
Homeostasis
Homeostasis or homoeostasis is the property of a system in which variables are regulated so that internal conditions remain stable and relatively constant. Examples of homeostasis include the regulation of temperature and the balance between acidity and alkalinity (pH).
How can a poor diet affect homeostasis?
Apr 05, 2020 · Subsequently, one may also ask, how does osmosis and diffusion help maintain homeostasis? Selective permeability helps the cell maintain homeostasis, a stable internal environment. Diffusion and osmosis are affected by the ratio of a cell's volume to its surface area. If the concentration of water and solutes are equal on both sides of the membrane, the cell is in …
What does diffusion use to help?
Nov 15, 2021 · How does diffusion maintain homeostasis? Diffusion helps maintain homeostasis by creating specific concentrations of molecules inside the body compared to outside. How is diffusion involved in homeostasis? Diffusion is process by which particles move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated.
How does diffusion help cells survive?
Diffusion helps maintain homeostasis by creating specific concentrations of molecules inside the body compared to outside. Let's look at an example. …
How do individual cells maintain homeostasis?
Oct 28, 2010 · Simple diffusion and osmosis help maintain homeostasis in cells and do not require the cell to expend energy. How does diffusion maintain homeostasis? diffusion is the transfer of a substance from...
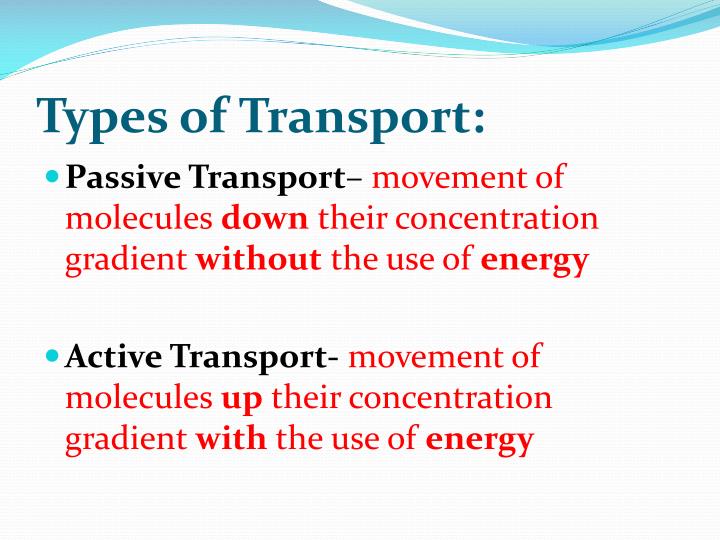
How is diffusion involved in homeostasis?
Diffusion is process by which particles move from an area where they are more concentrated to an area where they are less concentrated. When homeostasis is threatened in a cell, diffusion is used to keep the cell's concentration balanced. For example, calcium levels must be properly maintained.Jun 11, 2018
How does diffusion and osmosis help maintain homeostasis?
Osmosis helps maintain homeostasis by maintaining concentration of solvents and solutes constant inside cells.Feb 7, 2022
Why is diffusion important to cells?
Diffusion is important to cells because it allows them to gain the useful substances they require to obtain energy and grow, and lets them get rid of waste products. This table shows examples of substances required by cell and associated waste products.
How can eukaryotic cells maintain homeostasis?
Eukaryotic cells consist of a “selectively permeable” cell membrane and having this selectively permeable membrane is what helps the cell maintain homeostasis.Apr 25, 2015