What are the 3 steps in order of cellular respiration?
- Glycolysis. In glycolysis, glucose—a six-carbon sugar—undergoes a series of chemical transformations. ...
- Pyruvate oxidation. Each pyruvate from glycolysis goes into the mitochondrial matrix—the innermost compartment of mitochondria. ...
- Citric acid cycle. ...
- Oxidative phosphorylation. ...
What are the three pathways of cellular respiration?
What are the 3 pathways of cellular respiration?
- st- Glycolosis. Splitting sugars in cytoplasm, energy investment phase -> 2 ATP molecules combine with glucose molecule.
- nd- Oxidation. Pyruvates moving into mitochondria, through oxidation pyruvates broken into water.
- rd- Krebs Cycle/Citric Acid Cycle.
- th- Electron Transport Chain.
What are the different steps in cellular respiration?
What are the four stages of aerobic cellular respiration quizlet?
- Glycolysis.
- Acetyl-CoA Formation.
- Citric acid cycle.
- Electron transport.
What is the overall process of cellular respiration?
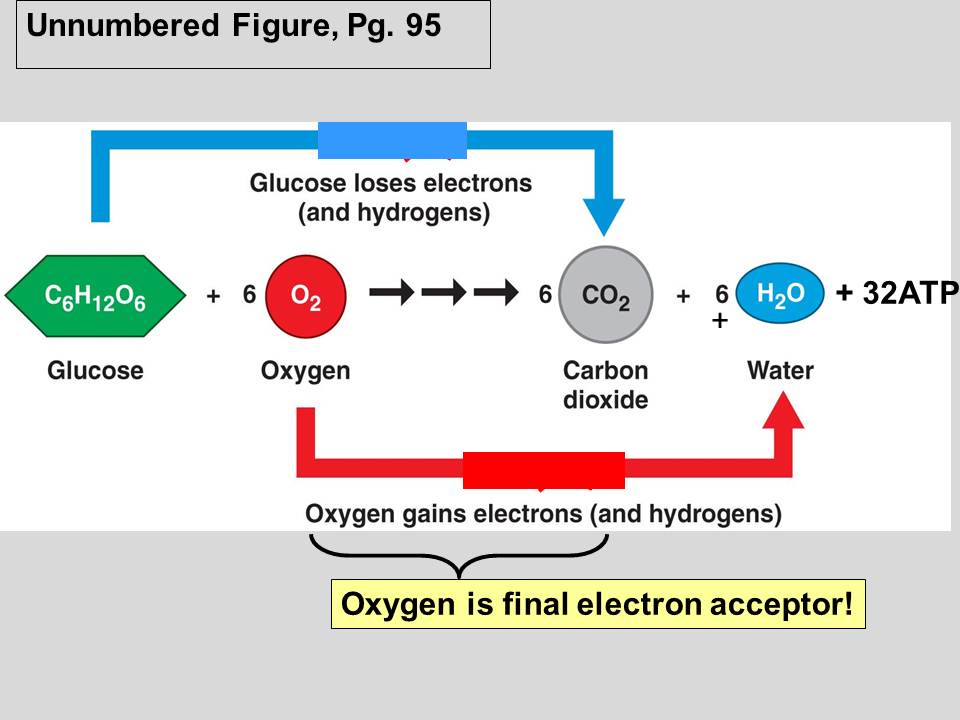
Cellular respiration is the process through which cells convert fuel into energy and nutrients. To create ATP and other forms of energy that they can use to power their life functions, cells require fuel and an electron acceptor which drives the chemical process of turning energy from that fuel into a useable form.

How does water come out of cellular respiration?
As electrons move down the chain, energy is released and used to pump protons out of the matrix, forming a gradient. Protons flow back into the matrix through an enzyme called ATP synthase, making ATP. At the end of the electron transport chain, oxygen accepts electrons and takes up protons to form water.
Does cellular respiration consume water?
During cellular respiration, glucose, in the presence of oxygen, is converted into carbon dioxide and water.
Do plants release water during cellular respiration?
The short answer is that when plants are doing cellular respiration, they produce carbon dioxide and water.
Does respiration in plants release water?
Aerobic Respiration This type of respiration takes place in the mitochondria of all eukaryotic entities. Food molecules are completely oxidised into the carbon dioxide, water, and energy is released in the presence of oxygen.
Does anaerobic respiration use water?
Answer: During anaerobic cellular respiration, glucose is broken down without oxygen. The chemical reaction transfers glucose energy to the cell. In fermentation, instead of carbon dioxide and water, lactic acid is produced which can lead to painful muscle cramps.
Is water used in glycolysis?
Glycolysis is the process of breaking down glucose. Glycolysis can take place with or without oxygen. Glycolysis produces two molecules of pyruvate, two molecules of ATP, two molecules of NADH, and two molecules of water. Glycolysis takes place in the cytoplasm.
How does cellular respiration help the water cycle?
Therefore, cellular respiration becomes a source of water to get added back to the water cycle through living beings. This is a crucial role played by cellular respiration of adding water back to the water cycle. So, we can conclude that cellular respiration plays the important role of releasing the water vapour from the living beings into ...
How many molecules of water are produced during cellular respiration?
Hence, it is at the electron transport chain stage that cellular respiration forms six molecules of water for each molecule of glucose. This water is exhaled by the living organisms in the form of water vapour and this evaporated water gets back into the water cycle, along with the other forms of evaporated water.
What is the process that releases H2O to the atmosphere during electron transport?
The correct answer is D: It releases H2O to the atmosphere during electron transport. Cellular respiration is the process that occurs in the living cells wherein sugar or glucose is oxidised into carbon dioxide and water resulting in the release of energy in the form of adenosine triphosphate (ATP). This is the process by which the chemical energy ...
Why is cellular respiration important?
So, we can conclude that cellular respiration plays the important role of releasing the water vapour from the living beings into the atmosphere so that the water gets added back to the water cycle.
Why does water come closer to each other?
The water that gets into the atmosphere in the form of water vapour goes higher up and changes into small water droplets or ice particles because of the low temperature. These tiny droplets come closer to each other to form clouds.
What are the raw materials of cellular respiration?
The raw materials for cellular respiration are the nutrients that the organism consumes in the form of sugar which are broken down using oxygen to form water and carbon dioxide as by-products. As a part of this reaction, ADP is converted into ATP that can be used by the cells. Essentially, cellular respiration is the conversion ...
What is the name of the gas released by the citric acid cycle?
C. It releases H2O to the atmosphere during the citric acid cycle.
How does cellular respiration work?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutri ents into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products . The reactions involved in respiration are catabolic reactions, which break large molecules into smaller ones, releasing energy because weak high-energy bonds, in particular in molecular oxygen, are replaced by stronger bonds in the products. Respiration is one of the key ways a cell releases chemical energy to fuel cellular activity. The overall reaction occurs in a series of biochemical steps, some of which are redox reactions. Although cellular respiration is technically a combustion reaction, it clearly does not resemble one when it occurs in a living cell because of the slow, controlled release of energy from the series of reactions.
What is the process of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions and processes that take place in the cells of organisms to convert chemical energy from oxygen molecules or nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products.
How many ATP molecules are produced in aerobics?
In aerobic conditions, the process converts one molecule of glucose into two molecules of pyruvate (pyruvic acid), generating energy in the form of two net molecules of ATP. Four molecules of ATP per glucose are actually produced, however, two are consumed as part of the preparatory phase.
How many ATP molecules can be made from glucose?
This potential is then used to drive ATP synthase and produce ATP from ADP and a phosphate group. Biology textbooks often state that 38 ATP molecules can be made per oxidized glucose molecule during cellular respiration (2 from glycolysis, 2 from the Krebs cycle, and about 34 from the electron transport system).
What is the Krebs cycle?
This is also called the Krebs cycle or the tricarboxylic acid cycle. When oxygen is present, acetyl-CoA is produced from the pyruvate molecules created from glycolysis. Once acetyl-CoA is formed, aerobic or anaerobic respiration can occur. When oxygen is present, the mitochondria will undergo aerobic respiration which leads to the Krebs cycle. However, if oxygen is not present, fermentation of the pyruvate molecule will occur. In the presence of oxygen, when acetyl-CoA is produced, the molecule then enters the citric acid cycle (Krebs cycle) inside the mitochondrial matrix, and is oxidized to CO 2 while at the same time reducing NAD to NADH. NADH can be used by the electron transport chain to create further ATP as part of oxidative phosphorylation. To fully oxidize the equivalent of one glucose molecule, two acetyl-CoA must be metabolized by the Krebs cycle. Two low-energy waste products, H 2 O and CO 2, are created during this cycle.
How is NADH converted to ATP?
The potential of NADH and FADH 2 is converted to more ATP through an electron transport chain with oxygen and protons (hydrogen) as the "terminal electron acceptors". Most of the ATP produced by aerobic cellular respiration is made by oxidative phosphorylation.
How many ATP molecules are produced in cellular respiration?
Although there is a theoretical yield of 38 ATP molecules per glucose during cellular respiration, such conditions are generally not realized because of losses such as the cost of moving pyruvate (from glycolysis), phosphate, and ADP (substrates for ATP synthesis) into the mitochondria. All are actively transported using carriers that utilize the stored energy in the proton electrochemical gradient .
How does water vapor come down?
Once all of those molecules get packed together, or condensed, the water falls to the earth again, where it either works its way down into the earth's crust to form aquifers, or rock that can hold groundwater, or creates runoff, which flows to water storage reserves like lakes and oceans. Eventually, the same molecules may again evaporate and follow the same cycle. Going back to our dog's breath example from the beginning of the lesson, you can now see how the water your dog breathes out can come down as rain at a later point in time.
Why is respiration important?
Respiration is the most important metabolic process for animals that can't make their own energy. It allows organisms to gather oxygen from the air in exchange for carbon dioxide and water vapor . Particularly, we're talking about respiration in the presence of oxygen.
What happens when you exhale water?
Another option is that the water we exhale is absorbed by plant life surrounding us. Photosynthesis is the complementary chemical reaction to respiration, meaning that plants need water and carbon dioxide to produce their energy. If we were to breathe in close quarters with plants, some portion of the water we exhale would be absorbed by pores in a plant's leaves.
What happens when water vapor cools down?
Then, the water vapor gathers and cools down in a process called condensation. When enough water condenses in the atmosphere, it falls back to the earth during a process called precipitation, also known as rain, snow, and hail. A lot of that precipitation then makes its way, above or underground, back to major bodies of water like lakes and oceans. There is more to this cycle as we'll see shortly, but it's important to know the basics.
How does water help plants?
From there, the water makes its way throughout the plant to complete the process of photosynthesis, allowing the plant to create its own energy and grow. It's important to note that much of the water used by plants is actually broken down into hydrogen and oxygen due to photosynthesis, and it's this hydrogen fuel that give plants part of their energy. When the plant has used all the water it needs, what's left exits the leaves and is released as water vapor into the atmosphere. From the atmosphere, the process is very similar to the one stated before in which water condenses and again falls to the ground.
Where is the water cycle stored?
A very basic explanation of the water cycle is that the majority of water is stored in our oceans. With added energy from the sun, much of that liquid water turns into gas, or water vapor, and is absorbed by the atmosphere in a process called evaporation.
