
Once implanted, the pacemaker works by monitoring the heart's electrical activity, and deciding whether and when to "pace.". If your heart rate becomes too slow, the device paces by transmitting a tiny electrical signal to the heart muscle, causing it to contract.
What does DDD mean for a pacemaker?
What does DDD mean in pacemaker? DDD = dual-chamber antibradycardia pacing; if atria fails to fire, it is paced. If the ventricle fails to fire after an atrial event (sensed or paced) the ventricle will be paced. DDI = Like above, but the atrial activity is tracked into the ventricle only when the atria is paced.
What to expect during pacemaker?
Possible risks of pacemaker include, but are not limited to, the following:
- Bleeding from the incision or catheter insertion site
- Damage to the vessel at the catheter insertion site
- Infection of the incision or catheter site
- Pneumothorax. If the nearby lung is inadvertently punctured during the procedure, leaking air becomes trapped in the pleural space (outside the lung but within the chest wall); this can cause ...
What are the modes of pacemaker?
There are three basic kinds of pacemakers:
- Single chamber. One lead attaches to the upper or lower heart chamber.
- Dual-chamber. Uses two leads, one for the upper and one for the lower chamber
- Biventricular pacemakers(used in cardiac resynchronization therapy).
What are the different types of pacemakers?
Types
- Single chamber pacemaker. This type usually carries electrical impulses to the right ventricle of your heart.
- Dual chamber pacemaker. This type carries electrical impulses to the right ventricle and the right atrium of your heart to help control the timing of contractions between the two chambers.
- Biventricular pacemaker. ...
What is a DDDR pacemaker?
What is the best pacemaker for sick sinus syndrome?
What is the greatest achievement of the 20th century?
Is a DDDR pacemaker life threatening?
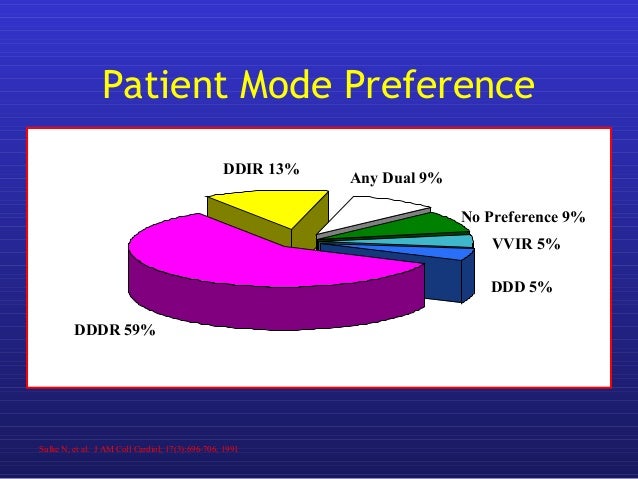
What is Dddr in pacemaker?
The latest cardiac pacing mode to become available is the dual-chamber, rate-modulated mode (referred to as DDDR), which restores both rate responsiveness and atrioventricular synchrony in patients with sinus node dysfunction and atrioventricular block.
What is the difference between DDD and DDDR pacemaker?
The DDD mode will control bradycardia and provide AV synchrony, but will not provide rate adaptation in patients with chronotropic incompetence. The DDDR mode will control bradycardia, maintain AV synchrony, and provide far rate adaptation in the presence of chronotropic incompetence.
When is a DDD pacemaker used?
DDD = dual-chamber antibradycardia pacing; if atria fails to fire, it is paced. If the ventricle fails to fire after an atrial event (sensed or paced) the ventricle will be paced. DDI = Like above, but the atrial activity is tracked into the ventricle only when the atria is paced. DOO = asynchronous A+V pacing.
How many leads are in a DDD pacemaker?
DDD pacemakers consist of two leads--one in the right atrium and one in the right ventricle (Fig. 4). The main indication for a DDD pacemaker is symptomatic failure in AV conduction (AV block °II and °III) in combination with sick sinus syndrome. The majority of newly implanted pacemakers are DDD pacemakers (4).
What is the purpose of Dddr?
Background— Dual-chamber (DDDR) pacing preserves AV synchrony and may reduce heart failure (HF) and atrial fibrillation (AF) compared with ventricular (VVIR) pacing in sinus node dysfunction (SND).
What does code Dddr mean?
Therefore, a pacemaker or ICD that is DDDR means the pacemaker is pacing electrical activity in both the atrium and the ventricle and it is sensing activity in both the atrium and the ventricle.
What are 4 things to be avoided if you have a pacemaker device?
Discuss the following in detail with your doctor:It is generally safe to go through airport or other security detectors. ... Avoid magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) machines or other large magnetic fields. ... Avoid diathermy. ... Turn off large motors, such as cars or boats, when working on them.More items...
What are the 4 types of pacemakers?
After our diagnostic evaluation, we discuss our recommendations with you to choose the right pacemaker for your needs.Single-chamber pacemaker.Dual-chamber pacemaker.Biventricular pacemaker.
What are the 3 types of pacemakers?
TypesSingle chamber pacemaker. This type usually carries electrical impulses to the right ventricle of your heart.Dual chamber pacemaker. ... Biventricular pacemaker.
What are the 3 primary problems that can occur with a pacemaker?
Patients with pacemakers generally face problems that can be grouped into the following categories3:1) Failure to pace the appropriate cardiac chamber: Output failure. Capture failure.2) Problem with detecting intracardiac signals: Undersensing. Oversensing.3) Pseudomalfunction: Crosstalk with resultant safety pacing.
What is the most advanced pacemaker?
Micra — the Newest Generation of Pacemaker Micra is a revolutionary new pacemaker for patients whose heart rhythm dysfunction can be treated by a pacemaker in the right lower chamber of the heart (the right ventricle). It is not appropriate for patients who need two- or three-chamber pacing.
What is a pacemaker with 3 leads called?
A biventricular pacemaker is an implantable device for people with advanced heart failure due to abnormal heart rhythms (arrhythmias) and/or function. The device consists of three wire leads and a pulse generator, which contains a battery and a tiny computer. Healthcare providers implant the device during a procedure.
What are the 3 types of pacemakers?
TypesSingle chamber pacemaker. This type usually carries electrical impulses to the right ventricle of your heart.Dual chamber pacemaker. ... Biventricular pacemaker.
What are the 4 types of pacemakers?
After our diagnostic evaluation, we discuss our recommendations with you to choose the right pacemaker for your needs.Single-chamber pacemaker.Dual-chamber pacemaker.Biventricular pacemaker.
What is a DDD device?
Pacemakers and Implantable Cardioverter–Defibrillators Dual-chamber (DDD) pacemakers have two leads (one in the right atrium, one in the right ventricle), each capable of sensing intrinsic electrical activity to determine the need for pacing in each chamber.
What do the 3 letters of a pacemaker stand for?
Letter 1: chamber that is paced (A = atria, V = ventricles, D = dual-chamber). Letter 2: chamber that is sensed (A = atria, V = ventricles, D = dual-chamber, 0 = none). Letter 3: response to a sensed event (T = triggered, I = inhibited, D = dual - T and I, R = reverse).
What is a DDDR pacemaker?
DDDR pacemaker marks atrial and ventricular rates and senses both chambers of the heart. DDDR pacemaker has a sensor that records a need for higher cardiac output and can regulate the heart rate automatically. If the heart natural pacemaker function is failing, DDDR pacemaker can take over their role and ensure further smooth functioning of the heart. Sometimes they are referred to a dual chamber pacemaker with adaptability, and can be adapted to the special needs of every patient who needs this type of pacemaker.
What is the best pacemaker for sick sinus syndrome?
DDDR pacemaker is recommended for treatment of the patients with any heart rate lower than sixty beats per minute and in patients who have sick sinus syndrome, AV block, or both of them.
What is the greatest achievement of the 20th century?
The therapy for bradycardia with pacemakers remains one of the greatest healthcare accomplishments of the 20th century. Many different types of devices are now on the market as a result of physiological discoveries and advances in engineering.
Is a DDDR pacemaker life threatening?
The majority of DDDR pacemaker system malfunctions are benign, but some can be life threatening such as: collapsed lung, blood building up in the pleural cavity, gas embolism, perforation, dislodgement, diaphragmatic stimulation, pericardial tamponade, hematoma, pacemaker infection, blood clot …
How Does a Pacemaker Work?
After you have a pacemaker, your heart still does all its own work. Rather, the pacemaker merely helps to regulate the timing and sequence of your heartbeat.
How Often Should Your Pacemaker Actually Pace Your Heart?
In the majority of people with pacemakers, the heart's own electrical system is actually generating most of the heartbeats. The pacemaker is there mainly as a "safety valve," to prevent occasional episodes of inappropriate bradycardia.
What Is Life Like With a Pacemaker?
Pacemakers are supposed to prevent or eliminate problems, not create them. And generally, that is what they do. As long as you follow a few simple precautions, avoid electromagnetic interference, and follow your healthcare provider's instructions for having your device checked periodically, you can plan on leading a life that is virtually free of restrictions caused by the pacemaker itself.
What is a pacemaker for heart failure?
These specialized pacemakers—which are called cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) devices —can significantly improve cardiac function and symptoms in many people with heart failure. 1
How many beats per minute does a pacemaker have?
Whenever the patient's own intrinsic heart rate dropped below that pre-set rate (say, 70 beats per minute), the pacemaker would begin to pace at that fixed rate. 3
What is a rate responsive pacemaker?
These pacemakers are called rate-responsive pacemakers. Rate-responsive pacemakers can use one of several technologies to determine the optimal heart rate, but two, in particular, have proven quite useful. One of these is the activity sensor, which detects body movement.
How long does it take for a pacemaker to be implanted?
The leads are threaded through a nearby vein and advanced to the appropriate position within the heart, and their ends are plugged into the generator. The implantation procedure usually takes an hour or more. 1
What is a DDD pacemaker?
DDD and DDDR are the most commonly used pacing modes in dual-chamber pacemakers. Dual-chamber pacemakers can be reprogrammed in a single-chamber mode as well; for example, if the patient develops permanent atrial fibrillation.
What is CRT therapy?
Cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT): biventricular or LV pacing to synchronize RV and LV contractions ( Fig. 97-1 ). With LV pacing alone, LV contraction must be timed with respect to atrial and RV contractions (i.e., RV conduction cannot be delayed).
What is the refractory period after a paced or sensed event?
The atrial channel is refractory after a paced or sensed event during the AV interval. This allows atrial senses occurring in the AV interval to be “seen” but not restart another AV interval. The postventricular atrial refractory period (PVARP) is the period of time after a ventricular pace or sense when the atrial channel is in refractory mode. In other words, atrial senses outside of blanking that occur during this period are “seen” (and marked “AR” on the marker channel) but do not initiate an AV interval. The purpose of PVARP is to avoid allowing retrograde P waves, far-field R waves, or atrial ectopies to start an AV interval, which would cause the pacemaker to pace in the ventricle at a high rate.
Why does automatic mode switching work?
Automatic mode switching changes the pacing mode from DDD to VVIR in response to sensing high atrial rates most often associated with atrial flutter or fibrillation. This functionality prevents ventricular tracking of very high atrial rates, thereby slowing and regularizing the ventricular pacing rhythm. A high number of mode-switch episodes recorded during pacemaker “interrogation” can be a clue that the patient may have developed atrial fibrillation. This finding is very important since the development of atrial fibrillation may have gone unnoticed due to regular heart rate during ventricular pacing.
Why does my pacemaker keep pacing?
A common cause of rapid pacing in a dual-chamber pacemaker capable of tracking the atrium is atrial fibrillation or any rapid atrial rhythm, such as flutter or atrial tachycardia. If automatic mode switching is not programmed (which it routinely should be in any tracking mode), the pacemaker attempts to track the atrium to the upper rate limit if one of these arrhythmias occurs. In some cases, mode switching is programmed on, but does not activate. This occurs with intermittent undersensing of atrial tachyarrhythmias resulting in failure of the pacemaker to detect a sufficient number of atrial events to engage the mode switching algorithm ( Fig. 37-45 ). The sensitivity of the pacemaker should be increased, or if it is already set to the maximum level, the device should be programmed to a nontracking mode (e.g., DDI [R] or VVI [R]).
How does ACM work?
ACM can be programmed to an adaptive setting that provides automatic adaptation of atrial amplitude based on periodic pacing threshold search results. The pacemaker applies a programmable amplitude safety margin to the amplitude threshold value measured at a pulse duration of 0.4 msec to determine the target amplitude. If the operating amplitude is above the target, the pacemaker adapts the amplitude down toward the target in one-step decrements. If the operating amplitude is below the target, the amplitude is immediately adapted to the target. ACM will not provide atrial outputs greater than 5.0 V or 1.0 msec. Atrial capture management has been shown to work well with the automatically determined threshold of 0.68 ± 0.35 V at 0.4 msec compared with 0.69 ± 0.38 V at 0.4 msec measured manually. 254,255 Importantly, atrial capture management worked equally well with epicardial and endocardial leads, probably because it does not rely on distinguishing an ER from polarization. 255
What is the total time that the atrial chamber of the pacemaker is in refractory period?
The total time that the atrial chamber of the pacemaker is in refractory period is during the AV interval and during the PVARP. The total atrial refractory period (TARP) is equal to the SAV interval plus the PVARP. The TARP is important to understand as it defines the highest rate that the pacemaker will track atrial events before 2:1 block occurs.
Why do pacemakers help with fatigue?
Because most of today's pacemakers automatically adjust the heart rate to match the level of physical activity , they may can allow you to resume a more active lifestyle.
Why do you need a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed under the skin in your chest to help control your heartbeat. It's used to help your heart beat more regularly if you have an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), particularly a slow one. Implanting a pacemaker in your chest requires a surgical procedure.
How many wires are in a pacemaker?
Depending on your condition, you may have a pacemaker with one to three flexible, insulated wires (leads) placed in a chamber, or chambers, of your heart. These wires deliver the electrical pulses to adjust your heart rate. Pacemakers are implanted to help control your heartbeat. They can be implanted temporarily to treat a slow heartbeat ...
What is a biventricular pacemaker?
Biventricular pacemaker. Biventricular pacing, also called cardiac resynchronization therapy, is for people with heart failure with abnormal electrical systems. This type of pacemaker stimulates the lower chambers of the heart (the right and left ventricles) to make the heart beat more efficiently.
What is a pacemaker called?
A pacemaker is also called a cardiac pacing device.
How long does it take to get a pacemaker implanted?
You'll likely be awake during the surgery to implant the pacemaker, which typically takes a few hours. You'll have an intravenous line placed, through which you might receive medication to help you relax.
What is an EKG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. Sticky patches (electrodes) are placed on the chest and sometimes the arms and legs. Wires connect the electrodes to a computer, which displays the test results. An ECG can show if the heart is beating too fast, too slow or not at all.
What does the D mean in PM?
Third letter - D - The PM uses the same two leads to sense what is going on with either the Atrial or Ventricular sections. A section of the heart may be either "Triggered" or "Inhibited" when activity is sensed. Here , the D means Dual, but that says that a section of the heart is both triggered AND inhibited. In other words, if native heart electrical activity that will cause normal contraction is sensed for one of the sections, the PM for that section is inhibited (prevented from occurring). Because you do not want TWO pacing signals sent to the section; If no native electrical pacing activity is sensed, you want the heart to contract, so a pacing signal is generated by the PM.
What does the second letter D mean?
Second Letter - D - tells which sections of PM perform Sensing function - D means DUAL, in other words both Atral & Ventricular sections are switched on to provide sensing data to the PM. This is a passive functiion and only tells the PM what the two sections of the heart are doing.
What does the letter D mean in PM?
First letter - D - tells which sections of PM generate pacing signals - D means DUAL , in other words both Atral & Ventricular sections are switched on to provide pacing spikes. (Other choices are A = Atrium; V= ventricles)
What does the fourth letter R mean in a heart rate responsive function?
Fourth letter - R - tells you that the Rate responsive function is turned on or off. R means it is turned on.
What is a DDDR pacemaker?
DDDR pacemaker marks atrial and ventricular rates and senses both chambers of the heart. DDDR pacemaker has a sensor that records a need for higher cardiac output and can regulate the heart rate automatically. If the heart natural pacemaker function is failing, DDDR pacemaker can take over their role and ensure further smooth functioning of the heart. Sometimes they are referred to a dual chamber pacemaker with adaptability, and can be adapted to the special needs of every patient who needs this type of pacemaker.
What is the best pacemaker for sick sinus syndrome?
DDDR pacemaker is recommended for treatment of the patients with any heart rate lower than sixty beats per minute and in patients who have sick sinus syndrome, AV block, or both of them.
What is the greatest achievement of the 20th century?
The therapy for bradycardia with pacemakers remains one of the greatest healthcare accomplishments of the 20th century. Many different types of devices are now on the market as a result of physiological discoveries and advances in engineering.
Is a DDDR pacemaker life threatening?
The majority of DDDR pacemaker system malfunctions are benign, but some can be life threatening such as: collapsed lung, blood building up in the pleural cavity, gas embolism, perforation, dislodgement, diaphragmatic stimulation, pericardial tamponade, hematoma, pacemaker infection, blood clot …

How Pacemakers Work
Types of Pacemakers
- There are a few different types of pacemakers: 1. Transvenous:This is the traditional type of pacemaker. It can be a single-lead or double-lead. It has a pulse generator, wires (leads), and electrodes. The wires are connected to the veins and send pulses to the heart. 2. Biventricular: This type of pacemaker sends pulses to both of the heart's ventricles(bottom chambers) and on…
Pacing and Programming
- Pacing can be done from the right atrium, the right ventricle, or both. When the pacemaker decides that pacing is needed, it prompts the heart chambers to pace. This is called “intelligent pacing” and it helps make sure that the heart rate is meeting the body’s needs and that the heart chambers are working together.1 Pacemakers are also "programmable," and the functions they …
Who Needs A Pacemaker?
- There are a few reasons why the heart might not beat correctly. Pacemakers are commonly used to treat cardiac arrhythmias that cause a person's heartbeat to be too slow (bradycardia). For example, sick sinus syndrome and heart block can cause bradycardia.1 The symptoms of bradycardiainclude weakness, fatigue, lightheadedness, dizziness, or fainting. A pacemaker can …
How Pacemakers Are Placed
- You may get a pacemaker put in if you're having heart surgery. It can also be done as an outpatient procedure with local anesthesia so you don't feel anything and medicine to help you feel relaxed. Here are the steps of placing a pacemaker: 1. First, the generator is put under the skin beneath the collarbone (clavicle). 2. Next, the leads are threaded through a nearby vein and …
What Is Life Like with A Pacemaker?
- Most people with a pacemaker find that it greatly improves their quality of life. They may even live longer with a pacemaker than they would have if they didn't have one. Living with a pacemaker does not exactly have "downsides," but because it is a medical device that uses special technology, there are some things you need to be aware of if you have one. You may need to tak…
Summary
- A pacemaker can be a lifesaving device. Most people who have a pacemaker to help their heart work better feel that it improves their quality of life and they may even live longer than they would have if they didn't have one. Living with a pacemaker does mean you'll have to stay aware of how it's working. If you're noticing signs of a problem with your pacemaker or you've had it for 7 to 1…