or no intervention from professional caregivers or family members.
What is the Freedom Bed?
The Freedom Bed by ProBed Medical Technologies helps many stroke survivors to experience improved quality of life and a renewed sense of fulfillment and independence by alleviating caregiver intervention and promoting healthy sleep routines to reduce the effects of pain and many chronic medical complications associated with strokes.
What is the term for the stoppage of blood flowing to the brain?
A stroke is a term used for a medical complication that describes the stoppage of blood flowing to any part of the brain. When the brain is unable to receive the oxygen-rich nutrients of the blood it needs to survive, the cells begin to die, seriously affecting the ability of an individual to speak, walk, and recall information.
What is the biggest hurdle in adjusting to the ramifications of immobility?
The biggest hurdle in adjusting to the ramifications of immobility is taking the first action toward a better quality of life. Our knowledgeable medical bed specialists are always ready to discuss your specific needs.
Can a stroke cause irreparable damage to the brain?
This interruption of blood flow can cause irreparable damage to the brain, but the effects of a stroke depend largely on the areas of the brain that are damaged, and the severity of the damage done . There are two main types of stroke.
Why is it important to change positions during stroke?
Regular changing of positions is important to minimise the patient's risk of skin breakdown, contractures and chest complications.
How to position a patient's head centrally?
If the patient is lying flat on the bed:Use a towel to position the head centrally. A pillow is then placed under the weaker shoulder and arm. Ensure the weaker leg is positioned in a neutral position. You can also use pillows to hold the leg in position.
How to help a patient who is sitting out on a chair?
If the patient is sitting out on a chair: Check that the patient is not slouched, but sitting well back into the chair. Ensure the patient is not leaning to one side. Place a pillow under the weaker arm to support it. Keep the patient's foot flat on the floor.
How to keep a patient from lying on the weak side?
If the patient is lying on the weak side: Keep the weak arm placed away from the body before turning the patient over. Roll the patient onto the side, allowing the body to rest on the pillows. Slide the weak shoulder forward to avoid excessive pressure over it. Place a pillow between the patient's legs.
How to help a patient with a weak arm?
Ensure the patient is not leaning to one side. Place a pillow under the weaker arm to support it. Keep the patient's foot flat on the floor. If the chair is too high for the patient, you can place a foot stool beneath the patient's feet. Keep the weaker leg in neutral position. You can place towels or cushions by the side of the patient's leg to keep it in position. Ensure that the weak arm is well supported when sitting and do ot let the arm drop when the patient moves to prevent injury.
How to hold a weak leg in position?
Ensure the weaker leg is positioned in a neutral position. You can also use pillows to hold the leg in position. If the patient is lying on the strong side: Ensure that the patient is well rolled over onto the side. Keep the head well supported and in good alignment.
How to keep a chair from getting too high?
Keep the weaker leg in neutral position. You can place towels or cushions by the side of the patient's leg to keep it in position.
Where should a wheelchair be placed?
Place the wheelchair on the right side of the patient.
Should knees bend every time when lifting patients?
Knees should bend slightly every time when lifting patient.
Can a stroke patient lift?
Lifting and transferring stroke patients require proper technique. If improper technique is used, it would result in injury to carers and stroke patients. Carers can suffer from low back pain as a result of improper of lifting and transferring techniques.
Where does the person performing the manoeuvre need to be positioned?
Move around the bed. The person performing the manoeuvre needs to be positioned at the side of the bed the rolling is being directed;
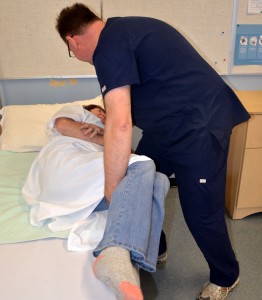
How to help a patient who is side lying?
Push gently across the hip and the shoulder so that the patient rolls away from you; Once the patient is in a side-lying position, ensure that the knees and the ankles of the patient do not rest on each other;
What is the same manoeuvre when a slide sheet is provided?
The same manoeuvre when a slide sheet is provided is as follows: Bend the leg that is away from the rolling direction or cross the ankles; Move around the bed. The person performing the manoeuvre needs to be positioned at the side of the bed the rolling is being directed;
What is the role of occupational therapists in single handed care?
Every Occupational Therapist with a mission to implement single handed care packages will have to risk assess, among other tasks, the manoeuvre of a carer to turn a patient in bed alone.
How to move a patient from a wheelchair to a bed?
Park the wheelchair next to the bed. If your patient can stand and bear some weight, they can do a pivot transfer. Explain to your patient that you are going to move from the bed to the chair, or from the chair to the bed, as the case may be.
What to do if you are transferring a patient at home?
If you’ll be transferring a patient at home after they are discharged from the hospital, practice at the hospital with the guidance of a trained staff member so you can learn the proper techniques to prevent injury to both you and the patient.
How to help a patient who is not dizzy?
If your patient is not dizzy or tilting, help them complete a pivot transfer. Put a gait/transfer belt on them. Help them scoot so that their bottom is at the edge of the seat or bed. Check that both feet are firmly on the floor. Instruct your patient to push up with their hands, leaning forward over their feet.
How to put a gait belt on a patient?
If the patient has suffered a stroke or other issues that affects their motor functions, attach a gait belt around their waist . The gait belt will also give you a better grip during the transfer so the patient does not fall out of your arms. Wrap the belt around the patient’s waist so it is snug, but not too tight. Tuck any extra fabric at the end of the belt into the belt so it is not a tripping hazard.
How to support a patient when lifting?
Make sure the patient keeps their hands by their sides so they can support themselves when you lift them. If the patient has strength in their legs, instruct the patient to support their weight with their legs as you transfer them.
How to know if a patient is dominant?
Identify the patient’s dominant side. Hold the patient’s hands, placing 1 hand in each of their hands. Ask the patient to squeeze your hands as hard as they can. Notice if 1 side feels stronger in your hands.
What to say to a new patient?
Offer words of encouragement as you go if the patient is new to this. You might say, "Nice and slow. Both feet on the floor. Great work."
