How does the Earth stay in orbit around the Sun?
The Earth stays in orbit by the massive tug of the gravity of the sun. The sun's mass equals its gravity power, and the sun has many times the amount of mass then the Earth, causing the Earth to be tugged into orbit around the sun.
How does the Earth's orbit change over the course of time?
The strength of this force changes slightly over the course of an orbit, being a bit stronger when the earth is a bit closer - at those times (currently, when the northern hemisphere is having winter) the earth actually orbits a bit faster.
What happens to a satellite in orbit around the Earth?
With gravity, it is pulled back toward Earth. A constant tug-of-war takes place between the satellite's tendency to move in a straight line, or momentum, and the tug of gravity pulling the satellite back. An object's momentum and the force of gravity have to be balanced for an orbit to happen.
What causes an object to orbit the Earth?
An object's momentum and the force of gravity have to be balanced for an orbit to happen. If the forward momentum of one object is too great, it will speed past and not enter into orbit.
What would happen if the Earth was stationary?
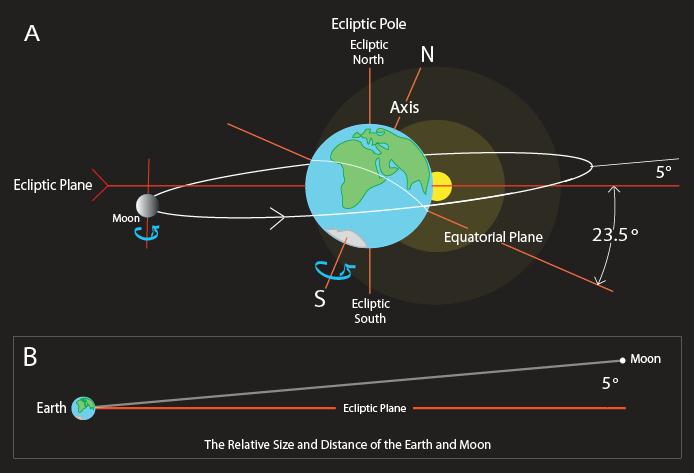
Why is the North Pole not always pointing to the North Star?
Does the Sun keep Earth from flying?
Is the Earth moving around the Sun?
See more
About this website

What keeps the Earth in the orbit?
The Sun's gravitational force is like the tetherball rope, in that it constantly pulls Earth toward it. Earth, however, like the tetherball, is traveling forward at a high rate of speed, which balances the gravitational effect. This means that the planet neither flies out into space nor falls into the Sun.
Why does the Earth not go out of orbit?
In fact, the earth is constantly falling down. It's a good thing too, because that is what keeps the earth from flying out of the solar system under its own momentum. Gravity is a centrally attractive force, meaning that objects in a gravitational field always fall towards the source of the gravity.
Can Earth be pushed out of orbit?
No. The Earth has a lot of mass and moves extremely quickly in its orbit around the Sun; in science speak, we say its 'momentum' is large. To significantly change the Earth's orbit, you would have to impart a very great change to the Earth's momentum.
What holds the Earth and the rest of the universe together?
Gravity is the powerful force that glues our universe together. Gravity helped form our solar system, the planets, and the stars. It holds the planets in orbit around the Sun, and moons in orbit around the planets. The gravitational pull of the Sun and Moon creates the tides on Earth.
18 questions with answers in EARTH'S ROTATION | Science topic
Review and cite EARTH'S ROTATION protocol, troubleshooting and other methodology information | Contact experts in EARTH'S ROTATION to get answers
How often does the International Space Station orbit Earth?
The International Space Station orbits Earth once every 90 minutes. The point at which a planet is closest to the sun is called perihelion. The farthest point is called aphelion. The Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter orbits the moon, which orbits Earth, which orbits the sun. This article is part of the NASA Knows!
What is an orbit?
An orbit is a regular, repeating path that one object in space takes around another one. An object in an orbit is called a satellite. A satellite can be natural, like Earth or the moon. Many planets have moons that orbit them. A satellite can also be man-made, like the International Space Station. Planets, comets, asteroids and other objects in ...
What is the angle of a satellite?
When a satellite orbits Earth, the path it takes makes an angle with the equator. This angle is called the inclination. A satellite that orbits parallel to the equator has a zero-degree orbital inclination. A satellite in a polar orbit has a 90-degree inclination. Words to Know.
What is a geosynchronous orbit?
Geosynchronous orbits are also called geostationary. Any satellite with an orbital path going over or near the poles maintains a polar orbit . Polar orbits are usually low Earth orbits. Eventually, Earth's entire surface passes under a satellite in polar orbit.
How far above the equator do satellites orbit?
Satellites that stay above a location on Earth are in geosynchronous Earth orbit, or GEO. These satellites orbit about 23,000 miles (37,015 km) above the equator and complete one revolution around Earth precisely every 24 hours.
How long does it take for the International Space Station to orbit?
LEO is the first 100 to 200 miles (161 to 322 km) of space. LEO is the easiest orbit to get to and stay in. One complete orbit in LEO takes about 90 minutes. Satellites that stay above a location on Earth are in geosynchronous Earth orbit, or GEO.
What do satellites look like?
They are highly eccentric or "squashed.". They look more like thin ellipses than circles. Satellites that orbit Earth, including the moon, do not always stay the same distance from Earth. Sometimes they are closer, and at other times they are farther away.
How do things stay in orbit?
Perhaps the first question to think about is how they get into orbit in the first place. Try a thought experiment that was first suggested by Sir Isaac Newton himself.
Lighting the Earth - Physics narrative
A Physics Narrative presents a storyline, showing a coherent path through a topic...
Support our manifesto for change
The IOP wants to support young people to fulfil their potential by doing physics. Please sign the manifesto today so that we can show our politicians there is widespread support for improving equity and inclusion across the education sector.
How do satellites stay in orbit?
Perhaps the first question to think about is how they get into orbit in the first place. Let's try a thought experiment that was first suggested by Sir Isaac Newton himself.
Orbits and satellites - Physics narrative
A Physics Narrative presents a storyline, showing a coherent path through a topic...
Support our manifesto for change
The IOP wants to support young people to fulfil their potential by doing physics. Please sign the manifesto today so that we can show our politicians there is widespread support for improving equity and inclusion across the education sector.
How does a satellite maintain its orbit?
So really, a satellites ability to maintain its orbit comes down to a balance between two factors: its velocity (or the speed at which it would travel in a straight line), and the gravitational pull between the satellite and the planet it orbits. The higher the orbit, the less velocity is required.
What is the orbit of the Sun and Moon?
Whereas the orbits of planets about the Sun and the Moon about the Earth were thought to be perfectly circular, Kepler stumbled onto the concept of elliptical orbits. In order for an object to stay in orbit around the Earth, it must have enough speed to retrace its path.
How much gravitational pull does the Earth have?
planets) that this force is felt. In Earth’s case, the gravitational pull is calculated to 9.8 m/s2. However, that is a specific case at the surface of the planet.
Why does a satellite have to travel faster?
From Kepler’s discovery, scientists were also able to infer that the closer a satellite is to an object, the stronger the force of attraction, hence it must travel faster in order to maintain orbit. Next comes an understanding of gravity itself.
What is artificial satellite?
An artificial satellite is a marvel of technology and engineering. The only thing comparable to the feat in technological terms is the scientific know-how that goes into placing, and keeping, one in orbit around the Earth.
When did Sky Lab change its orbit?
That’s exactly what happened with Sky Lab back in July 1979. So every once in awhile they need to boost its orbit back to where it should be. They also sometimes change the orbit in other directions to avoid being hit by dangerous pieces of space junk.
What would happen if the ISS was left unchecked?
Left unchecked, that loss of speed would eventually cause the ISS to fall back to Earth in a meteoric reentry and break up . That’s exactly what happened with Sky Lab back in July 1979.
How fast is the ISS?
Answer: The ISS is continuously falling toward the Earth. But its extreme horizontal speed of 27,724 kilometers per hour (17,227 mph) ensures that by the time it falls that distance the ISS has also moved over 8000 km (5000 miles) horizontally.
Is the ISS falling around the Earth?
One might say the ISS is falling around the Earth, and gravity is what holds it in a circular orbit. That’s a tough concept wrap your head around … how something can be falling toward the Earth and never hit it. So I did an animation of a Space Shuttle orbit that might help you see how this can be.
What would happen if the Earth was stationary?
If the Earth were stationary compared to the Sun, it would fall into the sun under the force of gravity. However the Earth is actually moving sideways compared to the center of the Sun at 3 km/second (~2 miles/second).
Why is the North Pole not always pointing to the North Star?
But, the orbits are pretty stable, because there is a fairly constant gravitational force between the sun and the earth keeping the earth in its orbit.
Does the Sun keep Earth from flying?
The Sun's gravity is enough to keep the Earth from flying off in a straight line, away from the Sun, but not enough to bring the Earth closer in - the Earth is continually changing its direction of movement, but in such a way that it follows a nearly circular path around the Sun.
Is the Earth moving around the Sun?
But the earth was born from a ring of material that was MOVING around the sun on a stable orbit. So after the debris coagulated to form the earth, this initial orbital energy was retained. Hence the earth is moving on a stable orbit of fixed radius.