A pacemaker is indicated when electrical impulse conduction or formation is dangerously disturbed. The pacemaker rhythm can easily be recognized on the ECG. It shows pacemaker spikes: vertical signals that represent the electrical activity of the pacemaker. Usually these spikes are more visible in unipolar than in bipolar pacing.
Can you do an EKG with a pacemaker?
Most modern devices are capable of transmitting ECG tracings continuously to cloud-based platforms, which enables the clinician to examine intracardiac ECGs at any time. However, most clinicians who encounter patients with pacemakers only have access to conventional surface ECGs.
Is an ECG and EKG the same thing?
There is no difference between an ECG and EKG, except for the spelling. Both ECG and EKG are correct terms, however, in America the procedure is usually referred to as an EKG to distinguish it from the similar sounding abbreviation for the electroencephalogram (EEG), which measures brain electrical waves instead of heart electrical waves.
Can a person with pacemaker use an electric blanket?
Yes, most electrical equipment in the home will not affect your pacemaker as long as they are in good condition and are properly grounded. Televisions, toasters, electric knives, microwaves, electric blankets, fitness wristbands and heart rate monitors are safe to use. Office equipment such as a computer is also safe to use.
What are the complications of a pacemaker?
Complications related to pacemaker surgery or having a pacemaker are uncommon, but could include: Infection near the site in the heart where the device is implanted; Swelling, bruising or bleeding ...
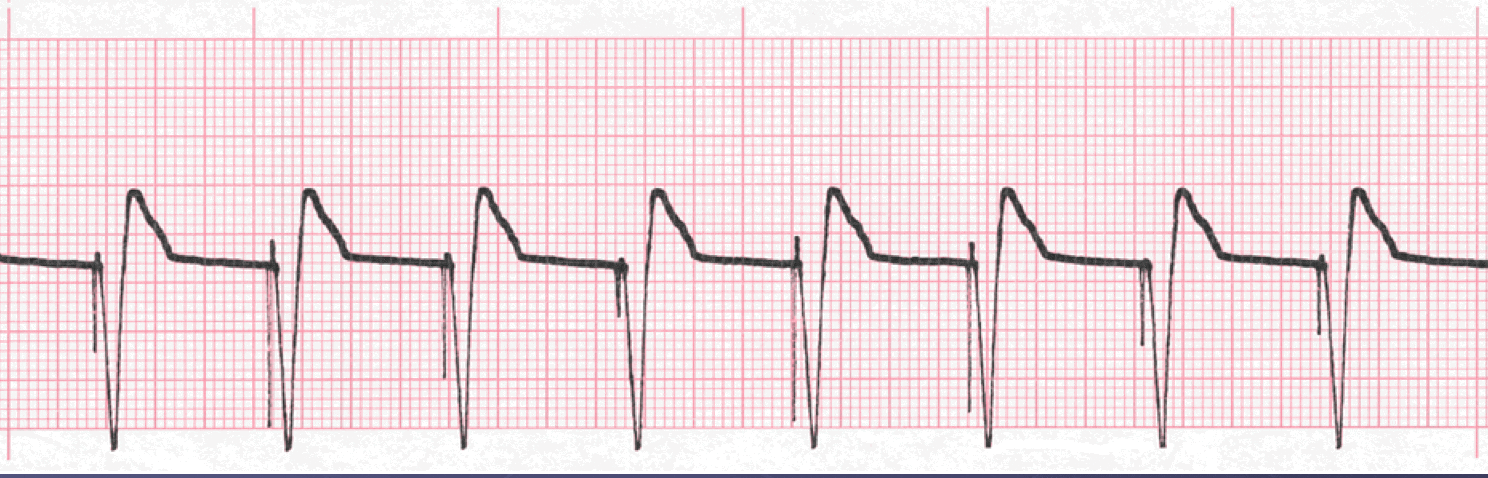
What happens if a pacemaker is not pacing properly?
If the pacemaker is pacing properly, there should be no periods where you see a sinus pause or asystole. The pacemaker should provide an electrical impulse when a set time interval has been reached. If it does not, this is failure to pace (FTP)!
What does it mean when a pacemaker is over sensing?
The pacemaker is over-sensing the rhythm. This means it incorrectly senses things other than a P or QRS and is being tricked into thinking the native rhythm is okay (e.g. seeing a T wave and thinking it is the QRS complex). As a result, it doesn’t fire a pacing spike when it should leading to FTP!
What does it mean when your pacemaker isn't sensing myocardial depolarization?
If your intrinsic cardiac rhythm is appropriate, your pacemaker should just sit back and relax. If you start seeing paced spikes during normal cardiac activity , this means the pacemaker isn’t sensing myocardial depolarization and thus is failing to sense (or under-sensing) the native rhythm!
What is a pacemaker box?
A pacemaker consists of a box (i.e. the pacemaker or pulse generator) and a lead or leads. When it malfunctions, the issue is with rate, pacing, capturing (i.e. delivering the spike to depolarize the myocardium), or sensing [1].
What is the purpose of ECG?
The purpose of the following steps is to provide the emergency physician with a simple way to approach pacemaker malfunction. An ECG is a helpful initial test in determining the cause of pacemaker malfunction. It is important to note that this diagnostic dilemma will often still require the help of our cardiology colleagues.
What is the pattern of a lead in the right ventricle?
If a lead is in the right ventricle (RV), it produces a left bundle branch block (LBBB) pattern on ECG, as the paced beat depolarizes across the myocardium. If, on the other hand, the lead is in the LV, it will produce a right bundle branch block (RBBB) pattern.
Can you interpret pacemaker ECGs?
It is important to go through a consistent approach when interpreting pacemaker ECGs, ideally the same one you use for non-paced ECGs. This way you won’t get distracted by a wide QRS following a pacing spike and miss something like ST elevation.
Why do pacemakers help with fatigue?
Because most of today's pacemakers automatically adjust the heart rate to match the level of physical activity , they may can allow you to resume a more active lifestyle.
Why do you need a pacemaker?
A pacemaker is a small device that's placed under the skin in your chest to help control your heartbeat. It's used to help your heart beat more regularly if you have an irregular heartbeat (arrhythmia), particularly a slow one. Implanting a pacemaker in your chest requires a surgical procedure.
How many wires are in a pacemaker?
Depending on your condition, you may have a pacemaker with one to three flexible, insulated wires (leads) placed in a chamber, or chambers, of your heart. These wires deliver the electrical pulses to adjust your heart rate. Pacemakers are implanted to help control your heartbeat. They can be implanted temporarily to treat a slow heartbeat ...
What is a biventricular pacemaker?
Biventricular pacemaker. Biventricular pacing, also called cardiac resynchronization therapy, is for people with heart failure with abnormal electrical systems. This type of pacemaker stimulates the lower chambers of the heart (the right and left ventricles) to make the heart beat more efficiently.
What is a pacemaker called?
A pacemaker is also called a cardiac pacing device.
How long does it take to get a pacemaker implanted?
You'll likely be awake during the surgery to implant the pacemaker, which typically takes a few hours. You'll have an intravenous line placed, through which you might receive medication to help you relax.
What is an EKG test?
Electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG). This quick and painless test measures the electrical activity of the heart. Sticky patches (electrodes) are placed on the chest and sometimes the arms and legs. Wires connect the electrodes to a computer, which displays the test results. An ECG can show if the heart is beating too fast, too slow or not at all.
How does a pacemaker work?
Upon sensing intrinsic atrial activity, the pacemaker stimulates the ventricle after a time delay in order to mimic the physiological delay in the AV node. Triggering allows for the ventricles to follow atrial activity, which is desirable.
What does a pacemaker sense?
Sensing. The pacemaker can record intrinsic cardiac activity and response appropriately. Specifically, the pacemakers sense intrinsic depolarizations. Depolarizations are represented by the P-wave (atrial lead) and QRS complex (ventricular lead). T-waves reflect repolarization and should not be sensed by the pacemaker.
What happens if the ventricular rate is slower than the base rate?
If atrial activity is slower than the basic rate of the pacemaker, then the pacemaker will pace. A VVI pacemaker stimulates and senses in the chamber and if it senses spontaneous ventricular activity (R-wave), it does not stimulate. If the ventricular rate is slower than the base rate, then the pacemaker will pace.
Why is a pacemaker called asynchronous pacing?
This is called asynchronous pacing because it is not synchronized with intrinsic cardiac activity. Similarly, VOO provides asynchronous pacing in the ventricle, and DOO provides asynchronous pacing in the atria and ventricles.
Why is asynchronous pacing important?
Then asynchronous pacing is suitable because it stimulates at a fixed rate and ignores the signals of the surrounding. Asynchronous pacing also sets in when the battery is drained, or when a pacemaker magnet is placed on the can (note that the effect of a pacemaker magnet may vary according to the manufacturer).
What is a dual chamber pacemaker?
Nowadays, most implanted pacemakers are dual-chamber systems, meaning that two leads are used: one in the atrium and one in the ventricle. Dual-chamber systems offer the possibility of sensing and pacing in both the atria and ventricles.
Where is the lead placed in a biventricular pacemaker?
In biventricular pacemakers, the additional lead is placed in the coronary sinus, from where it stimulates the left ventricle (Figure 5). The term cardiac resynchronization therapy (CRT) is synonymous with biventricular pacing. CRT reduces heart failure symptoms and prolongs survival.
Why is there a delay after a pacemaker senses the atrial beat?
The reason that the interval following a sensed atrial beat is that there is a time delay between when the pacemaker senses the atrial activity. When atrial activity is sensed, atrial contraction is likely to have begun. Rate hysteresis is present when the pacemaker escape interval is longer than the pacing interval.
Why is the magnitude of the spike from unipolar pacemakers larger?
Because of the greater distance between the two electrodes and therefore the bigger the dipole, the magnitude of the spike from unipolar pacemakers is larger.
What does the left axis deviation mean in a VVI pacemaker?
VVI pacemaker rhythm. Note the LBBB morphology with left axis deviation indicating the pacing lead in the right ventricular apex.
What happens if the atrial potential is inadequate?
If the atrial potential is inadequate or absent within a preset interval, then the pacemaker becomes an asynchronous ventricular pacemaker.
Why is ventricular pacing inhibited by the native QRS interval?
uncommitted: ventricular pacing is inhibited by the native QRS interval if the spontaneous AV conduction time is shorter than the programmed pacemaker AV interval.
What happens if a supraventricular beat is above a preset level?
If conducted supraventricular beats occur at a rate above a preset level, all activities of the pacemaker are suppressed.
What can be applied to a pacer to convert it to fixed rate mode?
If the patient's rate is too rapid, then a magnet can be applied to convert the pacer to a fixed-rate mode.

Overview
Why It's Done
- A pacemaker consists of a box (i.e. the pacemaker or pulse generator) and a lead or leads. When it malfunctions, the issue is with rate, pacing, capturing (i.e. delivering the spike to depolarize the myocardium), or sensing . It is important to go through a consistent approach when interpreting pacemaker ECGs, ideally the same one you use for non-p...
Risks
How You Prepare
What You Can Expect
Results
Clinical Trials
- Complications related to pacemaker surgery or having a pacemaker are uncommon, but could include: 1. Infection near the site in the heart where the device is implanted 2. Swelling, bruising or bleeding at the pacemaker site, especially if you take blood thinners 3. Blood clots (thromboembolism) near the pacemaker site 4. Damage to blood vessels or nerves near the pac…