Ethylene gas leads to fruit ripening and eventually spoiling in the following ways:
- The softness of a fruit depends on the condition of its cell walls, and the cell walls are made hard by the presence of polysaccharides. ...
- Enzymes that are activated by ethylene break down these polysaccharides and the cell walls soften. ...
- When the ethylene is produced in excess, your fruit will soften beyond normal levels, and start going bad.
What fruits produce ethylene gas?
and some common ethylene-sensitive foods:
- asparagus.
- bananas (unripe)
- broccoli.
- blackberries.
- brussels sprouts.
- cabbage.
- carrots.
- cauliflower.
What does fruit produce ethylene?
Ethylene (C2H4) is a gas produced naturally by fruits and vegetables during its metabolism. It is a hormone that controls the growth, ripening and ageing of fruits and vegetables. During the process of ripening, the ethylene produces a series of positive physiologic effects in vegetable products: The fruit becomes tastier and more energetic due ...
How is ethylene produced in plants?
List of plant responses to ethylene
- Seedling triple response, thickening and shortening of hypocotyl with pronounced apical hook.
- Stimulation of Arabidopsis hypocotyl elongation
- In pollination, when the pollen reaches the stigma, the precursor of the ethylene, ACC, is secreted to the petal, the ACC releases ethylene with ACC oxidase.
- Stimulates leaf senescence
Why do fruits change color when they ripen?
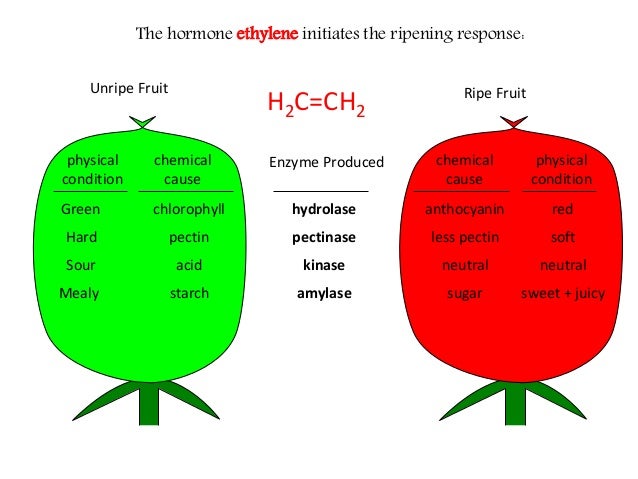
Why do fruits change color when they ripen? The green colour of the unripe fruit is due largely to the presence of chlorophylls, and the development of different colours during ripening is due to the disappearance of these pigments and the synthesis of carotenoids. Anthocyanins also make a contribution to colours in some ripe fruits and vegetables.
Why is ethylene used to ripen fruit?
Its level in under-ripe fruit is very low, but as the fruits develop, they produce larger amounts of the chemical that speeds up the ripening process or the stage of ripening known as the “climacteric.” Recent studies have shown ethylene regulates the expression of several genes, which are involved in fruit ripening.
How does ethylene affect fruit quality?
Ethylene enhances the appearance of many fruit by stimulating their ripening. Rapid development of the characteristic color can produce a higher quality fruit since less time will have elapsed from harvest for anabolic reactions to occur.
Why is ethylene called the ripening hormone?
It acts at trace levels throughout the life of the plant by stimulating or regulating the ripening of fruit, the opening of flowers, the abscission (or shedding) of leaves and, in aquatic and semi-aquatic species, promoting the 'escape' from submergence by means of rapid elongation of stems or leaves.
What causes fruit to ripen faster?
The key here is ethylene. Ethylene is a natural gas given off by fruit that helps in ripening. To speed things up even faster, we recommend adding in an apple or banana! These fruits give off more ethylene than other fruits and will really aid in moving the ripening process along!
What is the main effect of ethylene?
Ethylene effects include: fruit ripening, induction of flowering, loss of chlorophyll, abortion of plant parts, stem shortening, abscission (dropping) of plant parts, epinasty (stems bend), and dormancy. It can be produced when plants are injured, either mechanically or by disease.
Which enzyme is responsible for fruit ripening?
Pectin degrading enzymes such as polygalacturonase, pectin methyl esterase, lyase, and rhamnogalacturonase are the most implicated in fruit-tissue softening.
How does ethylene affect plant growth?
The gaseous hormone ethylene plays a key role in plant growth and development, and it is a major regulator of stress responses. It inhibits vegetative growth by restricting cell elongation, mainly through cross-talk with auxins.
What plant hormone is used for fruit ripening?
EthyleneEthylene is known to be a key player of plant aging, including fruit ripening, and flower and leaf senescence (Abeles et al., 1992).
What is the use of ethylene?
Ethylene is used in the production of fabricated plastics, antifreeze; making fibers; to manufacture ethylene oxide, polyethylene for plastics, alcohol, mustard gas, and other organics.
How can you speed up the ripening of fruit?
PAPER BAG METHOD All you need to ripen fruit is a paper bag. Yes, really! Simply place the unripe fruit in a paper bag and it will trap the ethylene gas, causing the fruit to ripen quicker! Place a ripe banana or apple in the bag with the unripe fruit to speed the process up even more!
Why do bananas ripen so fast?
Ripe fruits produce ethylene, and unripe fruits ripen faster when exposed to ethylene. Ethylene speeds up maturation and abscission of fruits. This applies to bananas too.
Which fruit has the most ethylene gas?
AppleSome of these fruits which produce the most ethylene are Apple, Kiwi, Banana, Peaches, Pears, Melons, Apricots, Avocados, Peppers, Tomatoes, Cantaloupe, etc. These must be stored away from other vegetables and fruits even if preserved in the fridge.
How does the ripening process affect the availability of some fruits?
How does the ripening process affect the availability of some fruits? The fruit reaches its full size; is pulp or flesh becomes soft and tender; its color changes.
What does ethylene do in plants?
Ethylene is regarded as a multifunctional phytohormone that regulates both growth, and senescence. It promotes or inhibits growth and senescence processes depending on its concentration, timing of application, and the plant species.
What happens when fruit ripens?
What happens as fruit ripens? As fruit continues to grow, its storage cells expand, engorging it with water, sugars, starches, organic acids, vitamins, and minerals, and its skin turns from green to other appealing colors, such as red, orange, or yellow.
What are the harmful effects of using these artificially ripened fruits?
It causes symptoms like headache, dizziness, high sleepiness, memory loss, cerebral oedema, numbness in the legs and hands, general weakness, cold and damp skin, low blood pressure and seizure.
Why is it important to know the ripening pattern of fruits?
Understanding the ripening pattern of the fruits you grow is very important for developing management strategies during development, determining their optimum harvest date, as well as designing postharvest storage practices.
What is the process of ripening fruit?
Fruit ripening is the set of processes that occur from the later stages of growth and development until the fruit is ready to be consumed. Fruit ripening results in changes in fruit quality characteristics. The firmness of the fruit flesh typically softens, the sugar content rises, and acid levels are reduced. Aroma volatiles are released, and the true flavor of the fruit develops. The color of fruit typically darkens, the skin and flesh soften, and the green background color fades.
How is ethylene measured?
Ethylene is a gas and is measured in the laboratory using a gas chromatograph, an analytical instrument that can measure different components in a gaseous sample. Ethylene production can be measured non-destructively by placing a single, or multiple fruits, inside a sealed container. After a determined amount of time, the gas inside the container is withdrawn with a syringe and analyzed with the gas chromatograph. For apples, a needle can be injected in the core cavity of the fruit and a gas sample is withdrawn for ethylene measurement. The amount of ethylene that a fruit produces can be used to determine the ripeness of a fruit and its storability potential.
What is Ethephon used for?
This can be applied as a preharvest growth regulator to promote fruit ripening. This would be used to accelerate the ripening process. However, Ethephon also accelerates fruit abscission, and may negatively impact fruit storability.
What hormone is used to ripen fruit?
Ethylene is a gaseous plant hormone that plays an important role in inducing the ripening process for many fruits, together with other hormones and signals. An unripe fruit generally has low levels of ethylene. As the fruit matures, ethylene is produced as a signal to induce fruit ripening. Ethylene production continues to increase after harvest, thus decreasing fruit shelf-life, storability capacity, and increasing its susceptibility to pathogen attacks. Thus, monitoring and managing ethylene production rates is of crucial importance so fruit does not become over-ripe on the tree or during postharvest storage, which will render it unmarketable and decrease profitability.
What are the two types of fruits?
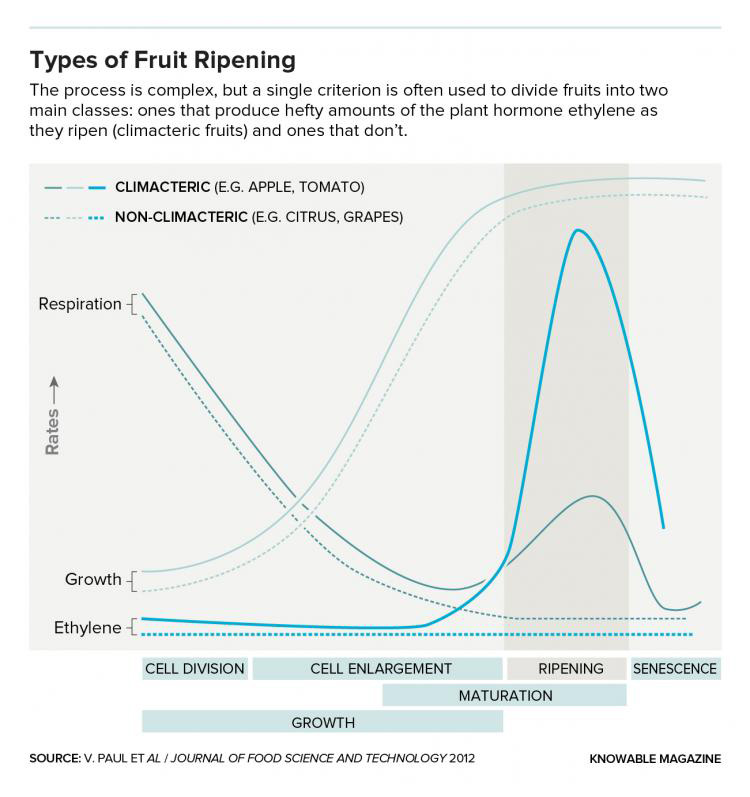
Fruits are generally divided in two categories: climacteric and non-climacteric fruits. In general terms, climacteric fruits can ripen after harvest, whereas non-climacteric fruits cannot ripen after harvest. Climacteric fruit ripening is characterized by an increased rate of respiration, and then a burst of ethylene biosynthesis during ripening (Figure 1). The production of ethylene in climacteric fruits is also known as autocatalytic, which means an initial concentration of ethylene causes an increase in production of ethylene. This means once ethylene production starts, the fruit naturally increases the amount of signal made accelerating ripening. Some examples of clima cteric fruits include peaches, bananas, apples, and avocados (Figure 2).
What are some examples of nonclimacteric fruits?
Some examples of nonclimacteric fruits include cherries, grapes, strawberries, and blueberries (Figure 2).
What is the cellular change of ethylene?
Cellular quantities of ethylene can reach a certain level and physiological changes called ripening will begin. The amount of ethylene can vary from fruit to fruit and is also affected by other gases like oxygen or carbon dioxide. The increase in ethylene follows changes in fruit texture (cell wall material is metabolized into smaller molecular weight units producing a softer texture), composition (generally increase in sugars and decrease in acids) and physiology (pigments - bananas go from green to yellow, and volatile flavor compounds increase in concentration.
Why do vegetables use ethylene gas?
For example, vegetable growers use ethylene gas to cause the ripening of many different fruits and vegetables such as tomatoes. The growers pick the tomatoes when they're large and green, then gas them to make them ripen.
What hormones regulate plant growth?
Typically, these hormones regulate plant growth and development, just as they do in animals, including humans. Ethylene is commonly known as the "senescence hormone" and has been well studied. It is actually a gaseous hormone and it hastens fruit ripening.
Does a transcription factor affect ripening specific genes?
The quick and easy answer to your question is that it either acts as a transcription factor or affects the activation or synthesis of a transcription factor controlling the expression of ripening-specific genes.
Why is ethylene produced?
Ethylene is produced in response to removing the fruit from its parent. You can design an experiment to determine whether fruit ripens more quickly on or off the plant. Consider using a smaller fruit, such as tomatoes, which you can find on/off the vine in supermarkets.
What is the purpose of the ripening experiment?
The purpose of this experiment is to measure fruit ripening caused by the plant hormone ethylene, by using an iodine indicator to detect the conversion of plant starch to sugar. A Hypothesis: The ripening of an unripe fruit will be unaffected by storing it with a banana.
How to tell if a fruit is ripe?
You can estimate how ripe a fruit is by whether or not it is darkened after painting it with an iodine solution. The unripe fruit is starchy, so it will be dark. The riper the fruit is, the more starch will have been converted to sugar. Less iodine complex will be formed, so the stained fruit will be lighter.
How is ethylene released?
Ethylene is produced and released by rapidly-growing plant tissues. It is released by the growing tips of roots, flowers, damaged tissue, and ripening fruit. The hormone has multiple effects on plants. One is fruit ripening. When the fruit ripens, the starch in the fleshy part of the fruit is converted to sugar.
What happens when a fruit ripens?
When the fruit ripens, the starch in the fleshy part of the fruit is converted to sugar. The sweeter fruit is more attractive to animals, so they will eat it and disperse the seeds. Ethylene initiates the reaction in which the starch is converted into sugar.
How to test for ripe pear?
Place one unripe pear or apple and one banana in each of the test bags. Seal each bag. Place the bags together. Record your observations of the initial appearance of the fruit. Observe and record the changes to the appearance of the fruit each day.
How to get iodine out of a pear?
Pour the iodine stain into the bottom of the shallow tray, so that it fills the tray about half a centimeter deep. Cut the pear or apple in half (cross-section) and set the fruit into the tray, with the cut surface in the stain. Allow the fruit to absorb the stain for one minute.
Why does the respiratory climacteric begin soon after the fruit is harvested?
The respiratory climacteric begins soon after the fruit is harvested because the tissue no longer receives from the shoot system a substance which inhibits ripening ; this substance may act by lowering the sensitivity of the fruit to ethylene.
Does ethylene stimulate ripening?
Recent studies employing gas chromatography show that an amount of ethylene large enough to stimulate ripening is always present within a fruit before the respiratory climacteric begins. This fact and data from experiments in which fruits were exposed to a partial vacuum or varying concentrations of O(2), CO(2), and ethylene oxide reinforces the view that ethylene is a ripening hormone. The respiratory climacteric begins soon after the fruit is harvested because the tissue no longer receives from the shoot system a substance which inhibits ripening; this substance may act by lowering the sensitivity of the fruit to ethylene. The threshold for ethylene action is also influenced by the composition of the atmosphere, for O(2) is a substrate in the reaction activated by ethylene and CO(2) inhibits the action of ethylene by competing with the olefin for the receptor site. Experiments indicate that ethylene is derived from acetate or acids of the Krebs cycle and acts by binding to a metal receptor site in the tissue.
What are the effects of ethylene gas on fruit ripening?
The effects of ethylene gas and fruit ripening may also be affected by other gases, such as carbon dioxide and oxygen, and varies from fruit to fruit.
What is the purpose of ethylene gas in fruits and vegetables?
Ethylene gas in fruits and vegetables is actually a plant hormone which regulates the plant’s growth and development as well as the speed at which these occur , such as hormones do in humans or animals.
How to use ethylene gas?
As a plant messenger that signals the plant’s next move, ethylene gas can be used to trick the plant into ripening its fruits and vegetables earlier. In commercial environments, farmers use liquid products that are introduced pre-harvest. The consumer may do this at home by simply placing the fruit or vegetable in question inside a paper bag, like a tomato. This will concentrate the ethylene gas inside the bag, allowing the fruit to ripen more quickly. Do not use a plastic bag, which will trap moisture and may backfire on you, causing the fruit to rot.
What are the effects of ethylene gas?
Other effects of ethylene gas are loss of chlorophyll, abortion of plant foliage and stems, shortening of stems, and bending of the stems (epinasty). Ethylene gas can be either a good guy when used to hasten ripening of fruit or a bad guy when it yellows vegetables, damages buds, or causes abscission in ornamental specimens.
How to ripen fruit at home?
The consumer may do this at home by simply placing the fruit or vegetable in question inside a paper bag, like a tomato. This will concentrate the ethylene gas inside the bag, allowing the fruit to ripen more quickly. Do not use a plastic bag, which will trap moisture and may backfire on you, causing the fruit to rot.
Where is ethylene produced?
Ethylene may be produced not only in ripening fruit, but from internal combustion exhaust engines, smoke, rotting vegetation, natural gas leaks, welding, and in some types of manufacturing plants.
When was ethylene gas discovered?
Ethylene gas was first discovered about 100 years ago when a student noticed that trees growing near gas street lamps were dropping leaves more rapidly (abscising) than those planted at a distance from the lamps.
What Does Ethylene Do to Fruit?
Ethylene is an aging hormone in plants. It leads to breakdown of the polysaccharides which make the skin of a fruit hard when it is unripe. When these polysaccharide chains are broken down, the skin of the fruit softens.
What is the effect of ethylene on other fruits and vegetables?
Ethylene gas is responsible for yellowing, increase in toughness, softening and rotting of vegetables such as kale, peppers, potatoes and tomatoes.
How to differentiate between fruits that produce high levels of ethylene and those that are highly sensitive to the gas?
An easy way to differentiate between fruits that produce high levels of ethylene and those that are highly sensitive to the gas is the classification into climacteric and non-climacteric types.
Why do fruits ripen faster?
Ethylene gas helps the fruits to ripen faster, however, it’s advisable to store them separately once they ripen and away from ethylene-sensitive foods as the gas can cause overripening and speed up rotting. Ethylene works by breaking down chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color on the skin of most fruits.
What causes a fruit to ripen?
Ethylene gas leads to fruit ripening and eventually spoiling in the following ways: 1 The softness of a fruit depends on the condition of its cell walls, and the cell walls are made hard by the presence of polysaccharides. The most common polysaccharides are cellulose, hemicellulose, and pectin. 2 Enzymes that are activated by ethylene break down these polysaccharides and the cell walls soften. This is why we feel the softness of fruit to determine its level of ripeness. 3 When the ethylene is produced in excess, your fruit will soften beyond normal levels, and start going bad.
What hormone is needed to ripen a fruit?
For a fruit to ripen naturally or artificially, it needs the hormone ethylene. Ethylene gas speeds up the ripening and activates the changes in the color, texture, and flavor of the fruit. But why should you know ethylene producing fruits?
How does ethylene work?
Ethylene works by breaking down chlorophyll, which is responsible for the green color on the skin of most fruits . When chlorophyll breaks down, the fruit produces and accumulates anthocyanin which is responsible for purple and blue hues in fruit. Other fruits will produce and accumulate carotenoids, which are responsible for yellow ...
How does ethylene affect plant life?
Presence of ethylene in amounts ranging from a few parts per billion (ppb) to a few parts per million (ppm) can reduce plant vigour, decrease life of various plant parts and reduce stock quality.
What is the effect of ethylene?
The overall effect of Ethylene is to hasten ripening, aging and eventually spoilage.
What is the ripening hormone?
Ethylene – The Ripening Hormone. Ethylene gas (C 2 H 4) is an odorless, colorless gas that exists in nature and which is triggered at maturity in climacteric fruits. . Ethylene, also known as the ‘death or ripening hormone’ plays a regulatory role in many processes of plant growth, development and eventually death.
What are the consequences of high concentrations of ethylene in warehouses and cold stores?
High concentration of ethylene causes premature aging and rotting of fruits and vegetables and wilting ...
What are the advantages of ethylene control?
Advantage of Ethylene Control. Extends the life cycle of the fruit/ vegetable after plucking. Warehouse owners can easily preserve freshness and reduces spoilage of fruits and vegetables. They are able to meet increasing demands of non-seasonal fruits and vegetables.
What is artificial ripening?
At the latter part of post-harvest, artificial ripening by using ethylene is general practice as it ensures that the produce reaches the consumers (retail outlets) with a degree of ripeness, which brings out its best in terms of taste, color, texture and nutritional value. One of the most common examples is the ‘forced’ ripening of bananas during high demand periods.
Where should ethylene be vented?
Ethylene should by vented from the ripening room to the outside after the exposure period is