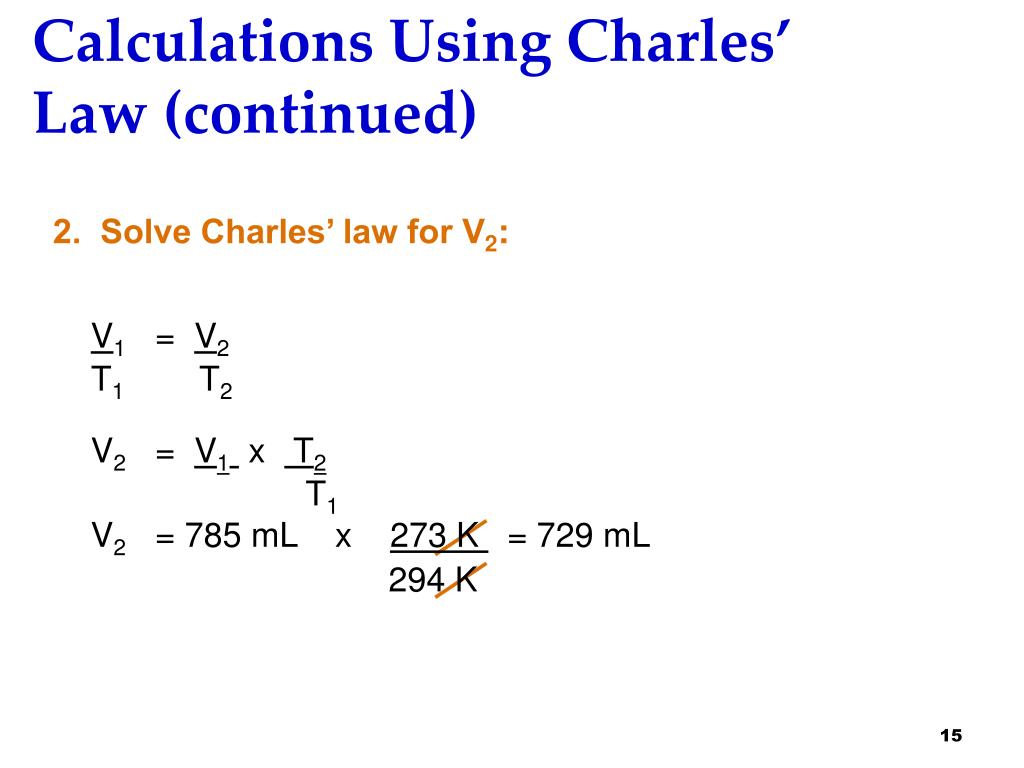
What is the formula for Charles'law?
Charles' law formula. Based on the definition of Charles' law, we can write the Charles' law equation in the following way: V₁ / T₁ = V₂ / T₂, where V₁ and T₁ are initial volume and temperature, respectively. Similarly, V₂ and T₂ are the final values of these gas parameters.
What is Charle's law in chemistry?
Define Charle's Law in Chemistry. The law of volumes, or Charles law, is an experimental gas law that describes how gases expand when heated. Charles law states that "When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion".
What can you do with a Charles'law calculator?
This is the Charles' Law Calculator. Start by entering some numbers. Tip: You don't need to go from the top to the bottom. You can calculate anything, in any order. What is Charles' law application in real life? The Charles' law calculator is a simple tool which describes the basic parameters of an ideal gas in an isobaric process.
How do you calculate temperature using Charles'law?
If you prefer to set the final volume and want to estimate the resulting temperature, then the equation of Charles' law changes to: T₂ = T₁ / V₁ * V₂. In advanced mode, you can also define the pressure and see how many moles of atoms or molecules there are in a container. We can use Charles' law calculator to solve some thermodynamic problems.
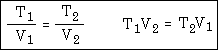
How do you express Charles Law in math?
Charles' law is represented mathematically as Vt=V0(1+273t) It can also be represented as Vt=V0(T0T) or V∝T. At constant pressure, volume of the given mass of the gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature.
What is Charles Law explain with example?
If you take a basketball outside on a cold day, the ball shrinks a bit as the temperature is decreased. This is also the case with any inflated object and explains why it's a good idea to check your car's tire pressure when the temperature drops.
Where do we use Charles Law?
Since pressure is kept constant, the only variable that is manipulated is temperature. This means that we can use Charles's law in order to compare volume and temperature. Since volume and temperature are on opposite sides of the ideal gas law, they are directly proportional to one another.
What are some examples of Charles Law in everyday life?
Top 6 Charles Law Examples in Real LifeHot Air Balloon.Bursting Of A Deodorant.Bakery Products.Turkey Pop Up Timer.Opening Of A Soda Can.Helium Balloon On Cold Day.
What is Charles Law class 11th?
Charles law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure.
What is an example of Charles law in real life?
Tyres of untouched vehicles get deflated during freezing winter days while get inflated in hot summer days. This unusual behaviour is because of Charles's law. In winter due to low temperatures, the air inside a tyre gets cooler, and they shrink. While in hot days, the air expands with temperature.
What is Charles formula?
Definition of Charles Law Formula is, “When the pressure on a sample of a dry gas is held constant, the Kelvin temperature and therefore the volume is going to be in direct proportion.” The equation of the law is PV = k. k may be a constant.
What is Charles Law and Boyle's law?
Boyle's Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the pressure decreases. Charles' Law tells us that the volume of gas increases as the temperature increases. And Avogadro's Law tell us that the volume of gas increases as the amount of gas increases.
What is Charles Law in simple terms?
Charles' Law relates the volume and the temperature of gas while its pressure remains the same. The law states that 'The volume of a given mass of...
What is Charles and Boyle's law?
Charles' Law states that 'The volume of a given mass of gas at constant pressure varies directly with its absolute temperature.' Boyle's Law state...
How do you calculate Charles Law?
Since the volume of a gas changes proportionately with its absolute temperature, mathematically Charles' Law can be expressed as: V=KT Where V, T...
How does Charles law work?
The application of Charles' Law can be observed in the working principle of a hot air balloon. As the inside air of the balloon's parachute, also c...
1. What is Charles Law?
Ans: If the pressure remains constant, Charles' law states that the volume occupied by a fixed amount of gas is precisely proportional to its absol...
2. What is the Charles Law Formula?
Ans: According to Charles law equationV ∝ TThe Charles law mathematical expression will be V = kTV/T = kWhere V is the volume of the gas.T is the t...
3. What is the Charles Law Formula Under 2 Different Conditions?
Ans: The mathematical expression of Charles law can be expressed as follows for comparing the same material under two different sets of conditions:...
Using the Charles's Law Equations and Vocabulary
Charles's Law: Charles's Law states that at a constant pressure, the volume of a sample of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature.
Using the Charles's Law Example
If a gas has an initial temperature of 300 K and an initial volume of 0.75 L, and its temperature is raised to 500 K, what is the new volume of the gas if the pressure and number of moles are constant?
Using the Charles's Law: Example
If a gas has an initial temperature of 30 degrees Celsius and an initial volume of 2.5 L. After being cooled, its new volume is 2.0 L. What is its new temperature if the pressure and number of moles are constant?
What is Charles Law?
Charles’ Law, also sometimes referred to as the law of volumes, gives a detailed account of how gas expands when the temperature is increased. Conversely, when there is a decrease in temperature it will lead to a decrease in volume.
Who created the law of physics?
This law was formulated in the year 1780 by French physicist Jacques Charles. This law was described extensively in his unpublished work.
What is the law of volume?
Charles law states that the volume of an ideal gas is directly proportional to the absolute temperature at constant pressure. The law also states that the Kelvin temperature and the volume will be in direct proportion when the pressure exerted on a sample of a dry gas is held constant. This law was formulated in the year 1780 by French physicist ...
How to equate V and T?
Since V and T are varying directly, we can equate them by making use of the constant k.
What happens to the volume of a gas at 0 degrees centigrade?
Similarly, lowering the temperature, the volume of the gas decreases. And at 0-degree centigrade, the volume of the also increases by 1/273 of its original volume for a unit degree increases in temperature. Also Read: Gas Laws.
Does the mass of a gas change?
It is very clear that the pressure is constant and the mass of the gas doesn’t change, so we can apply Charle’s law here.
Is the volume of the fixed amount of dry gas directly proportional to absolute temperature?
As we are aware of the fact that, at constant pressure, the volume of the fixed amount of the dry gas is directly proportional to absolute temperature according to Charle’s law. We can represent the statement in the following manner.
How does Charles' law work?
The application of Charles' Law can be observed in the working principle of a hot air balloon. As the inside air of the balloon's parachute, also called the envelope, is heated with a burner, the air expands and inflates the parachute. With the hot air being lighter than the relatively cold, surrounding air, the balloon starts to rise due to the upward buoyant force.
What is Charles' law?
Charles' Law relates the volume and the temperature of gas while its pressure remains the same. The law states that 'The volume of a given mass of gas at constant pressure varies directly with its absolute temperature.'
Which law states that the volume of a given mass of gas at constant pressure varies directly with its absolute temperature?
Charles' Law states that 'The volume of a given mass of gas at constant pressure varies directly with its absolute temperature.'
How to find the constant of proportionality?
To calculate the constant of proportionality measure the different sets of volume and the temperature of the gas at constant pressure. Plot the values on a graph with the temperature along the x-axis and volume along the y-axis. Draw the line of best fit of the plotted points. The slope of this line of best fit will give the value of K, the constant of proportionality. Using this value of K, either the volume or the temperature of a gas at constant pressure can be calculated if the other variable is known.
What is Charles law?
Charles Law is a gas law that defines how gases expand when heated in an experimental setting. The rule asserts that if an amount of gas is held at constant pressure, the volume and temperature, measured in degrees Kelvin, have a direct relationship. The molecules in any particular gas begin to move around more swiftly as the temperature increases.
What is the law of volumes?
The law of volumes, or Charles law, is an experimental gas law that describes how gases expand when heated.
What is the final temperature of a gas sample?
Therefore the final temperature of the gas sample is -97.250 C.
What is Charles' law calculator?
The Charles' law calculator is a simple tool which describes the basic parameters of an ideal gas in an isobaric process. In the text, you can find the answer to the question "What is Charles' law?", learn what the Charles' law formula looks like, and read how to solve thermodynamic problems with some Charles' law examples.
What is Charles' law?
Charles' law definition. Charles' law (sometimes referred to the law of volumes) describes the relationship between the volume of a gas and its temperature when the pressure and the mass of the gas is constant. It states that the volume is proportional to the absolute temperature. There are a few other ways we can write the Charles' law definition, ...
What is Charles' law application in real life?
There are actually various areas where we can use Charles' law. Here is a list of a few of the most popular and most interesting examples:
What happens when you put a ball in liquid nitrogen?
Liquid nitrogen experiments - have you ever seen an experiment where a ball or balloon is put inside the container filled with liquid nitrogen, and then moved outside? Firstly, it shrinks no matter how big it was at the beginning. Then, after it is freed, it comes back to its initial state. Once again, whenever the temperature changes, so does the volume.

Using The Charles's Law
Using The Charles's Law Equations and Vocabulary
- Charles's Law:Charles's Law states that at a constant pressure, the volume of a sample of gas is directly proportional to its absolute temperature. Charles's Law Equation:{eq}\frac{V_1}{T_1}=\frac{V_2}{T_2}{/eq} Kelvin: The Kelvin scale is an absolute temperature scale. It is the SI unit of temperature. It is represented by the capital letter K. We...
Using The Charles's Law Example
- If a gas has an initial temperature of 300 K and an initial volume of 0.75 L, and its temperature is raised to 500 K, what is the new volume of the gas if the pressure and number of moles are constant? Step 1:Determine the known values. We are given the initial temperature is {eq}T_1=300\ K{/eq}. The initial volume is {eq}V_1= 0.75\ L{/eq}. The final temperature is {eq}T_…
Using The Charles's Law: Example
- If a gas has an initial temperature of 30 degrees Celsius and an initial volume of 2.5 L. After being cooled, its new volume is 2.0 L. What is its new temperature if the pressure and number of moles are constant? Step 1:Determine the known values. We are given the initial temperature is {eq}T_1=30^o\ C{/eq}. The initial volume is {eq}V_1= 2.5\ L{/eq}. The final volume is {eq}V_2=2.0…