.jpg)
Will we ever Cure Alzheimer's?
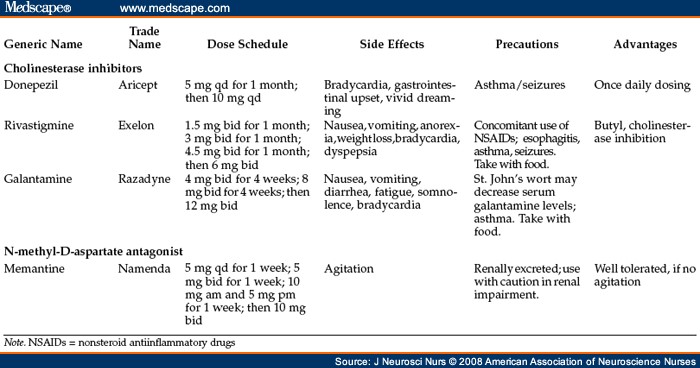
There are treatments that have been approved by the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for Alzheimer's. For example, cholinesterase inhibitors and memantine can help treat memory and thinking problems. But these drugs just help manage the symptoms; there is currently no cure for the disease.
What does Alzeimers do to you?
At its core, Alzheimer’s is an irreversible, progressive disease. The brain disorder — the most common form of dementia — begins with problems with an individual’s memory. But, as it slowly progresses, patients are less and less able to function cognitively.
How do you cure Alzheimers?
UB-311 is an immunotherapeutic vaccine candidate, which targets toxic forms of amyloid beta in the brain, in order to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Phase 1, phase 2 and phase 2a long-term extension trials have shown UB-311 to be well-tolerated and safe in patients over 3 years of repeat dosing.
How can you overcome Alzheimer disease?
One of the most powerful habits to overcome Alzheimer’s is heat therapy, explicitly getting in the sauna regularly. Sauna has been a critical player in ancestral cleansing in various cultures across the globe. From Finnish saunas to Native American sweat lodges, and Russian banyas, this heat therapy is well known among ancient cultures.

How does Alzheimer's begin?
The exact causes of Alzheimer's disease aren't fully understood. But at a basic level, brain proteins fail to function normally, which disrupts the work of brain cells (neurons) and triggers a series of toxic events. Neurons are damaged, lose connections to each other and eventually die.
What happens to a person when they have Alzheimer's?
As Alzheimer's worsens, people experience greater memory loss and other cognitive difficulties. Problems can include wandering and getting lost, trouble handling money and paying bills, repeating questions, taking longer to complete normal daily tasks, and personality and behavior changes.
How exactly does Alzheimer's cause death?
The vast majority of those with Alzheimer's die from aspiration pneumonia – when food or liquid go down the windpipe instead of the esophagus, causing damage or infection in the lungs that develops into pneumonia.
How does Alzheimer's start and progress?
Alzheimer's disease tends to develop slowly and gradually worsens over several years. Eventually, Alzheimer's disease affects most areas of your brain. Memory, thinking, judgment, language, problem-solving, personality and movement can all be affected by the disease.
Do Alzheimer's patients suffer?
As far as we know, the changes in the brain that occur in Alzheimer's disease and other forms of dementia do not cause pain. However, people with dementia are at increased risk of experiencing pain because they are at increased risk of other things that can cause pain, such as falls, accidents and injuries.
Can Alzheimer's be prevented?
Contents. As the exact cause of Alzheimer's disease is still unknown, there's no certain way to prevent the condition.
Does Alzheimer's run in families?
Another strong risk factor is family history. Those who have a parent, brother or sister with Alzheimer's are more likely to develop the disease. The risk increases if more than one family member has the illness.
Why Alzheimer's patients sleep so much?
The lethargy that many Alzheimer's patients experience is caused not by a lack of sleep, but rather by the degeneration of a type of neuron that keeps us awake, according to a study that also confirms the tau protein is behind that neurodegeneration.
Why do Alzheimer's patients get mean?
CAUSES OF ANGER Lack of sleep. Confusion – they often have no idea what is happening to them, and anger is just a way of expressing frustration. They may not know how to react in certain situations. If the caregiver is loud, aggressive, or forceful, the AD patient may respond in a similar manner.
Can you stop Alzheimer's from progressing?
There's no cure for or drug to stop Alzheimer's disease, but it may be possible to hold off dementia — even in people who have a genetic risk, researchers reported Sunday at the Alzheimer's Association International Conference.
How long do Alzheimer's stages last?
Mild impairment or decline While the entire stage lasts about 7 years, the symptoms will slowly become clearer over a period of 2 to 4 years. Only people close to someone in this stage may notice the symptoms.
How long does Alzheimer's last from early stages?
A small number of people have “early-onset” Alzheimer disease, which starts when they are in their 30s or 40s. People live for an average of 8 years after their symptoms appear. But the disease can progress quickly in some people and slowly in others. Some people live as long as 20 years with the disease.
What are the 7 stages of Alzheimer's?
The 7 Stages of Alzheimer's DiseaseStage 1: Before Symptoms Appear. ... Stage 2: Basic Forgetfulness. ... Stage 3: Noticeable Memory Difficulties. ... Stage 4: More Than Memory Loss. ... Stage 5: Decreased Independence. ... Stage 6: Severe Symptoms. ... Stage 7: Lack of Physical Control.More items...•
What is end stage Alzheimer's?
Late-stage Alzheimer's (severe) In the final stage of the disease, dementia symptoms are severe. Individuals lose the ability to respond to their environment, to carry on a conversation and, eventually, to control movement. They may still say words or phrases, but communicating pain becomes difficult.
What is the longest stage of Alzheimer's disease?
Middle-stage Alzheimer's is typically the longest stage and can last for many years. As the disease progresses, the person living with Alzheimer's will require a greater level of care. During this stage, the person may confuse words, get frustrated or angry, and act in unexpected ways, such as refusing to bathe.
Is Alzheimer's worse than dementia?
While dementia is a general term, Alzheimer's disease is a specific brain disease. It is marked by symptoms of dementia that gradually get worse over time. Alzheimer's disease first affects the part of the brain associated with learning, so early symptoms often include changes in memory, thinking and reasoning skills.
What Is Alzheimer’S Disease?
1. The most common type of dementia. 2. A progressive disease beginning with mild memory loss possibly leading to loss of the ability to carry on a...
Who Has Alzheimer’S Disease?
1. In 2013, as many as 5 million Americans were living with Alzheimer’s disease.1 2. The symptoms of the disease can first appear after age 60 and...
What Is Known About Alzheimer’S Disease?
Scientists do not yet fully understand what causes Alzheimer’s disease. There probably is not one single cause, but several factors that affect eac...
How Do I Know If It’S Alzheimer’S Disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is not a normal part of aging.Memory problems are typically one of the first warning signs of cognitive loss.According to the N...
How Is Alzheimer’S Disease Treated?
Medical management can improve the quality of life for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and their caregivers. There is currently no know...
Support For Family and Friends
Currently, many people living with Alzheimer’s disease are cared for at home by family members.Caregiving can have positive aspects for the caregiv...
What Is The Burden of Alzheimer’S Disease in The United States?
Alzheimer’s disease is 1. One of the top 10 leading causes of death in the United States.2 2. The 6th leading cause of death among US adults. 3. Th...
Alzheimer’S Disease Public Health Curriculum
A Public Health Approach to Alzheimer’s and Other Dementias is an introductory curriculum that is intended to increase awareness of the impact of A...
Preclinical Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease begins long before any symptoms become apparent. This stage is called preclinical Alzheimer's disease. You won't notice symptom...
Mild Cognitive Impairment (MCI) Due to Alzheimer's Disease
People with mild cognitive impairment have mild changes in their memory and thinking ability. These changes aren't significant enough to affect wor...
Mild Dementia Due to Alzheimer's Disease
Alzheimer's disease is often diagnosed in the mild dementia stage, when it becomes clear to family and doctors that a person is having significant...
Moderate Dementia Due to Alzheimer's Disease
During the moderate stage of Alzheimer's disease, people grow more confused and forgetful and begin to need more help with daily activities and sel...
Severe Dementia Due to Alzheimer's Disease
In the severe (late) stage of Alzheimer's disease, mental function continues to decline, and the disease has a growing impact on movement and physi...
Rate of Progression Through Alzheimer's Disease Stages
The rate of progression for Alzheimer's disease varies widely. On average, people with Alzheimer's disease live eight to 10 years after diagnosis,...
How does Alzheimer's affect the brain?
Eventually, rudimentary actions like swallowing become impaired or impossible. Alzheimer's destroys some of the brain's 100 billion neurons and shrink s it (significant shrinkage occurs by the disease's advanced stages).
How long does Alzheimer's last?
While each patient is an individual case, mild to moderate Alzheimer's usually lasts two to 10 years, while advanced Alzheimer's can persist for up to five years [source: Alzheimer's Association ]. The symptoms of Alzheimer's disease often aren't noticeable when they begin.
How do plaques and tangles affect Alzheimer's?
Both appear to inhibit the ability of neurons to communicate with each other. Tangles, which are knotted threads of tau proteins, likely contribute to cell death, a key effect of Alzheimer's. Normally, in the human brain, nutrients and cell parts are transported through straight, parallel channels. Tangles disrupt these transport avenues and prevent those vital nutrients and cell parts from getting where they need to go.
Why are women more likely to have Alzheimer's?
Women are more likely to have Alzheimer's because they live longer than men . There are three genes -- known as amyloid precursor protein, presenilin 1 and presenilin 2 -- associated with early-onset Alzheimer's.
How many people have Alzheimer's at 65?
Five percent of Americans ages 65 to 75 have the disease [source: NIH ]. The prevalence might be as high as 50 percent among those at least 85 years old [source: NIH ]. While Alzheimer's is frequently associated with old age, it can develop before the traditional retirement age of 65.
What happens to the brain when you have tangles?
Tangles disrupt these transport avenues and prevent those vital nutrients and cell parts from getting where they need to go. As Alzheimer's disease progresses, brain cells start to die and neurotransmitter levels decrease. (Neurotransmitters are the chemicals that transmit messages through the brain.)
What are the risk factors for Alzheimer's?
Genetic abnormalities certainly play a role in the development of the disease, but researchers have considered many other possible risk factors for Alzheimer's, including advanced age, high cholesterol, lack of folate, head injuries, lack of exercise and even exposure to toxic substances.
How is Alzheimer’s disease treated?
Medical management can improve quality of life for individuals living with Alzheimer’s disease and for their caregivers. There is currently no known cure for Alzheimer’s disease. Treatment addresses several areas:
Who has Alzheimer’s Disease?
In 2020, as many as 5.8 million Americans were living with Alzheimer’s disease. 1
What are the warning signs of Alzheimer’s disease?
Alzheimer’s disease is not a normal part of aging. Memory problems are typically one of the first warning signs of Alzheimer’s disease and related dementias.
What is the burden of Alzheimer’s disease in the United States?
Alzheimer’s disease is one of the top 10 leading causes of death in the United States. 2
How do you know if you have Alzheimer's?
Difficulty completing familiar tasks at home, at work or at leisure. Decreased or poor judgment. Misplacing things and being unable to retrace steps to find them. Changes in mood, personality, or behavior. Even if you or someone you know has several or even most of these signs, it doesn’t mean it’s Alzheimer’s disease.
What are the symptoms of Alzheimer's?
In addition to memory problems, someone with symptoms of Alzheimer’s disease may experience one or more of the following: Memory loss that disrupts daily life, such as getting lost in a familiar place or repeating questions. Trouble handling money and paying bills.
What is the most common type of dementia?
Alzheimer’s disease is the most common type of dementia. It is a progressive disease beginning with mild memory loss and possibly leading to loss of the ability to carry on a conversation and respond to the environment. Alzheimer’s disease involves parts of the brain that control thought, memory, and language. ...
How long does it take to live with Alzheimer's?
The rate of progression for Alzheimer's disease varies widely. On average, people with Alzheimer's disease live between three and 11 years after diagnosis, but some survive 20 years or more. The degree of impairment at diagnosis can affect life expectancy.
Why is it important to identify early deposits in Alzheimer's disease?
The ability to identify these early deposits may be especially important for clinical trials and in the future as new treatments are developed for Alzheimer's disease. Additional biomarkers — measures that can indicate an increased risk of disease — have been identified for Alzheimer's disease. These biomarkers can be used to support ...
What is the late stage of dementia?
In the late stage of the disease, called severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease, mental function continues to decline, and the disease has a growing impact on movement and physical capabilities. In late stage severe dementia due to Alzheimer's disease, people generally: Lose the ability to communicate coherently.
How many stages of Alzheimer's disease are there?
Memory, thinking, judgment, language, problem-solving, personality and movement can all be affected by the disease. There are five stages associated with Alzheimer's disease: preclinical Alzheimer's disease, mild cognitive impairment due to Alzheimer's disease, mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease, moderate dementia due to Alzheimer's disease ...
What is the preclinical stage of Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer's disease begins long before any symptoms become apparent. This stage is called preclinical Alzheimer's disease, and it's usually identified only in research settings. You won't notice symptoms during this stage, nor will those around you.
What is mild dementia?
Mild dementia due to Alzheimer's disease. Alzheimer's disease is often diagnosed in the mild dementia stage, when it becomes clear to family and doctors that a person is having significant trouble with memory and thinking that impacts daily functioning. In the mild dementia stage, people may experience:
What are the most common behaviors associated with Alzheimer's?
See what types of behaviors are common in each of the stages as the disease progresses. By Mayo Clinic Staff. Alzheimer's disease tends to develop slowly and gradually worsens over several years. Eventually, Alzheimer's disease affects most areas of your brain. Memory, thinking, judgment, language, problem-solving, ...
How Does Alzheimer’s Disease Affect the Brain?
In Alzheimer’s disease, however, damage is widespread, as many neurons stop functioning, lose connections with other neurons, and die. Alzheimer’s disrupts processes vital to neurons and their networks, including communication, metabolism, and repair.
Where do cellular changes occur in Alzheimer's patients?
Many molecular and cellular changes take place in the brain of a person with Alzheimer’s disease. These changes can be observed in brain tissue under the microscope after death. Investigations are underway to determine which changes may cause Alzheimer’s and which may be a result of the disease.
How do neurons communicate?
Communication. Neurons are constantly in touch with neighboring brain cells. When a neuron receives signals from other neurons, it generates an electrical charge that travels down the length of its axon and releases neurotransmitter chemicals across a tiny gap, called a synapse. Like a key fitting into a lock, each neurotransmitter molecule then binds to specific receptor sites on a dendrite of a nearby neuron. This process triggers chemical or electrical signals that either stimulate or inhibit activity in the neuron receiving the signal. Communication often occurs across networks of brain cells. In fact, scientists estimate that in the brain’s communications network, one neuron may have as many as 7,000 synaptic connections with other neurons.
What are the processes of the brain?
Key Biological Processes in the Brain 1 The cell body contains the nucleus, which houses the genetic blueprint that directs and regulates the cell’s activities. 2 Dendrites are branch-like structures that extend from the cell body and collect information from other neurons. 3 The axon is a cable-like structure at the end of the cell body opposite the dendrites and transmits messages to other neurons.
What is the effect of beta amyloid on Alzheimer's?
In the Alzheimer’s brain, abnormal levels of this naturally occurring protein clump together to form plaques that collect between neurons and disrupt cell function. Research is ongoing to better understand how, and at what stage of the disease, the various forms of beta-amyloid influence Alzheimer’s.
What happens to the brain when neurons die?
In Alzheimer’s disease, as neurons are injured and die throughout the brain, connections between networks of neurons may break down, and many brain regions begin to shrink.
Why is neurogenesis important?
Remodeling of synaptic connections and neurogenesis are important for learning, memory, and possibly brain repair. Neurons are a major player in the central nervous system, but other cell types are also key to healthy brain function. In fact, glial cells are by far the most numerous cells in the brain, outnumbering neurons by about 10 to 1.
How does Alzheimer's disease occur?
Less than 1% of the time, Alzheimer's is caused by specific genetic changes that virtually guarantee a person will develop the disease. These rare occurrences usually result in disease onset in middle age.
What are some tasks that people with Alzheimer's forget?
Eventually, people with advanced Alzheimer's often forget how to perform basic tasks such as dressing and bathing.
What is the most common cause of dementia?
Overview. Alzheimer's disease is a progressive neurologic disorder that causes the brain to shrink (atrophy) and brain cells to die. Alzheimer's disease is the most common cause of dementia — a continuous decline in thinking, behavioral and social skills that affects a person's ability to function independently.
What are the two proteins that cause Alzheimer's?
Researchers trying to understand the cause of Alzheimer's disease are focused on the role of two proteins: Plaques. Beta-amyloid is a fragment of a larger protein. When these fragments cluster together, they appear to have a toxic effect on neurons and to disrupt cell-to-cell communication.
How do you know if you have Alzheimer's?
At first, a person with Alzheimer's disease may be aware of having difficulty remembering things and organizing thoughts.
Why is it so hard to multitask with Alzheimer's?
Alzheimer's disease causes difficulty concentrating and thinking, especially about abstract concepts such as numbers. Multitasking is especially difficult, and it may be challenging to manage finances, balance checkbooks and pay bills on time. Eventually, a person with Alzheimer's may be unable to recognize and deal with numbers.
Where does brain damage start?
The damage most often starts in the region of the brain that controls memory, but the process begins years before the first symptoms. The loss of neurons spreads in a somewhat predictable pattern to other regions of the brains. By the late stage of the disease, the brain has shrunk significantly.
What is Alzheimer’s Disease?
Alzheimer's is a type of dementia that affects memory, thinking and behavior. Symptoms eventually grow severe enough to interfere with daily tasks.
How is Alzheimer's Disease Diagnosed?
Learn what to expect when visiting a doctor for symptoms of Alzheimer's disease.
What is dementia in psychology?
Dementia is an overall term that describes a group of symptoms associated with a decline in memory and thinking skills.
How many people are affected by Alzheimer's?
Worldwide, 50 million people are living with Alzheimer's and other dementias. Alzheimer’s disease is a degenerative brain disease and the most common form of dementia. Dementia is not a specific disease. It's an overall term that describes a group of symptoms. Know the 10 Signs.
What is the most common form of dementia?
Understanding Alzheimer’s Disease & Dementia. Alzheimer's is the most common form of dementia, a general term for memory loss and other cognitive abilities serious enough to interfere with daily life.
Is there a single cause of Alzheimer's?
Causes and Risk Factors for Alzheimer's Disease. Researchers believe there is not a single cause of Alzheimer's disease. It likely develops from multiple factors, such as genetics, lifestyle and environment. Learn More.
Does memory change as you age?
Your memory often changes as you grow older. But memory loss that disrupts daily life is not a typical part of aging.