- Stock value = Dividend per share / (Required Rate of Return – Dividend Growth Rate)
- Rate of Return = (Dividend Payment / Stock Price) + Dividend Growth Rate.
How do you calculate the present value of dividends?
- Figure out the net income of the company.
- Determine the number of shares outstanding.
- Divide net income by the number of shares outstanding.
- Determine the company's typical payout ratio.
- Multiply the payout ratio by the net income per share to get the dividend per share.
How does dividend affect share price?
How Does A Dividend Affect Share Price?
- When Dividends Go Down. If a company reduces the dividend it pays on its stock, the stock becomes less attractive to investors.
- When Dividends Go Up. When dividends go up, the stock becomes more attractive to buyers. …
- Company Signals. …
- Anticipating Dividend Changes. …
How do you calculate annual dividend?
To estimate the dividend per share:
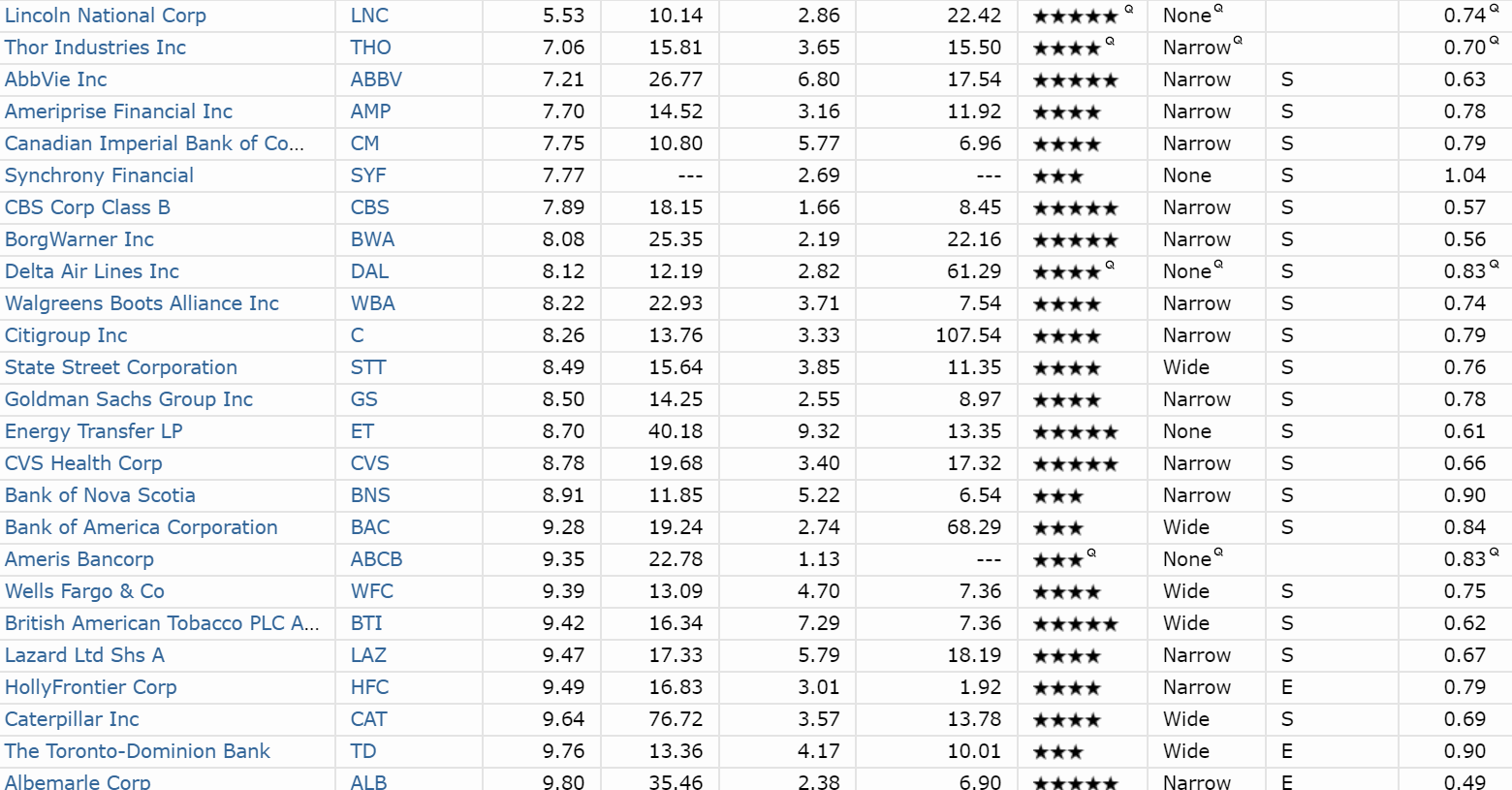
- The net income of this company is $10,000,000.
- The number of shares outstanding is 10,000,000 issued – 3,000,000 in the treasury = 7,000,000 shares outstanding.
- $10,000,000 / 7,000,000 = $1.4286 net income per share.
- The company historically paid out 45% of its earnings as dividends.
- 0.45 x $1.4286 = $0.6429 dividend per share.
What is the dividend discount formula?
The dividend discount model formula to calculate present stock value, expected growth rate, expected dividend, and cost of equity is as follows: First calculate, Present stock value = Expected dividend / (Cost of equity - Expected growth rate) Expected Growth Rate = (1 – Dividend …
How to calculate stock value?
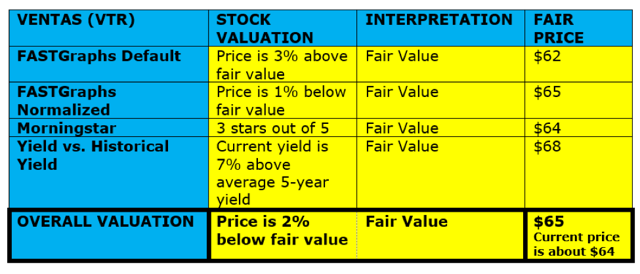
Divide the dividend per share by your result to calculate the stock’s value. In this example, divide $1.50 by 0.08 to get a stock value of $18.75.
How to calculate dividend discount?
Substitute the values into the dividend discount model: stock value = dividend per share/ (required rate of return - growth rate). In this example, substitute the values to get: stock value = $1.50/ (0.1 - 0.02).
What does discount rate mean in stock market?
It uses a discount rate to convert all of the stock’s expected future dividend payments into a single, theoretical stock price, which you can compare to the actual market price. If the market price is greater than the model’s price, the market may be overvaluing the stock.
What is the difference between a stock with less risk and a stock with more risk?
A stock with more risk has a higher required rate of return, while a stock with less risk has a lower required rate of return. In this example, assume you require a 10 percent rate of return on the stock. Estimate the stable rate at which you expect the company and its dividend payments to grow per year forever.
Does dividend discount work?
The dividend discount model works only for stocks that pay a dividend.
What is stock dividend?
A stock dividend, a method used by companies to distribute wealth to shareholders, is a dividend payment made in the form of shares rather than cash. Stock dividends are primarily issued in lieu of cash dividends when the company is low on liquid cash on hand. The board of directors. Board of Directors A board of directors is a panel ...
How does a dividend affect a company's stock?
Maintaining an “investable” price range. As noted above, a stock dividend increases the number of shares while also decreasing the share price. By lowering the share price through a stock dividend, a company’s stock may be more “affordable” to the public.
How many shares are in a small dividend?
A stock dividend is considered a small stock dividend if the number of shares being issued is less than 25%. For example, assume a company holds 5,000 common shares outstanding and declares a 5% common stock dividend. In addition, the par value per stock is $1, and the market value is $10 on the declaration date. In this scenario, 5,000 x 5% = 250 new common shares will be issued. The following entries are made:
Why do stock dividends depress the market?
The market may perceive a stock dividend as a shortage of cash, signaling financial problems. Market participants may believe the company is financially distressed, as they do not know the actual reason for management issuing a stock dividend. This can put selling pressure on the stock and depress its price.
Why do companies issue dividends instead of cash?
Issuing a stock dividend instead of a cash dividend may signal that the company is using its cash to invest in risky projects. The practice can cast doubt on the company’s management and subsequently depress its stock price.
Why does the price per share decrease?
Although it increases the number of shares outstanding for a company , the price per share must decrease accordingly. An understanding that the market capitalization of a company remains the same explains why share price must decrease if more shares are issued.
What is capital gain?
Capital Gain A capital gain is an increase in the value of an asset or investment resulting from the price appreciation of the asset or investment. In other words, the gain occurs when the current or sale price of an asset or investment exceeds its purchase price.
How do dividends affect stock valuation?
First of all, a dividend doesn't have a direct impact on a stock's valuation. Common valuation metrics such as the price-to-earnings (P/E) ratio, price-to-book (P/B) ratio, and most others are calculated in the same way regardless of whether a stock pays a dividend.
Why do dividends help stocks?
Dividends can also help to create a "price floor" in stocks that otherwise may not exist. For example, if a certain stock yields 4%, it may seem not worth the risk to many investors. If the price drops and the stock's yield jumps to 6%, they may reconsider.
What is dividend discount model?
The dividend discount model. There is one method of valuing stocks based on the dividends they pay, known as the dividend discount model. Simply put, this model uses the idea that a stock is worth the sum of all of its future dividends.
What happens to a stock after a dividend?
It's also important to mention that on a stock's ex-dividend date, the share price will fall by the amount of the dividend, lowering the stock's valuation accordingly in terms of P/E or similar price-based valuation metrics. For example, if a stock trades for $20 per share and earned $1 per share over the past 12 months, the stock's P/E is 20. However, if the stock pays a $0.50 dividend, the share price will theoretically drop to $19.50, making the stock's P/E 19.5.
What does it mean when a company raises its dividend?
For example, if a company raises its dividend higher than the market expects, it could be taken as a positive sign and boost the stock's price. Similarly, a dividend cut can be interpreted as a sign of trouble and could result in a depressed valuation.
Is dividends considered a good way to value a stock?
Naturally, this is a far from perfect way to value a stock. For starters, it only takes dividends into account -- not the company's financial condition, growth rate, or any other factors. It just tells you how much you should be willing to pay for a dividend stock to achieve a certain required rate of return.
Do dividends affect intrinsic value?
Dividends don't directly affect a company' s intrinsic value , but they can affect its stock valuation. Matt is a Certified Financial Planner based in South Carolina who has been writing for The Motley Fool since 2012.
How to calculate dividends per share?
DPS can be calculated by subtracting the special dividends from the sum of all dividends over one year and dividing this figure by the outstanding shares.
How do dividends affect stock prices?
Dividends can affect the price of their underlying stock in a variety of ways. While the dividend history of a given stock plays a general role in its popularity, the declaration and payment of dividends also have a specific and predictable effect on market prices .
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield and dividend payout ratio (DPR) are two valuation ratios investors and analysts use to evaluate companies as investments for dividend income. The dividend yield shows the annual return per share owned that an investor realizes from cash dividend payments, or the dividend investment return per dollar invested. It is expressed as a percentage and calculated as:
Why are dividends so attractive?
When companies display consistent dividend histories, they become more attractive to investors. As more investors buy in to take advantage of this benefit of stock ownership, the stock price naturally increases, thereby reinforcing the belief that the stock is strong. If a company announces a higher-than-normal dividend, public sentiment tends to soar.
What happens to stock after ex dividend?
After a stock goes ex-dividend, the share price typically drops by the amount of the dividend paid to reflect the fact that new shareholders are not entitled to that payment. Dividends paid out as stock instead of cash can dilute earnings, which can also have a negative impact on share prices in the short term.
How much does a dividend drop at $200?
As with cash dividends, smaller stock dividends can easily go unnoticed. A 2% stock dividend paid on shares trading at $200 only drops the price to $196.10, a reduction that could easily be the result of normal trading. However, a 35% stock dividend drops the price down to $148.15 per share, which is pretty hard to miss.
Why are dividends discounted?
Because share prices represent future cash flows, future dividend streams are incorporated into the share price, and discounted dividend models can help analyze a stock's value.
When to use the same format for dividend?from bostonifi.com
You use the same format for when the dividend is growing at different rates. Try this, and if you are still having difficulty, I will provide an example with how to compute the dividend when the rates are changing.
What is discounting dividend?from bostonifi.com
Discount the expected dividend and selling price at the required return.
What are the factors that determine the value of a stock?
Every stock has an underlying value, which is based on multiple factors such as past performance, quality of management, its profitability, management efficiency and expected growth in the future. Based on all these factors, you assess a price you are willing to pay for the stock.
What is Valuation?
Valuation is all about assessing the intrinsic value of a stock and compare it with the market price in order to understand whether the stock is trading at right price and if you should invest in it. What is intrinsic value? Let me explain, every stock has a business behind it, and every business has a value, which is calculated based on the assets it owns, the cash it has, and it’s estimated future growth and how much capital it can generate in the future from its business.
What is intrinsic value?
Based in all these factors, the value of a business is calculated called intrinsic value. Valuation of any stock is all about comparing the intrinsic value and the market value of the stock, and understand if the stock is cheap or expensive.
What is discounted cash flow method?
In discounted cash flow method, we take last few years of average free cash flow (free cash flow is the cash left with the company after paying for all the capital expenditures) and make predictions about future cash flows based on expected growth rate and discounting the same to the present value in order to arrive at a conclusion of the stock is under or overvalued.
What is the second approach to valuation?
The second approach on how to value a stock is relative valuation. Relative valuation is more popular, and a relatively easier method of valuing a stock.
What is absolute valuation?
Absolute valuation is all about understanding the value of a stock and determining the price you are willing to pay for it. If the value of the stock is lower than the price, it becomes a great investment. But how do you assess the value of a stock?
How many valuation models are there?
There are three different valuation models you can use to value a stock, Some of them are very easy to implement, others are slightly lengthy and little difficult. However, all these valuation models are widely used by analysts and investors. Let’s look at each of them and find out how to value a stock. Ready? Read on…
How to calculate dividends per share?
This represents the amount of dividend money that investors are awarded for each share of company stock they own. For a given time period, DPS can be calculated using the formula DPS = (D - SD)/S where D = the amount of money paid in regular dividends, SD = the amount paid in special, one-time dividends, and S = the total number of shares of company stock owned by investors.
How to find out how many shares of stock you own?
If you're not already aware of how many shares of company stock you own, find out. You can usually get this information by contacting your broker or investment agency or checking the regular statements that are usually sent to a company's investors via mail or email.
How do companies make money?
On one hand, it can reinvest this money in the company by expanding its own operations, buying new equipment, and so on. (Money spent this way is called "retained earnings.") Alternatively, it can use its profits to pay its investors. Money paid to investors in this way is called a "dividend". Calculating the dividend that a shareholder is owed by a company is generally fairly easy; simply multiply the dividend paid per share (or "DPS") by the number of shares you own. It's also possible to determine the "dividend yield" (the percentage of your investment that your stock holdings will pay you in dividends) by dividing the DPS by the price per share.
How much do you make on 7.5% stock?
Simple math will tell you that you will make approximately $.09 for each share in a year on the 7.5% stock, and $1.90 on the 6.8% stock. The % stated typically does not include special dividend payments. Dividends are not guaranteed and can be adjusted or taken away altogether at anytime with the approval of the board of directors.
What is dividend yield?
The dividend yield is the percentage of your investment that a stock will pay you back in the form of dividends. Dividend yield can be thought of as an "interest rate" on a stock. To get started, you'll need to find the current price per share of the stock you're analyzing.
What does it mean when a stock price falls?
Price movements reflect supply and demand. If a stock's price falls, that indicates the buying public is simply not as interested in acquiring shares of that stock as it used to be, or the drop may occur after the company has issued more shares.
What happens if there is no money in your stockholder's account?
If there's no money in your stockholder's account, there can't be any dividend payments contained there. Ask your accountant what's going on.
How do stock dividends work?
A dividend is paid per share of stock — if you own 30 shares in a company and that company pays $2 in annual cash dividends, you will receive $60 per year.
Why do investors prefer dividend stocks?
Investors typically prefer to invest in companies that offer dividends that increase year after year, which helps outpace inflation.
How to know if a dividend is safe?
Advisors say one of the quickest ways to measure a dividend’s safety is to check its payout ratio, or the portion of its net income that goes toward dividend payments. If a company pays out 100% or more of its income, the dividend could be in trouble. During tougher times, earnings might dip too low to cover dividends. Generally speaking, investors look for payout ratios that are 80% or below. Like a stock's dividend yield, the company's payout ratio will be listed on financial or online broker websites.
What is dividend reinvestment?
Instead of paying cash, companies can also pay investors with additional shares of stock. Dividend reinvestment programs (DRIPs). Investors in DRIPs are able to reinvest any dividends received back into the company's stock, often at a discount. Special dividends.
Why do investors devalue stocks?
However, once a company establishes or raises a dividend, investors expect it to be maintained, even in tough times. Because dividends are considered an indication of a company's financial well-being, investors often will devalue a stock if they think the dividend will be reduced, which lowers the share price.
What is special dividend?
Special dividends. These dividends payout on all shares of a company’s common stock, but don’t recur like regular dividends. A company often issues a special dividend to distribute profits that have accumulated over several years and for which it has no immediate need. Preferred dividends.
How are yield and stock price related?
Yield and stock price are inversely related: When one goes up, the other goes down. So, there are two ways for a stock’s dividend yield to go up:
How to value a stock without dividends?
There are many ways to value a stock without dividends. A company with high earnings and a low price will have a low P/E ratio regardless of dividends, and such a stock could be a good buy. Growth investors prefer to focus on metrics like earnings growth. The assets and liabilities of a firm can be summed to give the book value, ...
Why do investors buy stocks that do not pay dividends?
Thus, investors who buy stocks that do not pay dividends prefer to see these companies reinvest their earnings to fund other projects. They hope these internal investments will yield higher returns via a rising stock price. Smaller companies are more likely to pursue these strategies.
What happens when stocks fall below book value?
Firms that are currently losing money and cannot pay dividends may see their stock prices fall below book value. At the very least, stocks priced below book value make tempting takeover targets. The stocks of firms with long histories of success were often good buys when their prices fell below book value.
What is book value?
Book Value. Book value provides a way to value the stocks of companies that have no earnings and pay no dividends. Every company has assets and liabilities on its balance sheet that can be summed to give the book value of the company. Firms that are currently losing money and cannot pay dividends may see their stock prices fall below book value.
Why are growth companies not paying dividends?
In the past, many associated growth companies with non-dividend-paying stocks because their expansion expenses were close to or exceeded their net earnings. That is no longer the rule in today's modern market. Other firms have decided not to pay dividends under the principle that their reinvestment strategies will—through stock price appreciation—lead to greater returns for the investor.
What does it mean when a company's earnings went up 60% last year?
If a company's earnings went up 60% last year and 50% the year before, that is a sign the company is strong.
Can you invest in stocks with no dividends?
Stocks without dividends can be excellent investments if they have low P/E ratios, strong earnings growth, or sell for below book value.
