What is the function of an epiphyseal plate?
What is the main function of the epiphyseal plate quizlet? The epiphyseal plate enables the diaphysis from the bone to improve long until early their adult years. When growth stops, the epiphyseal plate cartilage is substituted for bone, then becoming the epiphyseal line.
What disease is caused from thick epiphyseal plates?
acromegaly seen in adults - after epiphyseal plate has closed enlarged and thickened bones soft tissue can continue to grow chronic hyperglycemia results in diabetes mellitus and atherosclerosis Hyposecretion of hGH
What does the epiphyseal plate represent?
What Are Growth Plates? The growth plate, which is also known by the name of epiphyseal plate, is an area of growing tissues along the end of the long bones in a child. Each long bone has two growth plates one at each end. The growth plate determines how the length and shape of the bone will be once the child attains puberty.
What happens when the epiphyseal plate closes?
When adolescence comes to an end (at about age 18 in females and age 21 in males), the epiphyseal plates close; that is, the epiphyseal cartilage cells stop dividing and bone replaces all remaining cartilage. What does it mean when epiphyseal lines are closed?
What stimulates growth at the epiphyseal plate?
Growth hormone (GH) and insulin-like growth factor-I (IGF-I) are the main stimulators of longitudinal bone growth. They are also important for the acquisition of bone mass during the prepubertal period and maintenance of bone homeostasis throughout life.
How do epiphyseal plates work?
1:062:04Bone elongation - processes at the epiphyseal plate - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipFrom the diathesis to deposit new bony matrix proliferation of chondrocytes increases cell numberMoreFrom the diathesis to deposit new bony matrix proliferation of chondrocytes increases cell number the proliferation results in moving the epiphysis. Away from the diathesis.
How is the growth plate formed?
The Growth Plate Endochondral bone formation begins early in the embryonic period when mesenchymal cells form condensations. These cell clusters differentiate into chondrocytes, which proliferate to form the growth plate or physis.
What are the steps of bone growth at the epiphysis?
Abstract. The process of bone formation is called osteogenesis or ossification. After progenitor cells form osteoblastic lines, they proceed with three stages of development of cell differentiation, called proliferation, maturation of matrix, and mineralization.
At which age growth plates close?
When Do Growth Plates Close? Growth plates usually close near the end of puberty. For girls, this usually is when they're 13–15; for boys, it's when they're 15–17.
Can you still grow if your growth plates are closed?
When puberty ends, the growth plates close, and the body does not produce new bone tissue. Although most people don't gain height after growth plates close, some individuals may grow a few more centimeters in early adulthood. However, height growth should not be expected after the growth plates are closed.
What activates growth plate?
The major systemic hormones that regulate longitudinal bone growth during childhood are GH and IGF-I, thyroid hormone (T3 and T4), and glucocorticoids (GC), whereas during puberty the sex steroids (androgens and estrogens) contribute a great deal to this process.
Which hormones promote epiphyseal plate growth and closure?
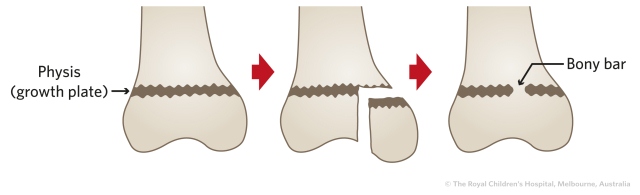
Estrogen and testosterone release at puberty initiates closure of the epiphyseal plates. When bone growth is complete, the epiphyseal cartilage is replaced with bone, which joins it to the diaphysis. Fractures of the epiphyseal plates in children can lead to slow bone growth or limb shortening.
What is the last process to occur in the epiphyseal plate?
Lengthening of Long Bones Long bones stop growing at around the age of 18 in females and the age of 21 in males in a process called epiphyseal plate closure. During this process, cartilage cells stop dividing and all of the cartilage is replaced by bone.
What are the 5 stages of bone growth?
Although bone initially forms during fetal development, it undergoes secondary ossification after birth and is remodeled throughout life....Intramembranous OssificationDevelopment of ossification center.Calcification.Formation of trabeculae.Development of periosteum.
What are the 4 steps of bone development?
There are four stages in the repair of a broken bone: 1) the formation of hematoma at the break, 2) the formation of a fibrocartilaginous callus, 3) the formation of a bony callus, and 4) remodeling and addition of compact bone.
What are the four steps of bone growth?
Following the fracture, secondary healing begins, which consists of four steps:Hematoma formation.Fibrocartilaginous callus formation.Bony callus formation.Bone remodeling.
How are bones with growth plates formed?
Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's chondrocytes are under constant division by mitosis.
Can we reopen growth plates?
Naturally - no. This is absolutely not possible since our body simply lose the ability to grow taller. It's like you can't grow a pair of wings. There is no way at this point of time to reverse the plates ossification process.
Can growth plates close at 14?
When bones finish growing, the growth plates close. Girls generally stop growing and reach their maximum height between ages 14 and 16, and boys finish their growth between 16 and 18 years of age.
Can growth plates close before puberty?
If a child starts puberty very early, their growth plates may close at a young age and the child will remain small. If a child starts puberty late, it is possible that there may be a hormonal problem and this may lead to reduced growth during puberty.
What is hereditary multiple exostoses?
Hereditary multiple exostoses is a genetic condition that is caused by growth irregularities of the epiphyseal plates of the long bones of the upper and lower limbs. It usually results in limb deformities and a certain degree of functional limitations.
What is the epiphyseal plate?
The epiphyseal plate (or epiphysial plate, physis, or growth plate) is a hyaline cartilage plate in the metaphysis at each end of a long bone. It is the part of a long bone where new bone growth takes place; that is, the whole bone is alive, with maintenance remodeling throughout its existing bone tissue, ...
What causes short stature?
However, various other types of osteochondrodysplasias can cause short stature and generalized deformities of bones and joints due to abnormal function of growth plate cartilage cells.
What happens to chondrocytes in puberty?
In puberty increasing levels of estrogen, in both females and males, leads to increased apoptosis of chondrocytes in the epi physeal plate.
What is Salter Harris fracture?
Salter–Harris fractures are fractures involving epiphyseal plates and hence tend to interfere with growth, height or physiologic functions. Osgood-Schlatter disease results from stress on the epiphyseal plate in the tibia, leading to excess bone growth and a painful lump at the knee.
What is the most common defect in epiphyseal plate?
The most common defect is achondroplasia, where there is a defect in cartilage formation.
What is the role of endochondral ossification in bone formation?
Endochondral ossification is responsible for the initial bone development from cartilage in utero and infants and the longitudinal growth of long bones in the epiphyseal plate. The plate's chondrocytes are under constant division by mitosis. These daughter cells stack facing the epiphysis while the older cells are pushed towards the diaphysis. As the older chondrocytes degenerate, osteoblasts ossify the remains to form new bone. In puberty increasing levels of estrogen, in both females and males, leads to increased apoptosis of chondrocytes in the epiphyseal plate. Depletion of chondrocytes due to apoptosis leads to less ossification and growth slows down and later stops when the entire cartilage have become replaced by bone, leaving only a thin epiphyseal scar which later disappears.
What is the role of cartilage in articular cartilage?
Articular cartilage performs a vital buffering function, with the ECM providing a smooth, low-friction surface at sites of skeletal articulation. Aggrecan, the principal proteoglycan of cartilage matrix, consists of a protein core with covalently bound sulphated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) chains, and these GAGs retain water in order to maintain themselves in an optimally spaced configuration. Upon compression, water is squeezed from the matrix, and sulphated GAGs are brought into close contact with one another. Upon release of compression, repulsive interactions and the re-absorption of water returns GAGs to their optimally spaced configuration, returning the cartilage ECM to its turgid state (Roughley and Mort, 2014 ). The dynamic expulsion and re-absorption of water by cartilage matrix allows this tissue to act as an effective buffer against compressive forces.
What is the radiolucent line in osteodystrophy?
Radiographically, the initial finding in hypertrophic osteodystrophy is a thin, radiolucent line in the metaphysis parallel to the epiphyseal plate, especially in the radius (Figure 24-7 ). Secondarily, there is an extraperiosteal cuff of calcification along the metaphysis ( Figure 24-8 ). The lucent line disappears and is replaced by an increased radiodensity. If relapses occur, a new radiolucent line appears between the physis and the radiodense region. 21 As the dog matures, these extraperiosteal thickenings often regress ( Figures 24-8 and 24-9) but may leave a permanently thickened metaphysis. 22 Stunting of axial growth and long-bone angular deformity may be observed in a small percentage of severely affected dogs. Pathologic fracture has been documented but is extremely rare.23
What is the epiphyseal plate?
Epiphyseal Plate. In children and young adults, the epiphyses are separated from the diaphysis by epiphyseal cartilage or plates, where bone grows in length. Estrogen and testosterone release at puberty initiates closure of the epiphyseal plates.
What happens when bone is replaced with bone?
When bone growth is complete, the epiphyseal cartilage is replaced with bone, which joins it to the diaphysis. Fractures of the epiphyseal plates in children can lead to slow bone growth or limb shortening. The coordinated activity of these bone cells allows bone to grow, repair itself, and change shape.
What is the first zone of osteogenesis?
Starting from the epiphyseal end of the plate and working inward toward the shaft, the first zone is a layer of resting cartilage ( Fig. 4.14). Immediately beneath is a region of chondrocyte proliferation. The resulting daughter cells line up into columns of flattened cells, much like a stack of pancakes. These cells hypertrophy, changing the shape of the flattened cells to an almost cuboidal configuration. This change of shape expands the epiphyseal plate toward the end of the bone, thereby lengthening the bone. Then the hypertrophied chondrocytes secrete type X collagen into the cartilaginous matrix, and the matrix begins to calcify. With the calcification of the matrix, most of the chondrocytes die. The dead cells and parts of the matrix are removed, leaving behind some vertical columns of calcified matrix. Blood vessels and other red marrow constituents fill in the spaces between the columns of remaining calcified cartilage matrix, and osteogenic cells accompanying them line up on the columns and begin to deposit a layer of osteoid upon the cartilage remnants. At the same time, chondrocytic proliferation on the epiphyseal side of the plate continues, adding to the total mass of viable cartilage.
What are the features of infantile scurvy?
(1950) suggest that scurvy is characterised by fractures within the trabecular bone at the epiphyseal plate in individuals in whom endochondral bone formation should be taking place. This leads to an area with limited trabecular development, as illustrated in sections of a scorbutic and normal guinea pig rib shown in Figure 4.11. These investigators observed fragments of mineralised trabecular bone lying at various angles in individuals who had scurvy, or who had recently started to recover (but importantly not all individuals with scurvy showed such changes). Fractures caused by scurvy may be present for a couple of months after recovery, but, this type of fracture is not pathognomic ( Follis et al., 1950 ). Histological changes can be used to help suggest a diagnosis in archaeological bone, but other features (macroscopic and radiological) would need to be present for a firm diagnosis to be considered.
What is Figure 4.14?
Figure 4.14. Structure and dynamics of an epiphyseal plate in a growing long bone.
What hormones are produced by the pituitary gland during puberty?
In the period of rapid growth at the age of puberty, the bone marrow produces a large amount of HGH and other hormones responsible for the stimulation of growth plates. These hormones are secreted from the pituitary gland under the influence of the thyroid and are then transported to the bone marrow. The growth plates are stimulated and expand rapidly and in due course of time to reach the epithelium, the outer covering of the bone that undergoes a metamorphosis.
What is the structure of the bone called?
As the epithelium hardens it forms a solid structure known as osteoid tissue. Osteoid tissue is a fissured mass of the bone termed as cranium , which is made up of a cancellous matrix. the expansion of the adult bones is facilitated by the method of bone growth at the epiphyseal plate. During the early growth period of children, the process of bone accretion takes place at the osteoid tissue. As the children get older, the process of bone accretion is inhibited by the effects of the HGH produced in the body. This inhibits the growth of the bone till the stage of adolescence.
What is the main mechanism of growth in the human body?
The growth of the adult human body continues throughout its lifetime. The main mechanism for the growth of the body is the stimulation of the human growth hormone. Human growth hormone is secreted in the human pituitary gland and stimulates the growth of the cells throughout the human body. There are various pituitary glands in the body and each secretes different types of HGH. While some secrete a specific type of HGH, the others stimulate the production of the various other hormones and consequently initiate the process of bone growth at the bone marrow.
What are the factors that affect bone growth?
There are many different factors that affect the process of bone growth in the bone marrow. They include age, gender, ethnicity, and nutrition. For the healthy and normal growth of bones, it is important to keep yourself fit and active. Apart from exercise and physical activity, there are certainly other things you can do to keep your bones strong and healthy. It is important to have a well-balanced diet and eat a balanced amount of food on a daily basis.
Where is the epiphyseal plate?
During the period when a person is growing up, the epiphyseal plate – which is a structure at the back of the thigh, right below the tail – contains lots of bones. Whenever a body part has to grow, it grows through the help of the epiphyseal plate. This process of bone growth at the epiphyseal plate is known as intramembranousization. When the growing process takes place at the level of the bone – as it does during the development of the breast, finger, and toenails – the process of bone growth at the epiphyseal plate goes through two distinct processes. the method of bone growth at the epiphyseal plate is understood as intramural growth and therefore the process of bone growth at the dermal layer is named dermal matrix expansion.
Where are the growth plates located?
Growth plates are present at the base of the hairs and at the base of the teeth in humans. The epiphyseal plate is present at the back of the thigh. In the period of rapid growth at the age of puberty, the growth plate becomes very big in size and extends across the whole of the thigh. In such a situation, the muscles and ligaments in the thigh begin to expand and stretch in response to the growing pressure created by the new size of the bone marrow. This can happen when young adolescents begin to exercise vigorously. It is believed that the process of bone growth at the epiphyseal plate is similar to the process of skeletal accretion in response to the growth in weight experienced by the children after puberty.
What are the factors that influence pubertal growth?
Important influencing factors include chondrocyte differentiation capacity, multiple molecular pathways active in the growth plate, and growth hormone-insulin-like growth factor -I axis activation and epiphyseal fusion through estrogen and its receptors. However, the exact mechanisms of these phenomena are still unclear. A better understanding of the detailed processes involved in the pubertal growth spurt and growth plate closure in longitudinal bone growth will help us develop methods to efficiently promote pubertal growth and delay epiphyseal fusion with fewer adverse effects.
What is the growth plate?
The growth plate is located between the epiphysis and metaphysis and composed of three zones (resting, proliferative, and hypertrophic zone). Each zone contains various chondrocytes in different stages of differentiation. The resting zone contains small chondrocytes that act as stem-like cells with a slow replication rate. The proliferative zone is composed of flat chondrocytes that line up along the long axis of the bone and have high replication rates. The hypertrophic zone is the layer of chondrocytes undergoing terminal differentiation and has an increased thickness, surrounding calcified matrix, and attracted factors for bone and vessel formation5).
What is the process of growth in height?
Growth in height is driven by elongation of long bones due to chondrogenesis at the epiphyseal plates, also known as the growth plate. This process results from chondrocyte proliferation, hypertrophy, and extracellular matrix secretion. It is organized by complex networks of nutritional, cellular, paracrine, and endocrine factors1).
What happens during a pubertal growth spurt?
During the pubertal growth spurt, proliferation and differentiation of chondrocytes, secretion of extracellular matrix , calcification of the hypertrophic zone, invasion and differentiation of osteoblast, and formation of blood vessel repeat continuously in the growth plate5,6).
Which receptor is secreted by prehypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes?
IHH is secreted by prehypertrophic and hypertrophic chondrocytes and positively regulates PTHrP production. And it also has independent effects on chondrocyte differentiation18). BMP signaling across the growth plate is considered to contribute to the progressive differentiation of resting to proliferative to hypertrophic chondrocytes20,21,22). FGF and its receptor (FGFR) system are also important for growth plate development. Results from various in vivo studies indicate that FGFR1 and FGFR3 are growth-inhibiting, while FGFR-2 is growth-promoting23,24).
Which paracrine factors are secreted by periarticular chondrocytes?
Of these paracrine factors, the best studied one is PTHrP that is known as secreted by periarticular chondrocytes of long bones16,17,18). Hirai et al.19)reported that PTHrP diffuses across the growth plate cartilage maintaining chondrocytes in the proliferative state.
Does estrogen stimulate growth?
During puberty, estrogen induces the stimulation of the GH-IGF-I axis and a pubertal growth spurt. In the classical pathway, estrogen acts after binding with its receptor (estrogen receptor, ER). There are two subtypes of ER, ERα, and ERβ. Both subtypes seem to be involved in the augmentation of GH secretion and are expressed in the resting, proliferative, and hypertrophic zones of the growth plate. Indirect evidence suggests that epiphyseal fusion occurs when the proliferative capacity of growth plate chondrocytes is exhausted and estrogen acts by advancing growth plate senescence. Therefore, the binding of estrogen with each subtype of ER is thought to be related to the pubertal growth spurt and epiphyseal fusion32,33,34,35).
Why do girls stop growing after their period?
Hence, an increase in levels of estrogen when the girl menstruates for the first time is partly the reason why girls stop growing within approximately 2 years from the time they get their first period. [ 1 ]
How do chondrocytes die?
Immature (stem-like) chondrocytes begin by multiplying rapidly, they mature and and finally die, there by forming new bone tissue to on the remaining cartilage matrix. For details on how bone growth is mediated in the growth plate zone, visit how long bones grow.
What hormones accelerate the growth plate?
Thus it’s the increased levels of estrogen towards the end of puberty that accelerate or catalyze the fusion of the growth plate.
What is the purpose of X-rays for bones?
X- ray scans can be taken for bones under investigation to check if growth plates are still open. X – ray showing Open and Closed plates. How Growth takes place at the Epiphyseal Plate. In brief, skeletal growth at the epiphyseal plate is active and constantly changing. There is the bony part, the fibrous and cartilaginous part ...
How long does it take for a growth plate to close?
This means that in most cases, growth plates close between 14 and 16 years for girls and between 16 and 19 years for boys. In case of Precocious puberty, the child transforms to an adult earlier than expected. The growth plate closes earlier leading to short stature. If a girl enters puberty before 8 years or if a boy enters puberty before 9 years, ...
Why does the growth plate eventually replace bone?
The growth plate is eventually replaced by bone or closes because proliferation of cells in growth plates declines as we age before it stops completely towards the end of puberty.
Why are rabbits given resveratrol?
Rabbits were chosen because the timing of growth plate fusion in rabbits normally occurs at the time of sexual maturation, just like in humans but not in small rodents. Resveratrol treatment in rabbits improved longitudinal bone growth and delayed growth plate closure.