Accumulators have a metering ejector device that picks up liquid, vaporizes it, and returns it to the compressor. This prevents liquid slugging and controls oil return. It is particularly important on hot gas defrost systems, heat pumps, etc., where surges of liquid refrigerant frequently go back down the suction line.
How does an AC accumulator work?
An AC accumulator is used to collect and store any liquid refrigerant that may flow out of the evaporator coil. Since liquids cannot be compressed, it’s critical that only refrigerant gas enters the AC compressor. The accumulator allows only a regulated amount of refrigerant oil and refrigerant gas to enter the AC compressor.
What is a suction accumulator on a refrigerator?
Suction Accumulators A suction accumulator is used to prevent liquid refrigerant floodback to the compressor. A compressor is designed to move vapor refrigerant, NOT liquid, and the accumulator can really help us win that battle.
What is a vertical accumulator on a refrigeration compressor?
Figure 1. A vertical accumulator. (Figures courtesy of Henry Technologies.) The refrigeration compressor is designed to compress vapor only. A suction line accumulator prevents compressor damage from a sudden surge of liquid refrigerant and oil that could enter the compressor from the suction line.
Why is a vertical accumulator used in a defrost system?
It is particularly important on hot gas defrost systems, heat pumps, etc., where surges of liquid refrigerant frequently go back down the suction line. Vertical accumulators use a U-tube or tube-within-a-tube design to draw gaseous refrigerant off the top of the vessel.
Where does the accumulator go?
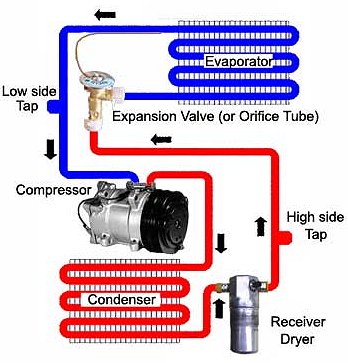
The accumulator contains a desiccant that absorbs moisture. The accumulator is located on the "suction" or "low-pressure side" of the AC system, between the evaporator and the compressor. The construction of an accumulator includes an inlet tube and outlet tube.
What is the difference between an accumulator and a receiver?
Your car may have either a receiver/dryer or accumulator, depending on the model of your vehicle. A receiver/dryer is used on vehicles that have a thermal expansion valve. Accumulators are in vehicles that have an orifice tube. The receiver/dryer is responsible for separating gas from liquid.
How do you know if an accumulator is bad?
Rattling noises during operation. One of the first warning signs that an accumulator has failed is a rattling noise when the AC is turned on. ... Noticeable refrigerant leaks. Another more obvious and more serious sign that an accumulator has failed is a visible refrigerant leak. ... Moldy smell when the AC is on.
What happens to liquid refrigerant in the suction accumulator?
The liquid refrigerant is temporarily held in the suction accumulator and metered back to the compressor at a controlled rate, through the metering orifice.
What is a AC accumulator?
The AC accumulator is a cylindrical component that functions as a filter for the AC system. It's mainly made up of pipes that work towards protecting the other parts of the air conditioning system. A typical AC accumulator consists of an input port and an output port.
Which AC system uses an accumulator?
A/C Accumulator Function Accumulators are used on (FOT)fixed orifice tube systems. They collect the excess liquid that may leave the evaporator's outlet tube. Compressors are incapable of compressing liquid.
What causes accumulator failure?
A failure of the pressure accumulator occurs when there no longer is sufficient pressure within the system. A lack of pressure is typically due to a leak or a hole in one of the parts of the pressure accumulator, like the chambers or hydraulic lines.
How do I test an accumulator?
Finally, a quick method to check accumulator charge is to shut off the supply pump. If the accumulator stays charged, slowly open the drain valve and watch the rate of pressure reduction. When the pressure suddenly drops to zero, this is the pre-charge of the accumulator.
When should the accumulator be replaced with a new one?
How often should my accumulators be serviced? The European Pressure Equipment Directive 2014-68-EU advises that accumulators need to be re-certified or replaced after 5 years.
What is the purpose of a suction accumulator?
The function of a suction line accumulator in a heat pump or refrigeration system is to catch and hold any unused portion of the system charge. The device must also prevent liquid slugging of the compressor and excessive refrigerant dilution of the compressor oil.
What is slugging a compressor?
Slugging is a short-term return of a mass of liquid, consisting of refrigerant or oil, or as a mixture of both. The slug enters the cylinders of the compressor instead of super-heated vapor. Slugging almost always occurs on startup, but a very rapid change in system operating conditions can also cause slugging.
What happens if liquid enters compressor?
In reciprocating compressors, when a large volume of liquid appears inside the cylinder, and the piston cannot expel it through the discharge valve during the short duration when it is open, it leads to excessive pressure buildup inside the cylinder.
What is an AC accumulator?
An AC accumulator is used to collect and store any liquid refrigerant that may flow out of the evaporator coil. Since liquids cannot be compressed, it’s critical that only refrigerant gas enters the AC compressor. The accumulator allows only a regulated amount of refrigerant oil and refrigerant gas to enter the AC compressor. ...
Where is the AC accumulator located?
The AC accumulator is located on the outlet tube of the evaporator coil, usually in the engine compartment and near the firewall. AC accumulator in engine compartment near the firewall.
What happens when a refrigerant is saturated with moisture?
When it’s saturated with moisture, the entire accumulator must be replaced. See the image below.
Why is my AC system open to the atmosphere?
Also, if the AC system is open to the atmosphere due to a broken hose or leaking evaporator or condenser, the desiccant bag in the accumulator can soak up too much moisture, rendering it useless. Most compressor manufacturers’ warranty terms require the installation of a new accumulator any time the compressor is replaced.
Where is the inlet of a compressor?
The inlet to the U-shaped tube is located near the top of the accumulator so it can’t suck any liquid refrigerant into the compressor. The tube contains an oil suction hole at the base. At the bottom of the accumulator, the liquid refrigerant contacts a bag of desiccant.
Where does oil go when it enters the accumulator?
As liquid refrigerant and oil enter the accumulator inlet, they hit a baffle near the top that distributes the oil and liquid to the sides of the accumulator, where it falls to the bottom. A U-shaped tube is attached to the outlet of the accumulator.
Can you use an accumulator on an AC?
Accumulators are only used on orifice tube style automotive AC systems. Orifice tube systems often don’t fully convert liquid refrigerant to a gas, which means liquid refrigerant could leave the evaporator and flow into the compressor, destroying it.
Bladder Accumulator Type
In this type of accumulator hydraulic fluid compresses a nitrogen-filled bladder to create pressure.
Piston Accumulator Type
In this type of accumulator, pressure is created when nitrogen is compressed in a thin-walled metal cylinder shell by the hydraulic fluid pushing on a metal piston. Advantage: Virtually no nitrogen escapes so they will not have to be recharged. Disadvantage: A bit heavier, and less efficient than the bladder model.
How much refrigerant can an accumulator hold?
The accumulator is too small to catch all of the refrigerant. Double-check to make sure that the accumulator can hold 50% of the system charge. Also check to make sure that there is sufficient superheat on each evaporator.
Why does my accumulator meter back more refrigerant?
This problem will cause the orifice to meter back more refrigerant due to the increased gas flow past the orifice. Double-check the sizing of the accumulator, ensuring that the tonnage is not above the maximum capacity.
What happens if a fusible element leaks?
On accumulators with fusible elements, if the fusible element leaks, the accumulator must be replaced. The fusible element is a UL requirement for venting of gas during a fire to prevent rescue personnel from injury due to a tank rupture.
How does a heat exchanger work?
The heat exchanger can be used on low-temperature systems to subcool the liquid line while helping to boil off liquid refrigerant in the accumulator by passing the liquid line through the heat exchanger coil. This can increase system efficiency while helping oil flow in the suction line. Do not use discharge gas through ...
How does an orifice work in a U tube?
At the bottom of the U-tube, an orifice picks up a small amount of oil and liquid refrigerant and meters it back with the gaseous refrigerant. The small amount of liquid refrigerant will boil off in the suction line. The oil will be carried with the gaseous refrigerant back to the compressors.
Why is a vertical accumulator important?
This prevents liquid slugging and controls oil return. It is particularly important on hot gas defrost systems, heat pumps, etc., where surges of liquid refrigerant frequently go back down the suction line. Vertical accumulators use a U-tube or tube-within-a-tube design to draw gaseous refrigerant off the top of the vessel.
Why is oil not returned in a horizontal accumulator?
If a horizontal accumulator is used on a system in which the evaporator temperature is too low, oil will not be returned in sufficient quantity due to the sluggish flow at colder temperatures. A heat band may help in this case, but if oil return continues to be a problem, replace the accumulator with a vertical model.
Why do accumulators have connections?
Some accumulators have connections so that a liquid line loop can be piped into the bottom of the accumulator. This improves the system's performance by subcooling the liquid refrigerant and protects the compressor against liquid slugging by providing additional superheat to the suction gas. —Louie Molenda. Share this:
Why do you flush an accumulator?
Accumulators need to be kept clean and free of debris, or that screen at the bottom of the U-bend can potentially block as well, which is why the accumulator should be emptied and flushed when a system has a significant burnout or another type of contamination event.
What is a suction accumulator?
A suction accumulator is used to prevent liquid refrigerant floodback to the compressor. A compressor is designed to move vapor refrigerant, NOT liquid, and the accumulator can really help us win that battle.
What is hydraulic accumulator?
Hydraulic accumulators are energy storage devices. Analogous to rechargeable batteries in electrical systems, they store and discharge energy in the form of pressurized fluid and are often used to improve hydraulic-system efficiency. An accumulator itself is a pressure vessel that holds hydraulic fluid and a compressible gas, typically nitrogen.
Why are accumulators used in shocks?
They also enjoy wider mounting flexibility, are insensitive to contamination and quickly respond to changes in pressures, making them suited for shock applications. Accumulators store energy that can be used to supplement pump flow, improve system response or serve as a back-up during power failure.
What is a piston accumulator?
Similar to other accumulators, a typical piston accumulator consists of a fluid section and gas section, with the movable piston separating the two. Less common are piston accumulators that replace high-pressure gas with a spring or heavy weight to apply force to the piston.
How much volume can a diaphragm accumulator hold?
A diaphragm accumulator can handle higher compression ratios of up to 8 to 10:1 because the rubber barrier does not distort to the same degree as a bladder.
How many gallons of water should a piston accumulator hold?
Piston accumulators are generally recommended for large stored volumes—to 100 gallons or more—and can have high flow rates. Pressure ratio is limited only by the design, but they’re usually not recommended for shock applications. They are often built for rugged, heavy-duty applications.
What is the housing of a hydropneumatic unit made of?
The housing or shell is made of materials like steel, stainless steel, aluminum, titanium and fiber-reinforced composites. Inside, a moveable or flexible barrier—usually a piston or rubber bladder—separates the oil from the gas. In these hydropneumatic units, hydraulic fluids only compress slightly under pressure.
Can a piston accumulator be replaced?
They come in a wide range of standard sizes, and good response characteristics make them well suited for shock applications. Depending on the design, a bladder can be easily replaced in the event of failure or damage. A piston accumulator is much like a hydraulic cylinder without a rod.
