
In the labor market, businesses and households meet to transact labor services. Firms represent the demand side, and households represent the supply side. Supply-demand interactions determine the level of wages and employment. Higher salary encourages more labor supply. But, it reduces the demand for labor.
What are the five factors that affect the labor market?
What Factors Affect the Labor Market - WHAT FACTORS AFFECT
- ation, unions, and income inequality as factors that can affect the labor market and economic analysis. ...
- imum. Even so, several factors dictate what businesses end up paying employees. ...
- labor practices will be less likely to take place within the enterprise or company. The workplace atmosphere will move toward a win-win outcome. ...
What factors influence labor demand?
What factors determine the demand for labor?
- Nominal and real nominal wages. Nominal wages are the money wages paid to labour in a given period of time.
- The wage rate.
- Marginal productivity.
- The demand for the products.
- Productivity of labour.
- Profitability of firms.
- Substitutes.
- The number of ‘buyers’ of labour.
How do the laws of supply and demand affect the labor market?
By the laws of supply and demand, the quantity of a good or service supplied (such as labor) rises as the market price rises and falls as the price falls. On the demand side, the quantity of a good or service demanded falls as the price rises. The trick is setting prices (or wages) at just the right level such that supply and demand are equal.
How does the labor market affect business?
The labour market is where businesses hire workers. A business needs people to help the day to day running of the operation. The amount of labour needed depends on whether the business is a labour intensive or capital intensive. A business that needs more people and less machinery is known a labour-intensive business. Hairdressing, house ...

What is labor market and how does it work?
The labor market is where people and employers come together to bargain for labor and wages or other forms of compensation. The number of people willing to work is based upon the level of pay that employers are offering. The higher the wage being offered, the more people will enter the labor market to compete for jobs.
What happens in a labor market?
In the labor market, firms demand labor and individuals such as you and I supply that labor. Employers demand labor because workers are an important part of the production process. Workers use tools and equipment to turn inputs into output.
What is a labor market example?
The labor market or job market is a platform where the demand for (by employers) and supply of (by workers) employment meet....Example #1.ParticularsValueLabor Force Participation Rate (C/B)93.8%Non-Labor Force (B-C)5,000Number of Unemployed (D)4,000Unemployment Rate (D/C)5.3%6 more rows
What determines labor market?
In a competitive labor market, the equilibrium wage and employment level are determined where the market demand for labor equals the market supply of labor. Like all equilibrium prices, the market wage rate is determined through the interaction of supply and demand in the labor market.
Why is the labor market important?
In developing countries, labour markets play a central role in determining economic and social progress since employment status is one of the key determinants of exiting poverty. Ultimately, having a decent, well-paid and secure job is the most sustainable path to increasing incomes and consumption levels.
How does the labour market affect businesses?
High unemployment, though it can be bad for local sales, can provide a business with a good source of cheap labour. On the other hand a shortage of labour might cause difficulties for a business: It may be more difficult to recruit new people - which might prevent the business from growing as fast as it wishes.
What are the types of labor markets?
In general, labor markets vary from job to job. They may be local, regional, or national, both private sector and public sector, including higher education. They may include a broad range of employers or a specific type of employer.
How do you do a labor market analysis?
Identify the area within which employers are competing for labor. Conduct or participate in market surveys within the labor market to determine the salaries being paid for specific positions. Work with management to validate the market areas, market competitors, and job matches (benchmarks).
What are the 4 types of labor?
The Four Types of LaborThe Four Categories of Labor.Proffesional Labor: Examples.Semiskilled Labor: Examples.Unskilled Labor: Examples.Skilled Labor: Examples.
What are four things that are important to know about the labor market?
The labor market comprises four components: the labor force population, applicant population, applicant pool, and the individuals selected.
Who demands labor in the labor market?
The demand and supply of labor are determined in the labor market. The participants in the labor market are workers and firms. Workers supply labor to firms in exchange for wages. Firms demand labor from workers in exchange for wages.
What are characteristics of labour market?
The labour market is characterised by stability and lack of fluidity and diversity of rates for similar jobs. A rise in the price of labour offered by a particular employer does not cause employees of other firms receiving fewer wages to leave their jobs and go to high wage employer.
What is a labor market quizlet?
Definition of Labor Market. usually informal market where workers find paying work, employers find willing workers, and where wage rates are determined.
What are four things that are important to know about the labor market?
The labor market comprises four components: the labor force population, applicant population, applicant pool, and the individuals selected.
What are the five labor market trends?
Five key U.S. labor market trends impacting CRE:Recovering after Severe Impact.Overcoming Labor Shortages & Skill Mismatches.Where have all the Workers Gone.Navigating the Disconnect between Labor & CRE Markets.Identifying Sectors that are Thriving.
What is labor market?
What is the Labor Market? The labor market is the place where the supply and the demand for jobs meet, with the workers or labor providing the services that employers demand. The worker may be anyone who wishes to offer his services for compensation.
What are the components of the labor market?
The labor market comprises four components: the labor force population, applicant population, applicant pool, and the individuals selected. 1. Labor force population. The labor force population or labor force participation refers to the number of individuals who are available to work in a labor market. It considers all workers who are offering ...
What is LMI in economics?
Economic Indicators An economic indicator is a metric used to assess, measure, and evaluate the overall state of health of the macroeconomy. Economic indicators.
What do recruiters look for in a job?
Recruiters look first at the labor market and then look next for individuals who meet the skills and qualifications set for a particular job. For example, the people looking for IT, graphics design, and similar jobs belong to the same applicant population, which is targeted by recruiters looking for this type of professional. 3.
What is labor market analysis?
Generally speaking, labor market analysis involves the following processes: Identifying the various labor markets for a given type of position. It involves looking at the appropriate labor market based on a specific position. Checking the market for salaries for a common position.
What is the second component of the job application?
It considers all workers who are offering their skills and services for employment regardless of the industry they are in. 2. Applicant population. The second component is the applicant population which refers to the people who are applying for a particular job that suits their expertise and skills.
What is replaceable in labor market?
Moreover, they are also replaceable, which means that a person who can do the job better can be tapped to take over the other worker’s job.
How does labor market work?
It’s just that the roles of business and household are reversed. In the goods market, economists use price as the primary determinant of the quantity supplied and the quantity demanded of a good.
What is labor market?
What it is: The labor market is where the demand and supply of labor interact. That is an example of a factor market, which is a market for production factors transactions. In this market, businesses demand labor services offered by households.
What is the role of wages in the labor market?
In the labor market, wages represent labor services’ price and determine the demand and supply of labor. In the labor market, businesses and households meet to transact labor services. Firms represent the demand side, and households represent the supply side. Supply-demand interactions determine the level of wages and employment.
What would happen if you plotted a graph on a labor supply curve?
Thus, instead of increasing supply, higher wage increases lead to a decrease in labor supply. Therefore, if you plotted it on a graph, it would form a backward-bending supply curve of labor. What are the factors that affect the labor market. Apart from wage levels, many factors influence the labor market.
What is equilibrium in the labor market?
Equilibrium in the labor market. As in the product market, the labor market equilibrium occurs when the quantity supplied matches the quantity demanded. At that point, the number of employed workers and the equilibrium wage are determined. A higher wage than the equilibrium wage indicates an excess supply.
What are the factors that affect the shifts in the labor curve?
Meanwhile, shifts in the labor curve are influenced by factors other than wages, such as population, immigration, worker expectations, and income levels. Equilibrium in the labor market.
How does unemployment affect aggregate demand?
Changes in the unemployment rate affect aggregate demand because it impacts the income and consumption of goods and services by the household sector.
What is the labor market?
The labor market or the job market is a widely tracked market that functions through the supply and demand dynamics of people seeking employment (workers) and organizations/people rendering employment (employers). Microeconomics Microeconomics is a study in economics that involves everyday life, including what we see and experience.
Why is labor market important?
A wide range of government decisions is taken based on the shape of labor markets. The labor market is an important gauge of structural changes happening in the economy or industry. It helps policymakers draft and implements new policies if they are aware of the structural trends.
How does the labor market change?
Labor markets change based on the level of economic activity (recessions and booms) and structural changes in the economy (technological changes, change of habits , etc.) The high rate of immigration can distort equilibrium in the market result in high unemployment rates.
What are the advantages of labor market?
Some of the advantages of the labor market are as follows: Labor market and analysis are useful in forming broader level economic policies for the benefit of citizens of the country. A wide range of government decisions is taken based on the shape of labor markets.
What is microeconomics?
Microeconomics Microeconomics is a study in economics that involves everyday life, including what we see and experience. It studies individual behavioural patterns, households and corporates and their policies.
Is labor market applicable in a market dominated by a few employers?
It is not applicable in a market dominated by a few employers or where the normal economic activity if distorted due to extraordinary reasons. Labor markets also do not factor in the role of unpaid labor like unpaid interns, who are employed, not paid but contributing to the economic activity.
Does labor market analysis factor in psychological factors?
Labor market analysis does not factor in the emotional and psychological factors that go into employment or unemployment status of individuals. The analysis is majorly applicable in capitalist countries, where the job market is fairly developed.
How does the labor market work?
The labor market is governed, as we have said, by the guidelines of labor law , that is, the labor laws of each country. This means that, when establishing employment contracts, a series of legal agreements, benefits and individual and collective rights, and even prohibitions, must be taken into account.
Labor market indicators
The relationship between salary and cost of living is one of its indicators.
Labor market conditions
There are different social, economic and even technological elements that condition the performance of the labor market in the countries:
Labor law
The violation of any labor regulation is resolved through judicial mediation.
The workforce
The labor force is understood as the set of physical and mental work capacities available to the people of a country. The total set of its potential workers, employed or not, are the workforce of a nation, which can be well or poorly used by their employers.
Consequences of unemployment
A society with high unemployment rates can increase criminal activities.
The new labor market
The new labor market in the world of the 21st century is governed by new demands, such as specialized, highly technological work . It even usually occurs over long distances, since the Internet makes it possible.
What Does the Labor Market Mean?
The labor market, also called the job market, refers to the supply and demand for employment.
How Does the Labor Market Work?
To understand how the labor market works, let’s examine it from two lenses: macroeconomic and microeconomic levels.
Why Is the Labor Market Important?
Understanding how the labor market works can help employers assess how many employees to hire and how to leverage their skills to win long-term success.
What Does Labor Market Mean?
Like any kind of market, a free, competitive labor market is the most efficient way to allocate labor resources and to establish salaries. Workers offer their skills and organizations offer payment in exchange. The amount and kind of work demanded and supplied at a certain moment is the force that drives results.
Example
Hannah Smith is a young professional recently graduated from college. She was an excellent student that aspired to have a great life in the future thanks to well-remunerated jobs. Hannah told her father that she would demand an annual wage of US$70,000. Her father explained that she is not in total control of her next salary.
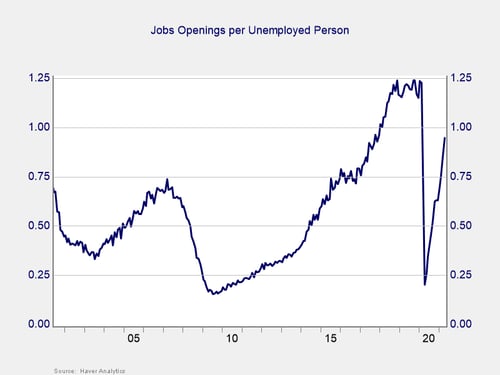
Understanding The Labor Market
- At the macroeconomic level, supply and demand are influenced by domestic and international market dynamics, as well as factors such as immigration, the age of the population, and education levels. Relevant measures include unemployment, productivity, participation rates, tot…
The U.S. Labor Market
- The macroeconomicview of the labor market can be difficult to capture, but a few data points can give investors, economists, and policymakers an idea of its health. The first is unemployment. During times of economic stress, the demand for labor lags behind supply, driving unemployment up. High rates of unemployment exacerbate economic stagnation, contribute to social upheaval…
The Labor Market in Macroeconomic Theory
- According to the macroeconomic theory, the fact that wage growth lags productivity growth indicates that the supply of labor has outpaced demand. When that happens, there is downward pressure on wages, as workers compete for a scarce number of jobs and employers have their pick of the labor force. Conversely, if demand outpaces supply, there is upward pressure on wag…
The Labor Market in Microeconomic Theory
- The microeconomic theory analyzes labor supply and demand at the level of the individual firm and worker.6Supply—or the hours an employee is willing to work—initially increases as wages increase. No workers will work voluntarily for nothing (unpaid interns are, in theory, working to gain experience and increase their desirability to other employers), and more people are willing t…
The Bottom Line
- The labor market is an economic term for the availability and price employment. Like other markets, the price for labor is largely determined by supply and demand, although the labor market is also heavily regulated in many countries.
Components of The Labor Market
- The labor market comprises four components: the labor force population, applicant population, applicant pool, and the individuals selected.
Understanding Labor Market Analysis
- Labor market analysis is an integral part of an organization’s recruitment process because it not only helps it find the most qualified workers for the jobs that it offers but also ensures that it provides a competitive compensation package to its workers. This is important in order for an organization to be able to keep its competent workers and, ...
What Is Labor Market Information (LMI)?
- Labor Market Information (LMI) is basically everything there is to know about a specific labor market. Information about occupations, their locations, wages, supply and demand, and demographicsare all included in the LMI.
How Is The LMI Helpful?
- The LMI is very helpful for people who are looking at getting a job that is sustainable. A worker who looks at the LMI enjoys a higher chance of getting recruited because he or she knows what industries or jobs are exactly looking for. For example, an individual who finds out that the hospitality industryis looking to hire 1,000 food and beverage specialists over the next two year…
Related Readings
- Thank you for reading CFI’s guide on Labor Market. To keep learning and advancing your career, the following CFI resources will be helpful: 1. Economic Indicators 2. Employee Background Check 3. Five Highest Paying Jobs in the Financial Industry 4. Structural Unemployment