With caffeine blocking the adenosine, you have increased neuron firing in the brain. The pituitary gland sees all of the activity and thinks some sort of emergency must be occurring, so it releases hormones that tell the adrenal glands to produce adrenaline (epinephrine).
Is caffeine an adenosine blocker?
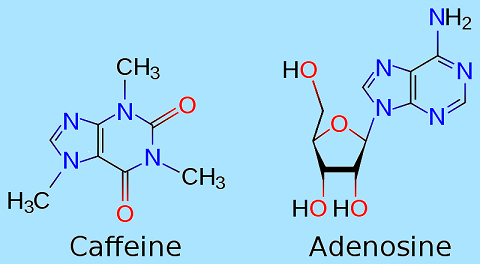
Caffeine is considered an adenosine blocker. It comes into play by similarly attaching itself to the same receptors that adenosine would normally latch onto. In turn, it prevents the drowsinessthat occurs as the levels of adenosine in the body increase.
How does caffeine affect adenosine levels in nerve cells?
As a result, the cell can no longer identify adenosine because caffeine is taking up all the receptors that adenosine would normally bind to. Instead of slowing down because of the adenosine's effect, the nerve cells speed up.
How does caffeine affect blood vessels in the brain?
In the brain, this also causes blood vessels to dilate, most likely to let more oxygen into that organ during sleep. To a nerve cell, caffeine looks like adenosine: Caffeine binds to the adenosine receptor. However, caffeine doesn't slow down the cell's activity like adenosine would.
What is the mechanism of action of caffeine?
Caffeine causes most of its biological effects via antagonizing all types of adenosine receptors (ARs): A1, A2A, A3, and A2B and, as does adenosine, exerts effects on neurons and glial cells of all brain areas. In consequence, caffeine, when acting as an AR antagonist, is doing the opposite of activ …

How can caffeine stop adenosine?
Abstract. Caffeine, the most widely used psychoactive compound, is an adenosine receptor antagonist. It promotes wakefulness by blocking adenosine A2A receptors (A2ARs) in the brain, but the specific neurons on which caffeine acts to produce arousal have not been identified.
How does caffeine affect adenosine receptors?
The levels of cortical and striatal At adenosine receptors are increased by 15-20% by chronic caffeine, while the level of striatal A2a-adenosine receptors is unaltered.
How do you block adenosine receptors?
Caffeine is emerging as a protective agent against Alzheimer's disease by blocking the A2a adenosine receptor whose expression and function become aberrant throughout aging and in age-related pathologies such as AD (Marques et al., 2011).
Does Coffee block adenosine?
Over the course of a day, you get sleepy as adenosine binds to A1 receptors in your brain. Caffeine blocks adenosine from binding, thus making you feel alert and also helping you feel better.
Does decaf block adenosine?
For example, some decaf coffees can have up to 15 milligrams in an 8-ounce cup, which is enough caffeine to disrupt sleep and also keep your adenosine receptors from resetting.
Does caffeine give you energy or block receptors?
Because caffeine acts as a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant, people usually take it to feel more alert and energetic. Caffeine can improve mood and help people feel more productive. It is believed to work by blocking the neurotransmitter adenosine's receptors, increasing excitability in the brain.
Does tea block adenosine?
When you drink coffee or tea in an effort to stay awake, you block those adenosine receptors and the sensation of tiredness. When you sleep, your brain metabolizes all the excess adenosine accumulated during the day. This is one of the major restorative functions of sleep.
Does caffeine block dopamine?
Caffeine, the most widely consumed psychoactive substance in the world, is used to promote wakefulness and enhance alertness. Like other wake-promoting drugs (stimulants and modafinil), caffeine enhances dopamine (DA) signaling in the brain, which it does predominantly by antagonizing adenosine A2A receptors (A2AR).
How does caffeine affect ATP?
At high ATP concentrations caffeine decreases the coupling between ATP hydrolysis and Ca inflow. It either inhibits inflow without any inhibition of the rate of ATP hydrolysis, or it stimulates the ATPase activity without stimulating Ca inflow.
Does caffeine bind to adenosine receptors?
To a nerve cell, caffeine looks like adenosine: Caffeine binds to the adenosine receptor. However, caffeine doesn't slow down the cell's activity like adenosine would. As a result, the cell can no longer identify adenosine because caffeine is taking up all the receptors that adenosine would normally bind to.
What drug blocks adenosine receptors?
Adenosine receptor antagonist, istradefylline is a selective antagonist at the A2A receptor (Kase et al., 2003; Nomoto et al., 2000). It has been found to be useful in the treatment of Parkinson's disease (PD) and has been approved for the treatment of PD (Mizuno, Kondo, & Japanese Istradefylline Study Group, 2013).
Is caffeine a competitive inhibitor for adenosine receptors?
Caffeine is a competitive antagonist at adenosine receptors. Receptor up-regulation during chronic drug treatment has been proposed to be the mechanism of tolerance to the behavioral stimulant effects of caffeine.
What receptors does caffeine stimulate?
Caffeine causes most of its biological effects via antagonizing all types of adenosine receptors (ARs): A1, A2A, A3, and A2B and, as does adenosine, exerts effects on neurons and glial cells of all brain areas.
How do you increase adenosine receptors?
Following a high-fat low-carb (ketogenic) diet can increase adenosine levels. The ketogenic diet alters energy metabolism and increases both ATP and adenosine [109].
How does caffeine affect ATP?
At high ATP concentrations caffeine decreases the coupling between ATP hydrolysis and Ca inflow. It either inhibits inflow without any inhibition of the rate of ATP hydrolysis, or it stimulates the ATPase activity without stimulating Ca inflow.
What is the biological effect of caffeine?
Caffeine causes most of its biological effects via antagonizing all types of adenosine receptors (ARs): A1, A2A, A3, and A2B and, as does adenosine, exerts effects on neurons and glial cells of all brain areas. In consequence, caffeine, when acting as an AR antagonist, is doing the opposite of activ ….
Does caffeine interfere with GABA receptors?
Besides AR antagonism, xanthines, including caffeine, have other biological actions: they inhibit phosphodiesterases (PDEs) (e.g., PDE1, PDE4, PDE5), promote calcium release from intracellular stores, and interfere with GABA-A receptors.
Does caffeine affect the brain?
Caffeine causes most of its biological effects via antagonizing all types of adenos ine receptors (ARs): A1, A2A, A3, and A2B and, as does adenos ine, exerts effects on neurons and glial cells of all brain areas. In consequence, caffeine, when acting as an AR antagonist, is doing the opposite of activation of adenosine receptors due to removal ...
How to reduce adenosine?
The best way to reduce it is with other chemicals that have the effect of blocking it by binding themselves to adenosine molecules and creating a blockage in the bloodstream.
How to lower adenosine levels?
The best way to lower adenosine is with good sleep. The best way to solve any problem is the natural way of the body. Remember that it’s really smart, in fact, definitely smarter than your conscious brain (especially when it comes to repairing health issues naturally).
Why is caffeine good for you?
As adenosine helps you fall asleep, caffeine makes you more awake. The reason caffeine is great not only for this but for anything related to productivity, is that it creates an effect on the brain that can increase your output immediately.
What happens if you don't reduce adenosine?
When you don’t reduce the levels of adenosine in your body, it affects the brain negatively. Basically, you become less productive and sleepy. This not only hinders your productivity, but also your overall health. So, having either low, or excessive levels could lead to auto-immune diseases.
Why is adenosine important?
Adenosine Helps Control The Immune System. Another important function that it has, is to help control your immune system. Now, the problem is that when adenosine levels are high, the opposite can happen. This means that your body would produce auto-immune responses.
Does caffeine help with adenosine?
While most people try to resolve a low amount of adenosine in the brain by taking caffeine, there are actually other ways to fix the issue that aren’t related to caffeine. But, you have to read everything in this blog post to find out.
Is adenosine an endogenous nucleoside?
Adenosine is an endogenous nucleoside that is present in every cell of your body. If you remember biology 101, your cells are basically you. Everything that you know as your body and your organs is made up of cells. This also means that it is in all of you.
How does caffeine work in the brain?
How does caffeine work in your brain? Over the course of a day, you get sleepy as adenosine binds to A1 receptors in your brain. Caffeine blocks adenosine from binding, thus making you feel alert and also helping you feel better. Written by Kamal Patel.
What does adenosine do to the brain?
Once adenosine (the key) locks into a certain receptor (the lock) in the brain, it has a unique effect on the brain. There are a host of different receptors in your brain, so different ones have different effects. The one we’re interested in is the A1 receptor. Once adenosine locks with the A1 receptor, it promotes muscle relaxation and sleepiness, ...
How long does it take for caffeine to peak?
Blood concentrations of caffeine tend to peak within two hours, which also means that brain concentrations of caffeine are at their peaks. The caffeine in your brain is competing with adenosine and preventing it from binding to A1 receptors. This is what gives you a jolt of wakefulness.
How long does caffeine stay in your system?
The half-life (the amount of time it takes for the concentration of a substance to be halved) of caffeine in the body ranges from three to ten hours de pending on the amount of CYP1A1 in the body, which varies from individual to individual.
Does caffeine metabolize in the morning?
By early evening, most of the caffeine from your morning cup of coffee has metabolized. There are significantly fewer caffeine molecules occupying the A1 receptors, so adenosine starts binding to them.
Can you drink caffeine at one time?
This then takes us back to the "Before Caffeine" step. Of course, you can always attempt to drink a larger dose of caffeine at one sitting, or drink caffeine multiple times during the day to keep sleepiness at bay. But that’s not really a sustainable strategy.
Does adenosine bind to dopamine?
Furthermore, adenosine can bind to the A2A receptor. When it binds, this interferes with the release of mood-improving neurotransmitters, such as dopamine. Adenosine itself is produced primarily from physical work and intensive brain use. Thus, over the course of the day, your body accumulates adenosine. If only there was something that could get ...
What is the role of adenosine in the body?
This breaks down further into Adenosine Tri-Phosphate (ATP). This is responsible for energy transference between cells.
What causes adenosine to accumulate in the body?
The accumulation of adenosine in the body is related to the quantity of caffeine consumed during the day. By drinking beverages with high levels of caffeine, the body builds up an excessive amount of adenosine. Often this excess is not fully flushed from the body during sleep.
Is caffeine an adenosine blocker?
Caffeine is considered an adenosine blocker. It comes into play by similarly attaching itself to the same receptors that adenosine would normally latch onto. In turn, it prevents the drowsiness that occurs as the levels of adenosine in the body increase.
Can caffeine cause sleep problems?
Balancing caffeine and sleep health. Due to this reaction, too much caffeine, especially over long periods, can lead to a disrupted sleep cycle. Experts recommend avoiding caffeine before bed or late in the day, as it blocks the normal process of adenosine.
