Diffusion is important for the following reasons:
- During the process of respiration, this process helps in diffusing the carbon dioxide gas out through the cell membrane into the blood.
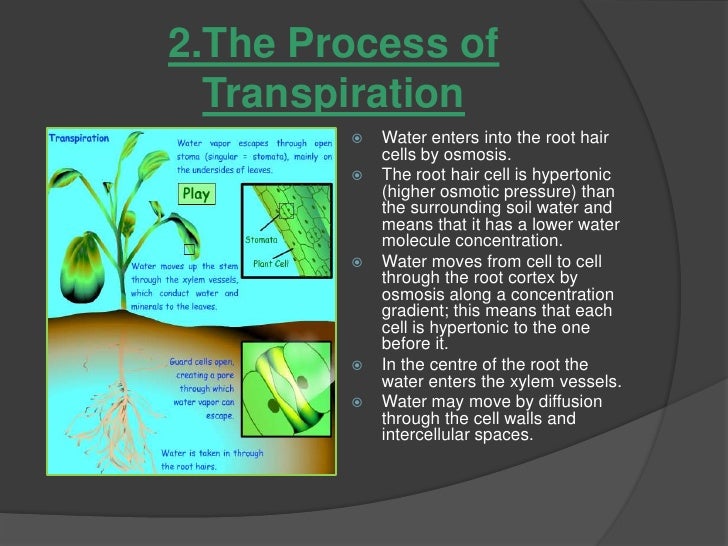
- Diffusion also occurs in plant cells. In all green plants, water present in the soil diffuses into plants through their root hair cells.
- The movement of ions across the neurons that generates electrical charge is due to diffusion.
Which is major function of diffusion in cells?
Cells import nutrients to use in the various chemical processes that go on inside them. These processes produce waste which a cell needs to get rid of. Small molecules such as oxygen, carbon dioxide and ethanol get across the cell membrane through the process of simple diffusion. This is regulated with a concentration gradient across the cell ...
Why is diffusion important to a living cell?
Importance of diffusion to living organisms. Diffusion is important to cells because it allows them to gain the useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow, and lets them get rid of ...
What role does diffusion play in the cell?
What role of diffusion play in the activities of the living cells? Diffusion is an essential function in living organisms. Diffusion is the random but directional movement of molecules from a place of high concentration to a place of low concentration. Diffusion also makes it possible to reduce the loss of body heat to the surrounding environment.
Why do cells need faciliated diffusion?
Why do cells make proteins to carry out facilitated diffusion? Facilitated diffusion is the diffusion of solutes through transport proteins in the plasma membrane. However, due to the hydrophobic nature of the lipids that make up cell membranes, polar molecules (such as water) and ions cannot do so.

How does diffusion affect cells?
2:003:52Transport in Cells: Diffusion and Osmosis | Biology | FuseSchoolYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipIt is the movement of water into or out of a cell. Again it is the movement from a dilute solutionMoreIt is the movement of water into or out of a cell. Again it is the movement from a dilute solution so high concentration of water molecules. Down the concentration gradient to a more concentrated.
What is diffusion and why is it important for cells?
Diffusion is the process of movement of molecules under a concentration gradient. It is an important process occurring in all living beings. Diffusion helps in the movement of substances in and out of the cells.
How is diffusion used in a cell?
Diffusion is a process where molecules and ions move naturally from an intracellular region of high concentration to an area of lower concentration, or vice versa. Diffusion occurs spontaneously without the expenditure of energy by the cell in a procedure known as passive transport.
What is the purpose of diffusion?
Both diffusion and osmosis aim to equalize forces inside cells and organisms as a whole, spreading water, nutrients and necessary chemicals from areas that contain a high concentration to areas that contain a low concentration.
What would happen without diffusion?
The dependence of life processes on diffusion mechanisms could not be more prevalent. Diffusion occurs throughout the human body, and without it, cells and body tissue could not get important nutrients for survival, the eyes would dry out, and many medicines could not be absorbed into the body.
What are the advantages of diffusion in daily life?
Removal of Toxins and Waste Substances from Our Body Nephron first separate waste chemicals and toxic from the blood and then reabsorb water and nutrients in the blood through diffusion. Hence, diffusion plays a significant role also in the filtration of the blood.
What is diffusion in cells biology?
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of high concentration of the molecules to an area with a lower concentration. The difference in the concentrations of the molecules in the two areas is called the concentration gradient.
Why is diffusion important to the human body?
In humans, diffusion helps move substances in and out of cells. Lungs and Gas: During the respiratory process, oxygen and carbon dioxide gases reach to cells and are removed from cells respectively by diffusion.
What is the result of diffusion?
Since diffusion moves materials from an area of higher concentration to the lower, it is described as moving solutes "down the concentration gradient." The end result of diffusion is an equal concentration, or equilibrium, of molecules on both sides of the membrane.
What is diffusion and how does it work?
diffusion, process resulting from random motion of molecules by which there is a net flow of matter from a region of high concentration to a region of low concentration. A familiar example is the perfume of a flower that quickly permeates the still air of a room.
What is diffusion in the cell membrane?
The simplest mechanism by which molecules can cross the plasma membrane is passive diffusion. During passive diffusion, a molecule simply dissolves in the phospholipid bilayer, diffuses across it, and then dissolves in the aqueous solution at the other side of the membrane.
What is diffusion in biology respiration?
Diffusion is the process whereby gases move from an area of high pressure to low pressure. This includes during - Internal respiration - this is the movement in the internal tissues between cells and capillaries, and - External respiration - when gas is exchanged between the alveoli and lung capillaries.
What is diffusion short answer?
Diffusion is the movement of a substance from an area of high concentration to an area of lower concentration . Diffusion occurs in liquids and gases when their particles collide randomly and spread out. Diffusion is an important process for living things - it is how substances move in and out of cells.
What you mean by diffusion?
Diffusion is defined as the movement of individual molecules of a substance through a semipermeable barrier from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration [34].
Why is diffusion important to the human body?
In humans, diffusion helps move substances in and out of cells. Lungs and Gas: During the respiratory process, oxygen and carbon dioxide gases reach to cells and are removed from cells respectively by diffusion.
Why is diffusion and osmosis important to cells?
Answer and Explanation: Diffusion and osmosis are crucial for cells as they help in balancing the cellular forces present within the cells. They play an essential role in absorption of nutrients by the cells to gain their nourishment.
What process does the gaseous exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide rely on?
Simple diffusion.
What is the waste product of the breakdown of amino acids? How does it enter the blood?
Urea. There is a higher concentration of urea in liver cells than in the blood. This concentration gradient means urea diffuses into the blood vi...
Define facilitated diffusion.
The movement of molecules down their concentration gradient, using membrane proteins.
What are channel proteins?
Transmembrane proteins which provide a hydrophilic channel for the passage of charged molecules, like ions.
What are the different types of stimuli that trigger the opening or closing of channel proteins?
Voltage, mechanical pressure and ligand binding.
What are carrier proteins?
Transmembrane proteins which undergo a reversible conformational change for the passage of molecules.
What processes require the presence of carrier proteins?
Both passive and active transport across the cell membrane.
What kind of process allows the nerve impulse to travel along axons? Identify a protein that is required for this process.
Facilitated diffusion. Voltage-gated sodium ion channels are needed for the passage of ions.
Describe the molecular properties of glucose and what it means for its transport across cell membranes.
Glucose is a large and highly polar molecule. This means it needs membrane proteins for its transport across cell membranes.
Molecule diffusion
The cell membrane is a partially permeable membrane which favours the passage of specific molecules for simple diffusion. Small, uncharged polar molecules can freely diffuse through the phospholipid bilayer without any assistance.
What is facilitated diffusion?
This type of diffusion follows all the rules of simple diffusion but here, membrane proteins are needed to transport the molecule across the phospholipid bilayer. Recall the cell membrane structure - the hydrophobic nonpolar core of tails makes the cell membrane impermeable to charged molecules, like ions.
What factors affect the rate of diffusion?
Certain factors will affect the rate at which substances will diffuse. Below are the main factors you need to know:
Adaptations for gas exchange in the lungs
So we have discussed the factors that affect how quickly molecules can diffuse across a membrane. A great example of how our body has adapted for efficient diffusion is the gaseous exchange that occurs between the capillaries and alveoli.
Adaptations for rapid transport in the ileum
Facilitated diffusion occurs in the epithelial cells of the ileum to absorb molecules like glucose. The ileum also has adaptations that help increase the rate of transport.
Cell Diffusion - Key takeaways
Simple diffusion is the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient whereas facilitated diffusion is the movement of molecules down their concentration gradient using membrane proteins.
Cell Diffusion
Diffusion is the movement of molecules from an area of higher concentration to an area of lower concentration. Molecules move down their concentration gradient. This form of transport relies on the random kinetic energy of molecules.
