(4) Acetylcholine binds to postsynaptic receptors. (5) This binding causes ion channels to open and allows sodium ions to flow into the muscle cell. (6) The flow of sodium ions across the membrane into the muscle cell generates an action potential which induces muscle contraction.
How to increase acetylcholine levels naturally?
- Meditate
- Practice deep breathing
- Do Yoga
- Listen to calming music
What is the mechanism of action of acetylcholine?
Functions of acetylcholine
- Motor functions. It is probably the most important activity of acetylcholine. ...
- Neuroendocrine functions. Another key function of acetylcholine is to increase the secretion of vasopressin by stimulation of the posterior lobe of the hypophysis .
- Parasympathetic functions. ...
- Sensory functions. ...
- Cognitive functions. ...
Is too much acetylcholine bad?
Too high acetylcholine primarily operates by inhibiting other neurotransmitters. The symptoms of too high acetylcholine may be similar to the symptoms of too low serotonin, as they have a close balancing relationship. Once we have identified potential neurotransmitter imbalances, it is time to treat them.
What are the benefits of acetylcholine?
- Cognitive Enhancement
- Optimizing Cognitive Performance
- How to Get Rid of Brain Fog
- How to Improve Memory
- Best Brain Exercises for Memory
- How to Focus Better
- How to Improve Brain Function
- How to Improve Cognitive Function
- How to Improve Mental Performance
- How to Improve Mental Alertness
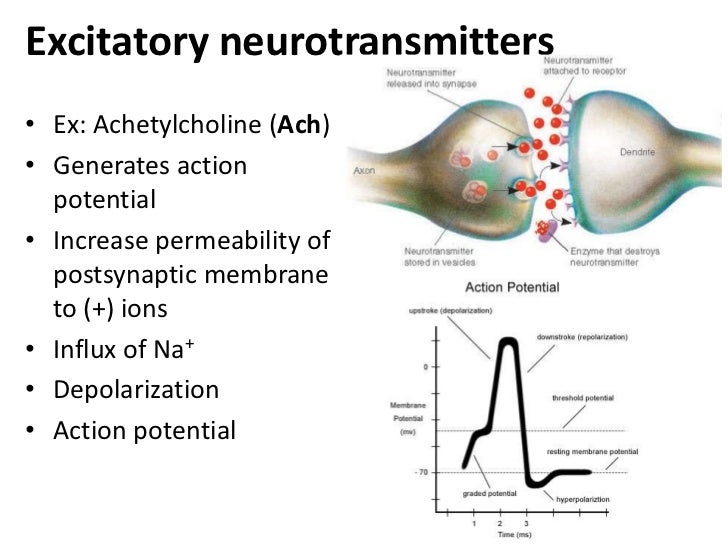
How does acetylcholine cause action potential?
1:011:562-Minute Neuroscience: Neuromuscular Junction - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipWhen an action potential travels down the motor neuron it causes the release of acetylcholine intoMoreWhen an action potential travels down the motor neuron it causes the release of acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft acetylcholine binds to acetylcholine receptors.
How do acetylcholine receptors trigger an electrical impulse?
When acetylcholine binds to its receptor, it causes a change in the protein structure, opening a channel through which Na+ ions4 move (with the concentration gradient) inside the cell. The influx of Na+ generates a membrane current that triggers a new electrical impulse (Figure 5).
How does acetylcholine cause depolarisation?
Acetylcholine is a neurotransmitter at various synapses, nerves, and at the motor end plate of vertebrate muscles. When a nerve impulse arrives at the nerve ending, acetylcholine stored in vesicles, is released, and binds to a postsynaptic receptor, causing depolarization.
How does ACh stimulate the production of action potentials in skeletal muscle fibers?
Skeletal muscle contraction and changes with exercise. (A) Neurotransmitter (acetylcholine, ACh) released from nerve endings binds to receptors (AChRs) on the muscle surface. The ensuing depolarization causes sodium channels to open, which elicits an action potential that propagates along the cell.
How does acetylcholine work in the nervous system?
In the somatic nervous system, acetylcholine is used at the neuromuscular junctions, triggering the firing of motor neurons and affecting voluntary movements.
What happens when acetylcholine stimulates its receptors?
What happens when acetylcholine stimulates its receptors in the neuromuscular junction? The release of Ca2+ from the sarcoplasmic reticulum decreases. The permeability of the sarcolemma to Na+ increases.
What happens to acetylcholine after the action potential passes?
After the arrival of an action potential, vesicles containing acetylcholine fuse with the presynaptic membrane and release acetylcholine into the synaptic cleft.
Is acetylcholine sympathetic or parasympathetic?
Acetylcholine is the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system (a branch of the peripheral nervous system) that contracts smooth muscles, dilates blood vessels, increases bodily secretions, and slows heart rate.
Is acetylcholine excitatory or inhibitory?
excitatoryThe neurotransmitter acetylcholine is excitatory at the neuromuscular junction in skeletal muscle, causing the muscle to contract. In contrast, it is inhibitory in the heart, where it slows heart rate.
How is muscle action potential generated?
A skeletal muscle action potential is generated when the motor endplate potential is sufficient to raise the surrounding sarcolemmal potential above the threshold for activation of the voltage gated Na+ channels that are abundant throughout the sarcolemma.
What triggers muscle action potential?
1. A Muscle Contraction Is Triggered When an Action Potential Travels Along the Nerves to the Muscles. Muscle contraction begins when the nervous system generates a signal. The signal, an impulse called an action potential, travels through a type of nerve cell called a motor neuron.
What initiates action potential on a muscle cell?
ACh binds to the nicotinic receptors located at the motor endplate, depolarizing it, which initiates the action potentials in the muscle fiber.
What causes electrical impulses in the brain?
Neurons conduct electrical impulses by using the Action Potential. This phenomenon is generated through the flow of positively charged ions across the neuronal membrane.
What is the role of acetylcholine in a neuron to neuron synapse?
We propose that the role of ACh as a neuromodulator in the brain is to increase neurotransmitter release in response to other inputs, to promote burst firing and/or suppress tonic firing, depending upon the system and the neuronal subtypes stimulated. Further, ACh contributes to synaptic plasticity in many brain areas.
How are nerve impulses initiated?
A nerve impulse begins when a neuron receives a chemical stimulus. The nerve impulse travels down the axon membrane as an electrical action potential to the axon terminal. The axon terminal releases neurotransmitters that carry the nerve impulse to the next cell.
How does nerve impulse get generated and conducted in the human body?
A nerve impulse is generated when the stimulus is strong. This stimulus triggers the electrical and chemical changes in the neuron. As mentioned already there are different ions on either side of the cell membrane. The exterior side has sodium ions that are positively charged and are more in number.
1. When acetylcholine is increased, what happens?
By inhibiting the acetylcholinesterase enzyme, several ACh receptor agonists function indirectly. Continuous stimulation of the muscles, glands, an...
2. What is the acetylcholine antagonist?
In the parasympathetic nervous system, Atropine, an antagonist of muscarinic ACh receptors, decreases the parasympathetic activity of muscles and g...
3. How does the heart rate decrease with acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine's binding to M2 receptors slows the heart rate until it reaches a natural sinus rhythm. This is accomplished by slowing the rate of d...
What receptors does acetylcholine work on?
Acetylcholine also works on cholinergic muscarinic receptors in organ systems to stimulate secretions by all glands receptive to parasympathetic nerve impulses. 7
What neurotransmitter is released when your heart rate increases?
Acetylcholine is the predominant neurotransmitter in the parasympathetic nervous system. When your heart rate increases beyond what's normal, acetylcholine is released to slow your heart rate and contractions until it goes back to baseline. 6
Why should anticholinergics be avoided?
Anticholinergics have shown cognitive slowing effects and should be avoided in people over 70 due to the risk of confusion or hallucination. 10
What is the function of acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine sends messages along nerve cells through the nervous systems. All of your body’s movements depend on this communication. This means any disruption to acetylcholine functioning compromises this process and can result in illness.
What neurotransmitter is involved in muscle movement?
Acetylcholine plays an important role in muscle actions, so any drugs that influence this neurotransmitter can cause movement disruption and even paralysis.
What is the role of acetylcholine in blood pressure?
Acetylcholine plays a role in regulating blood pressure. When blood flows, it creates friction that can be seen on image signaling technology focusing on the endothelium, the cell barrier between your blood and blood vessel wall.
Why is acetylcholine important?
Acetylcholine is critical in the healthy functioning of your heart. It helps to regulate your heartbeat, blood pressure, and heart muscle contractions.
How does acetylcholine work?
As we have seen, in the mammalian brain information between neurons is transmitted through a chemical called the neurotransmitter.
What is a neurotransmitter?
Neurotransmitters are biomolecules that transmit information from one neuron to another neuron in a row.
How does a neurotransmitter work?
When the synapse occurs, a neurotransmitter is released by the vesicles at the tip of the presynaptic neuron (the one that emits the information).
What happens when the action potential of acetylcholine is released?
And is that for the acetylcholine to be released, an action potential must reach the nerve terminal in which the neurotransmitter is . When this happens, the same action potential generates a membrane potential, a fact that motivates the activation of the calcium channels. Due to the electrochemical gradient, an influx of calcium ions is generated ...
What is the oldest substance in the brain?
It was the first isolated neurotransmitter, conceptualized and characterized, so according to many scientists is the"oldest"substance of the brain. Acetylcholine was pharmacologically described by Henry Hallet Delt in 1914 and was later confirmed by Otto Loewi as a neurotransmitter. The main activity of acetylcholine lies in the cholinergic system, ...
What is a segregated neurotransmitter?
The segregated neurotransmitter acts in specialized and highly selective receptor sites, thus, as different types of neurotransmitters exist, each acts on certain systems.
Where are acetylcholine and cholinergic found?
These three elements are found in the specific regions of the brain where acetylcholine will be produced, which is why acetylcholine makes a neurotransmitter belonging to a specific system, the cholinergic system. When in a neuron we find these three substances that we just mentioned, we know that it consists of a cholinergic neuron and ...
Do You Know?
Acetylcholine is synthesized from the compounds choline and acetyl-CoA by the enzyme choline acetyltransferase in some neurons. Cholinergic neurons have the capacity to generate ACh. An example of a central cholinergic area is the nucleus basalis of Meynert in the basal forebrain. The enzyme acetylcholinesterase converts acetylcholine into the inactive metabolites choline and acetate. In the synaptic cleft, this enzyme is abundant, and its role is important for proper muscle function in rapidly clearing free acetylcholine from the synapse. Some neurotoxins function by inhibiting acetylcholinesterase, thus leading to excess neuromuscular junction acetylcholine.
What is the chemical structure of acetylcholine?
Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an acetic acid and choline ester. Sections of the body that use or are influenced by acetylcholine are considered cholinergic elements. Cholinergic and anticholinergics, respectively, are called substances that increase or decrease the overall cholinergic system function.
What is the role of acetylcholine in the brain?
There are a variety of cholinergic areas in the brain, each with different roles, such as playing an important role in excitement, concentration, memory, and motivation. It is believed to play a major role in memory and learning, and in the brain ...
What system does acetylcholine affect?
Acetylcholine tends to have several functions in the central nervous system.
Which neurotransmitter decreases parasympathetic activity?
In the parasympathetic nervous system, Atropine, an antagonist of muscarinic ACh receptors, decreases the parasympathetic activity of muscles and glands. Neostigmine is an indirect agonist of the ACh receptor that inhibits acetylcholinesterase, preventing acetylcholine breakdown.
What is acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine (ACh) is an organic chemical that acts as a neurotransmitter in the brain and body of several animal types (including humans), a chemical message produced by nerve cells to send signals to other cells, such as neurons, muscle cells, and cells of the gland. Its name derives from its chemical structure: it is an ...
Where does acetylcholine enter the neuromuscular junction?
In the peripheral nervous system, acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction when a nerve impulse arrives at the terminal of a motor neuron. There, it interacts with a receptor molecule in a muscle fiber’s postsynaptic membrane (or end-plate membrane).
How does acetylcholine affect the nervous system?
Within the autonomic nervous system, acetylcholine behaves in a similar manner, being discharged from the terminal of one neuron and binding to receptors on the postsynaptic membrane of other cells. Its activities within the autonomic nervous system affect a number of body systems, including the cardiovascular system, where it acts as a vasodilator, decreases heart rate, and decreases heart muscle contraction. In the gastrointestinal system, it acts to increase peristalsis in the stomach and the amplitude of digestive contractions. In the urinary tract, its activity decreases the capacity of the bladder and increases voluntary voiding pressure. It also affects the respiratory system and stimulates secretion by all glands that receive parasympathetic nerve impulses. In the central nervous system, acetylcholine appears to have multiple roles. It is known to play an important role in memory and learning and is in abnormally short supply in the brains of persons with Alzheimer disease.
What is the purpose of acetylcholine?
acetylcholine, an ester of choline and acetic acid that serves as a transmitter substance of nerve impulses within the central and peripheral nervous systems. Acetylcholine is the chief neurotransmitter of the parasympathetic nervous system, the part of the autonomic nervous system (a branch of the peripheral nervous system) ...
How many molecules are in the nerve terminal?
The nerve terminal contains many small vesicles (membrane-enclosed structures) about 50 nm in diameter, each of which contains 5,000–10,000 molecules of acetylcholine. Mitochondria are also present, providing a source of energy in the form of ATP. Acetylcholine is formed in…
Where is acetylcholine stored?
Acetylcholine is stored in vesicles at the ends of cholinergic (acetylcholine-producing) neurons. In the peripheral nervous system, when a nerve impulse arrives at the terminal of a motor neuron, acetylcholine is released into the neuromuscular junction. There it combines with a receptor molecule in the postsynaptic membrane (or end-plate membrane) ...
What is the nicotinic acetylcholine receptor?
The nicotinic acetylcholine receptor is an example of a ligand-gated ion channel. It is composed of five subunits arranged symmetrically around a central conducting pore. Upon binding acetylcholine, the channel opens and allows diffusion of sodium (Na +) and potassium (K +) ions through the conducting pore. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.
What enzyme destroys acetylcholine?
Acetylcholine is rapidly destroyed by the enzyme acetylcholinesterase and thus is effective only briefly. Inhibitors of the enzyme (drugs known as anticholinesterases) prolong the lifetime of acetylcholine.
When was acetylcholine first discovered?
Naturally occurring acetylcholine was first isolated in 1913 by English chemist Arthur James Ewins, at the urging of his colleague, physiologist Sir Henry Dale, who in 1914 described the chemical’s actions. The functional significance of acetylcholine was first established about 1921 by German physiologist Otto Loewi.
Which neuron reabsorbs the neurotransmitter for reuse?
b. The sending neuron reabsorbs the neurotransmitter for reuse.
What does it mean to be able to name the parts of the brain?
e. "Being able to name the parts of the brain helps us understand the basis of behavior."
What is Professor Seif's research interest?
Her research interests best represent the psychological specialty known as
What is the mind pumping into the body?
b. The mind pumps warmth and vitality into the body.
Which sheath absorbs the excess neurotransmitters?
c. The myelin sheath absorbs the excess neurotransmitters.
Which cells release neurotransmitters into the axon?
e. Glial cells must release neurotransmitters into the axon.
Do serotonin and dopamine have to be present in equal amounts?
a. Dopamine and serotonin must be present in equal amounts .
Which ventricle is the vagal input?
vagal input to the mammalian ventricle was both
Does acetylcholine alter the action potential duration?
acetylcholine did not alter action potential duration In ventricula. r muscle from cats after bilateral
Which nervous system is involved in the regula- tion?
the parasympathetic nervous system in the regula-
Is muscarinic cholinergic stimulation a response?
response to muscarinic cholinergic stimulation is not
Is the heart different in mammals?
the mammalian heart are different in atrial and
What is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential?
Hypopolarization is the initial increase of the membrane potential to the value of the threshold potential. The threshold potential opens voltage-gated sodium channels and causes a large influx of sodium ions. This phase is called the depolarization. During depolarization, the inside of the cell becomes more and more electropositive, until the potential gets closer the electrochemical equilibrium for sodium of +61 mV. This phase of extreme positivity is the overshoot phase.
How does action potential work?
So, an action potential is generated when a stimulus changes the membrane potential to the values of threshold potential . The threshold potential is usually around -50 to -55 mV. It is important to know that the action potential behaves upon the all-or-none law. This means that any subthreshold stimulus will cause nothing, while threshold and suprathreshold stimuli produce a full response of the excitable cell.
What are the two types of synapses?
Each synapse consists of the: 1 Presynaptic membrane – membrane of the terminal button of the nerve fiber 2 Postsynaptic membrane – membrane of the target cell 3 Synaptic cleft – a gap between the presynaptic and postsynaptic membranes
What happens to the sodium permeability after an overshoot?
After the overshoot, the sodium permeability suddenly decreases due to the closing of its channels. The overshoot value of the cell potential opens voltage-gated potassium channels, which causes a large potassium efflux, decreasing the cell’s electropositivity.
Why does myelin increase the speed of propagation?
The propagation is also faster if an axon is myelinated. Myelin increases the propagation speed because it increases the thickness of the fiber. In addition, myelin enables saltatory conduction of the action potential, since only the Ranvier nodes depolarize, and myelin nodes are jumped over.
What causes action potential?
From the aspect of ions, an action potential is caused by temporary changes in membrane permeability for diffusible ions. These changes cause ion channels to open and the ions to decrease their concentration gradients. The value of threshold potential depends on the membrane permeability, intra- and extracellular concentration of ions, and the properties of the cell membrane.
Does action potential always propagate forward?
We need to emphasize that the action potential always propagates forward, never backwards. This is due to the refractoriness of the parts of the membrane that were already depolarized, so that the only possible direction of propagation is forward. Because of this, an action potential always propagates from the neuronal body, through the axon to the target tissue.
