
Similarly, when you add small amounts of strong acid (H 3 O +) to a buffer, the buffer will resist changes in its pH by sending an equal amount (stoichiometric amount) of its weak base to accept a proton from the strong acid. Once the base accepts the proton, it turns into its conjugate acid, while the strong acid turns into water.
How do buffers reduce change in the pH of solutions?
In effect, a buffer solution behaves somewhat like a sponge that can absorb H+ and OH− ions, thereby preventing large changes in pH when appreciable amounts of strong acid or base are added to a solution. Does a buffer change pH when a strong acid is added? A buffer’s pH changes very little when a small amount of strong acid or base is added to it.
Do buffer solutions prevent or inhibit changes in pH?
Buffer solution: what is it and how does it work to resist changes in its pH? A buffer is a solution that resists changes in its pH when small amounts of strong acid or base is added to it.Small amount is bolded to stress the fact that if you add too much strong acid or base to your buffer, it’s pH will change.
How do buffers moderate pH changes?
Buffers work by neutralizing any added acid (H+ ions) or base (OH- ions) to maintain the moderate pH, making them a weaker acid or base. Now, because all the extra H+ ions are locked up and have formed a weaker acid, NH4+, thus the pH of the system does not change significantly. How do buffers prevent changes in pH?
How do I make a buffer with a specific pH?
To prepare a buffer solution of known pH from scratch, we must carry out the following steps:
- choose a conjugate acid-base pair
- calculate the ratio of buffer components
- determine the buffer concentration
- mix and adjust the buffer’s pH
How does a buffer resist change in pH upon addition of a strong acid?
What happens when a strong acid reacts with a weak base?
About this website
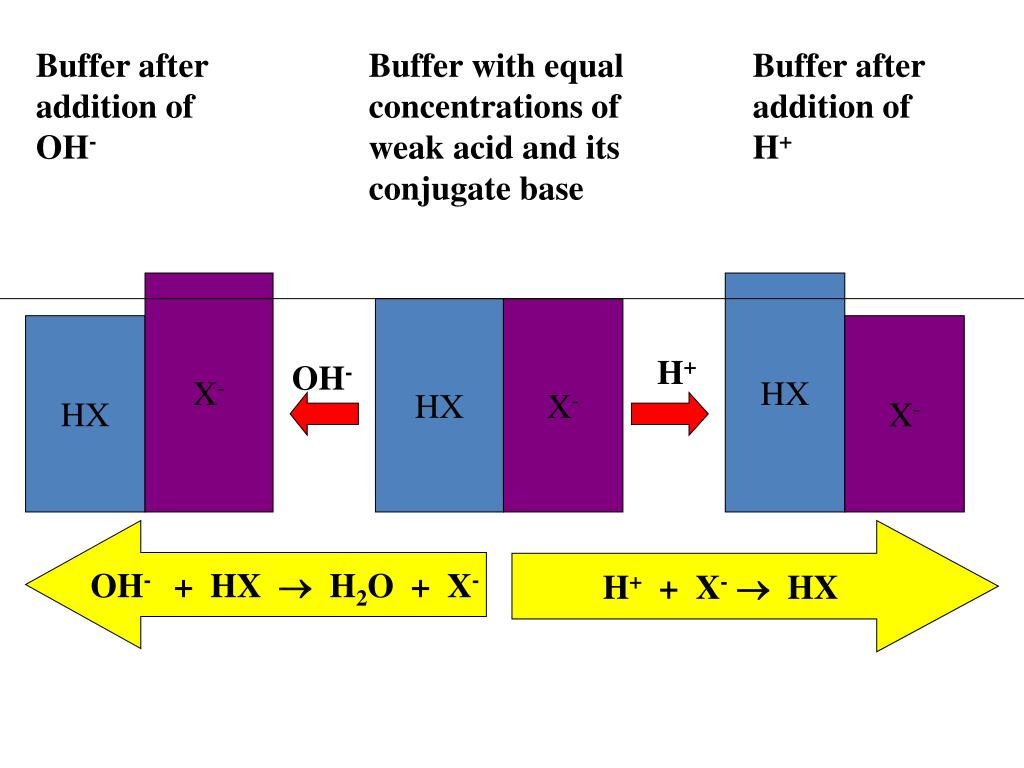
How does a buffer resist a change in pH upon addition of a strong acid?
Answer: When a strong acid is added to buffer solution then conjugate base present in buffer solution takes its hydronium ion converting it into weak acid of conjugate base and water. Due to this, amount of weak acid increases and amount of conjugate base decreases.
What happens when a strong acid is added to a buffer?
When a strong acid (H3O+) is added to a buffer solution the conjugate base present in the buffer consumes the hydronium ion converting it into water and the weak acid of the conjugate base. This results in a decrease in the amount of conjugate base present and an increase in the amount of the weak acid.
How does buffer solution resist changes in pH?
Buffer, as we have defined, is a mixture of a conjugate acid-base pair that can resist changes in pH when small volumes of strong acids or bases are added. When a strong base is added, the acid present in the buffer neutralizes the hydroxide ions (OH -start superscript, start text, negative, end text, end superscript).
How does a buffer resist change in pH upon addition of a strong acid quizlet?
How does a buffer resist change in pH upon addition of a strong acid? The strong acid reacts with the weak base in the buffer to form a weak acid, which produces few H ions in solution and therefore only a little change in pH.
When adding a strong base to a buffer solution the pH will?
When a base is added to a buffer solution, the pH does not change. The buffer solution prevents the base from neutralizing the acid.
What happens when you add HCl to a buffer solution?
When HCl (strong acid) is added to this buffer system, the extra H+ ions added to the system are consumed by the NH3 to form NH4+. Now, because all the extra H+ ions are locked up and have formed a weaker acid, NH4+, thus the pH of the system does not change significantly.
What are buffer solution Why do resist change in pH give one example each of acidic and basic buffer?
Solution : (i) Buffer is a solution which consists of a mixture of a weak acid and its conjugate base (or) a weak base and its conjugate acid.
(ii) This buffer solution resists drastic changes in its pH upon addition of a small quantity of acids(or) bases and this ability is called buffer action.
Can resist the change of pH when you add acid or base?
bufferA buffer is a solution that resists changes in pH upon the addition of a small amount of strong acid or strong base.
How does a basic buffer solution resist small changes in its pH when an acid or base is added to it?
This mechanism involves a buffer, a solution that resists dramatic changes in pH. Buffers do so by being composed of certain pairs of solutes: either a weak acid plus a salt derived from that weak acid, or a weak base plus a salt of that weak base.
What reaction occurs when strong acid is added to a buffer solution quizlet?
When a strong acid is added to a buffer system, it converts the conjugate base to the weak acid, raising the weak acid's concentration slightly, causing the pH to drop slightly at most.
What is a buffer How does a buffer work How does it neutralize added acid added base?
A buffer is a solution that can resist pH change upon the addition of an acidic or basic components. It is able to neutralize small amounts of added acid or base, thus maintaining the pH of the solution relatively stable. This is important for processes and/or reactions which require specific and stable pH ranges.
What must a buffer solution include in order to resist changes in pH on addition of acid or base quizlet?
What constitutes a good buffer? -A solution containing a compound whose pKa is within 1 unit of the pH of the solution. Within that range the solution can resist changes in pH due to the addition of strong acid or strong base because it will have sufficient concentration of both a weak acid and a conjugate base.
Why strong acid is not used in buffer solution?
Strong acids cannot be used as buffers because they dissociate completely in solution.
Why can't a strong acid make a buffer solution?
Buffers cannot be made from a strong acid (or strong base) and its conjugate. This is because they ionize completely!
When an acid is added to a buffer solution the pH quizlet?
When additional acid is added to a buffer, the conjugate base reacts with the acid, neutralizing it (generating more of the buffer system conjugate acid). In this way, a buffer can maintain a nearly constant pH. 3.
When strong acid is added to a buffer there is a small pH change because the added acid?
When a small amount of strong acid is added, it reacts with the conjugate base of the buffer system, converting it to the weak acid of the buffer system. Then the weak acid concentration increases, the conjugate base concentration decreases, and the pH drops slightly at most.
How does buffer solution resist changes in its pH?
How does buffer solution resists changes in its pH? When you add small amounts of strong base (OH –) to a buffer, the buffer will resist changes in its pH by sending an equal amount of its weak acid to donate a proton to the base.
What is buffering in chemistry?
A buffer is a solution that resists changes in its pH when small amounts of strong acid or base is added to it. Small amount is bolded to stress the fact that if you add too much strong acid or base to your buffer, it’s pH will change. This means buffer solutions have a limit to how much acid or base you can add to it without changing its pH that much. This limit is usually called the buffer capacity.#N#If this limit is too high because of the high concentration of buffer components, then its buffering capacity will be high as well. If this limit is too low because of the low concentration of buffer components, then its buffering capacity will be low as well. This means the buffer capacity is affected by the relative concentrations of the buffer components. As buffer works to resist changes in its pH, the concentration of one component decreases, while the concentration of the other increases.
What are the components of a buffer solution?
To understand how buffers work, we must first discuss the concept of conjugates in acid-base chemistry? What is a conjugate? A conjugate means a “mate.” If we translate this meaning to acid-base chemistry, then we can say that every acid is tied to its mate called “conjugate base,” and together, they are called “conjugate acid-base pair.” Similarly, every base is tied to its mate called “conjugate acid,” and together, they are called “conjugate acid-base pair.” Here is a model showing this relationship between acetic acid, CH 3 COOH and its conjugate base, acetate ion, CH 3 COO –:
What is the conjugate base of HCl?
For instance, on paper, the conjugate base of hydrochloric acid (HCl) is the chloride ion (Cl). Yet, in real life, the chloride ion is usually reluctant to accept a proton and turn into its conjugate acid, HCl. Because of this behavior, strong acids and their conjugate bases do not usually form buffer solutions. So too do strong bases.
What is an example of a weak acid?
Here is an example of a weak acid—acetic acid with its conjugate base—acetate ion. Together, they can form a buffer:
What is the buffering capacity of a solution?
This means buffer solutions have a limit to how much acid or base you can add to it without changing its pH that much. This limit is usually called the buffer capacity. If this limit is too high because of the high concentration of buffer components, then its buffering capacity will be high as well. If this limit is too low because of the low ...
How are acid and base related?
And when a proton is added to a base, the base turns into its conjugate acid. Thus, the acid and its conjugate base are related by the loss and gain of a proton.
What is buffer in pH?
A buffer is a special solution that stops massive changes in pH levels. Every buffer that is made has a certain buffer capacity, and buffer range. The buffer capacity is the amount of acid or base that can be added before the pH begins to change significantly. It can be also defined as the quantity of strong acid or base that must be added to change the pH of one liter of solution by one pH unit.
What happens when strong base is added to a pH?
If strong base is added, it transfers its OH- to HA, creating more A- , but leaving the ratio ( [A-]/ [HA]) only slightly raised. Thus, the pH is raised, but only slightly.
Why is methanoate ion abundant?
However, the methanoate ion is also there in abundance because of the contribution by the salt.
What is a buffer solution?
A buffer solution usually consists of mixture of solutions of a weak acid or base and its salt. The buffer action can be understood in the following way. Suppose we have a mixture of acid HA and its salt BA in solution.
Why does pH not change?
4. pH does not change very much when a small amount of strong acid or strong base are added to a buffer. The pH does not change very much because (A"] I (HA] does not change very much. This is true as long as the amount of strong acid or base added is small compared to the amount of conjugate acid and conjugate base in the buffer. If you add too much strong acid or base, you will exceed the buffering capacity.
What happens when you add a bit of H+?
The principle behind the buffer is that, when you add a bit of H + (aq), the equilibrium shifts backwards to form more HCO 2 H (aq). When you add base, the equilibrium shifts forward to create more HCO 2 −. Since both are in large amounts, the shift of equilibrium makes it that the amount of change is negligible hence it resists a change of pH.
What is buffering capacity?
What is meant by "buffering capacity"? What determines "buffering capacity"? Buffering capacity refers to the amount of added acid or added base that can be neutralized by a buffer. It is determined by the concentrations of the conjugate acid and conjugate base. Buffering capacity increases as these concentrations increase.
How does a buffer resist change in pH upon addition of a strong acid?
How does a buffer resist change in pH upon addition of a strong acid? The strong acid reacts with the weak base in the buffer to form a weak acid, which produces few H + ions in solution and therefore only a little change in pH. The strong acid reacts with the weak acid in the buffer to form a weak base, which produces few H+ ions in solution and therefore
What happens when a strong acid reacts with a weak base?
The strong acid reacts with the weak base in the buffer to form a weak acid, which produces few H + ions in solution and therefore only a little change in pH. The strong acid reacts with the weak acid in the buffer to form a weak base, which produces few H+ ions in solution and therefore only a little change in pH.
