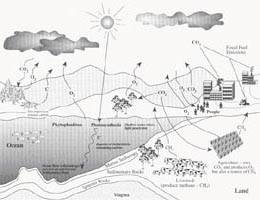
What is the movement of carbon from one reservoir to another?
It is stored in what are known as reservoirs, and it moves between these reservoirs through a variety of processes, including photosynthesis, burning fossil fuels, and simply releasing breath from the lungs. The movement of carbon from reservoir to reservoir is known as the carbon cycle.
How does the amount of carbon on Earth change over time?
Because Earth is a closed system, the amount of carbon on the planet never changes. However, the amount of carbon in a specific reservoir can change over time as carbon moves from one reservoir to another.
What are the forms of carbon compounds found in reservoirs?
Forms of carbon compounds found in each reservoir and indicate whether each is a solid (s), liquid (l) or gas (g). (examples: carbohydrate (s), calcium carbonate (s), CO 2 (g)) As you draw your arrows between the reservoirs, think about about how long it takes for these carbon atoms to move from one reservoir to another.
How is carbon trapped and transformed into natural resources?
When these organisms died, slow geologic processes trapped their carbon and transformed it into these natural resources. Processes such as erosion release this carbon back into the atmosphere very slowly, while volcanic activity can release it very quickly.

What are the 4 processes that move carbon?
Photosynthesis, Decomposition, Respiration and Combustion.
How does carbon get transferred?
Through food chains, the carbon that is in plants moves to the animals that eat them. Animals that eat other animals get the carbon from their food too. Carbon moves from plants and animals to soils. When plants and animals die, their bodies, wood and leaves decays bringing the carbon into the ground.
What are the three main reservoirs in which carbon moves between?
Most of Earth's carbon is stored in rocks and sediments. The rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. These are the reservoirs through which carbon cycles.
How does carbon move throughout the environment?
Plants constantly exchange carbon with the atmosphere. Plants absorb carbon dioxide during photosynthesis and much of this carbon dioxide is then stored in roots, permafrost, grasslands, and forests. Plants and the soil then release carbon dioxide when they decay.
How do you explain the carbon cycle?
Carbon Cycle Steps Carbon present in the atmosphere is absorbed by plants for photosynthesis. These plants are then consumed by animals and carbon gets bioaccumulated into their bodies. These animals and plants eventually die, and upon decomposing, carbon is released back into the atmosphere.
What are the 6 steps of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle depicts the natural flow of the element carbon through the atmosphere in different forms. There are six main processes in the carbon cycle: photosynthesis, respiration, exchange, sedimentation, extraction, and combustion.
What are the 7 steps of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle is divided into the following steps:Entry of Carbon into the Atmosphere. ... Carbon Dioxide Absorption By Producers. ... Passing of the Carbon Compounds in the Food Chain. ... Return of the Carbon To the Atmosphere. ... Short Term. ... Long Term. ... Essential For Life. ... Important For the Maintenance of the Balance in Ecosystems.More items...•
What are the 4 major carbon reservoirs?
Then students are introduced to the carbon cycle and create a simple model to diagram their understanding of carbon's movements through Earth's four major reservoirs: biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
What are the carbon reservoirs from largest to smallest?
Below are all the major carbon reservoirs on Earth and the approximate amount of carbon they have sequestered in them.Deep oceans = 38,400 gigatons.Fossil fuels = 4,130 gigatons.Terrestrial biosphere = 2,000 gigatons.Surface oceans = 1,020 gigatons.Atmosphere = 720 gigatons.Sediments = 150 gigatons.
How does carbon move throughout the environment quizlet?
Carbon moves from the atmosphere to plants. In the atmosphere, carbon is attached to oxygen in a gas called carbon dioxide (CO2). With the help of the Sun, through the process of photosynthesis, carbon dioxide is pulled from the air to make plant food from carbon. Carbon moves from plants and animals to the ground.
What is a carbon reservoir examples?
Carbon is stored in four main reservoirs -- oceans (the largest reservoir), geological reserves of fossil fuels, the terrestrial surface (plants and soil, mainly), and the atmosphere.
What is the largest carbon reservoir on Earth?
the deep-oceanThe largest reservoir of the Earth's carbon is located in the deep-ocean, with 37,000 billion tons of carbon stored, whereas approximately 65,500 billion tons are found in the globe. Carbon flows between each reservoir via the carbon cycle, which has slow and fast components.
What carries carbon dioxide to the lungs?
Carbon dioxide is transported in the blood from the tissue to the lungs in three ways:1 (i) dissolved in solution; (ii) buffered with water as carbonic acid; (iii) bound to proteins, particularly haemoglobin. Approximately 75% of carbon dioxide is transport in the red blood cell and 25% in the plasma.
How is energy transferred within organisms?
There are three types of energy transfer: photosynthesis, chemosynthesis, and consumption.
Is transportation part of the carbon cycle?
The carbon cycle monitors the exchange of carbon throughout Earth's "carbon reservoirs" which store and transport carbon in many ways.
How do these processes move carbon atoms from one pool to another?
There are many types of processes that move carbon from one reservoir to another. These processes include photosynthesis, plant and soil organisms' respiration, combustion, decomposition, and deforestation. Geological processes, include weathering, erosion, and sedimentation.
How does carbon move from one storage reservoir to another?
Carbon moves from one storage reservoir to another through a variety of mechanisms. For example, in the food chain, plants move carbon from the atmosphere into the biosphere through photosynthesis. They use energy from the sun to chemically combine carbon dioxide with hydrogen and oxygen from water to create sugar molecules.
Where is carbon stored on Earth?
Most of Earth’s carbon is stored in rocks and sediments. The rest is located in the ocean, atmosphere, and in living organisms. These are the reservoirs through which carbon cycles.
How does burning fossil fuels affect the atmosphere?
Burning fossil fuels, changing land use, and using limestone to make concrete all transfer significant quantities of carbon into the atmosphere. As a result, the amount of carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is rapidly rising; it is already greater than at any time in the last 3.6 million years.
What are the natural resources that contain carbon?
Rocks like limestone and fossil fuels like coal and oil are storage reservoirs that contain carbon from plants and animals that lived millions of years ago. When these organisms died, slow geologic processes trapped their carbon and transformed it into these natural resources.
How do animals get energy from plants?
Animals that eat plants digest the sugar molecules to get energy for their bodies. Respiration, excretion, and decomposition release the carbon back into the atmosphere or soil, continuing the cycle. The ocean plays a critical role in carbon storage, as it holds about 50 times more carbon than the atmosphere.
What is the process of lowering the pH of the ocean?
This extra carbon dioxide is lowering the ocean’s pH, through a process called ocean acidification . Ocean acidification interferes with the ability of marine organisms (including corals, Dungeness crabs, and snails) to build their shells and skeletons.
What are the major reservoirs on Earth that all carbon objects come from?
Task each student pair or team to collaboratively identify the major reservoirs on Earth that all carbon objects come from: biosphere, lithosphere, hydrosphere, and atmosphere.
What process would remove money from the reservoir?
Ask students what processes would remove money. “Spending” is the process that removes money from the reservoir; draw an arrow labeled “Spending,” pointing out from the reservoir. Ask for examples of reservoirs that money might go into. It could be anything they would spend money on.
What process might put money into the “Money in Wallet” reservoir?
Ask what process might put money into the “Money in Wallet” reservoir. One answer might be “Earning, ” which would be illustrated as an arrow pointing to the “Money in Wallet” reservoir. Ask for examples of reservoirs that would be the source of the earned money (e.g., a job, a neighbor or parent that paid the student for a chore). Before moving to the next step, review again with students which parts of the example are processes and which are reservoirs.
Where is carbon found in the universe?
Carbon is one of the most abundant elements in the universe and, on Earth, it is contained in the biosphere, the atmosphere, the hydrosphere, and the lithosphere. Carbon moves through these four reservoirs in slow and fast cycles, and many Earth systems keep it all in balance, preventing too much carbon from being moved from one reservoir into another. This complex system is impacted by human activities, which in turn impacts the functioning of various systems on Earth, creating a feedback loop which alters the carbon cycle as well.
When should a reservoir cycle diagram be recorded?
When they have a clear set of one to three processes in and out of each reservoir, they should then record them on their Cycle Diagram.
Is the biosphere based on land?
Note that the biosphere is not entirely based on land but also includes living things in the ocean, and that the hydrosphere is not entirely located in the ocean but also includes water on land and in the atmosphere.
Is carbon an element?
Students should be familiar with the fact that carbon is an element on the Periodic Table, an atom that bonds with other atoms to form various compounds.
How many carbon pathways must go through the ocean?
At least one of your two carbon pathways must go through part of the ocean. One of the two carbon pathways must illustrate a fast carbon cycle. (Note: Fast carbon cycle pathways are completed in short timescales of minutes up to several hundred years.) The other carbon pathway must illustrate a slow carbon cycle.
How long can carbon stay in sedimentary rocks?
For example, a carbon atom can stay in sedimentary rocks for millions of years before moving to a different carbon reservoir. This would be an example of a "very long and slow time scale.". If the information is available, indicate a time scale for movement of carbon from one reservoir to the next reservoir.