
The Effect of the Expansionary Monetary Policy
Monetary policy
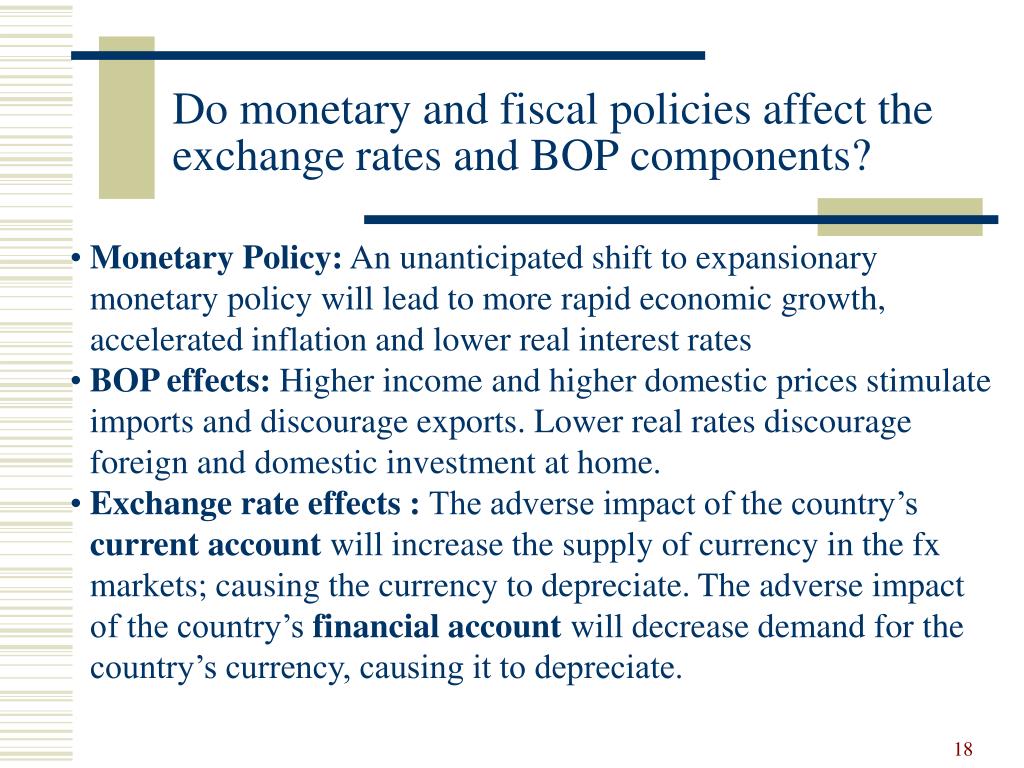
Monetary policy is the process by which the monetary authority of a country controls the supply of money, often targeting an inflation rate or interest rate to ensure price stability and general trust in the currency.
What is the effect of monetary policy on aggregate demand?
The Effect of the Expansionary Monetary Policy on Aggregate Demand When interest rates are cut (which is our expansionary monetary policy), aggregate demand (AD) shifts up due to the rise in investment and consumption. The shift up of AD causes us to move along the aggregate supply (AS) curve, causing a rise in both real GDP and the price level.
How does expansionary monetary policy work to increase real GDP?
In our model of aggregate supply and aggregate demand, how does expansionary monetary policy work to increase real GDP and the price level? Sort the following in the order in which they occur. 1. The Federal Reserve buys bonds 2. The federal funds rate falls 3. Banks have excess reserves and lend more¸ causing the money supply to increase. 4.
What is expansionary fiscal policy in macroeconomics?
Expansionary fiscal policy is the use of government spending, taxation and transfer payments to stimulate aggregate demand. Whether the government is increasing its own purchases, lowering taxes or raising transfer payments, expansionary fiscal policy always increases at least one component of aggregate demand.
How does crowding out affect expansionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary fiscal policy is illustrated as an increase, or a rightward shift, of the aggregate demand curve (AD). This means that real GDP increases and so does inflation (or the price level). One of the things that reduces the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy is what economists call 'crowding out.'
How does expansionary monetary policy affect aggregate demand?
An expansionary (or loose) monetary policy raises the quantity of money and credit above what it otherwise would have been and reduces interest rates, boosting aggregate demand, and thus countering recession.
Does expansionary monetary policy increase demand?
Expansionary monetary policy is when a central bank uses its tools to stimulate the economy. That increases the money supply, lowers interest rates, and increases demand.
Does monetary policy shift aggregate demand?
Monetary policy affects interest rates and the available quantity of loanable funds, which in turn affects several components of aggregate demand. Tight or contractionary monetary policy that leads to higher interest rates and a reduced quantity of loanable funds will reduce two components of aggregate demand.
Does expansionary policy shift aggregate demand?
Expansionary fiscal policy occurs when the Congress acts to cut tax rates or increase government spending, shifting the aggregate demand curve to the right.
What is the effect of expansionary monetary policy?
Effects of an Expansionary Monetary Policy An expansionary monetary policy reduces the cost of borrowing. Therefore, consumers tend to spend more while businesses are encouraged to make larger capital investments.
What policy increases aggregate demand?
Some typical ways fiscal policy is used to increase aggregate demand include tax cuts, military spending, job programs, and government rebates. In contrast, monetary policy uses interest rates as its mechanism to reach its goals.
What causes aggregate demand to shift up?
Since modern economists calculate aggregate demand using a specific formula, shifts result from changes in the value of the formula's input variables: consumer spending, investment spending, government spending, exports, and imports.
What happens to aggregate demand when money supply increases?
As such, changes in the money supply induces changes in aggregate demand. An increase in the money supply increases aggregate demand and a decrease in the money supply decreases aggregate demand.
What happens to aggregate demand during expansionary fiscal policy quizlet?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, thus, shifting it to the right.
How does monetary policy shift the aggregate supply curve?
The Fed can shift the aggregate demand curve when it changes monetary policy. An increase in the money supply shifts the money supply curve to the right. Without a change in the money demand curve, the interest rate falls. Falling interest rates increase the quantity of goods and services demanded.
What curve does expansionary monetary policy shift?
Expansionary monetary policy shifts the LM curve down (figure 2). The money supply increases, and the interest rate falls. The economy moves down along the IS curve: the fall in the interest rate raises investment demand, which has a multiplier effect on consumption.
Does expansionary fiscal policy increase or decrease aggregate demand?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, either through increases in government spending or through reductions in taxes. Expansionary fiscal policy is most appropriate when an economy is in recession and producing below its potential GDP.
What is the effect of expansionary monetary policy on the economy quizlet?
An expansionary monetary policy causes investment in an economy to decrease. An expansionary monetary policy shifts the aggregate demand curve to the left. An expansionary monetary policy will result in inflation if there is full employment in an economy.
How does expansionary and contractionary monetary policy affect the demand and supply of money in circulation?
Monetary policy employs tools used by central bankers to keep a nation's economy stable while limiting inflation and unemployment. Expansionary monetary policy stimulates a receding economy and contractionary monetary policy slows down an inflationary economy.
What is contractionary monetary policy?
Contractionary monetary policy is enacted to halt exceptionally high inflation rates or normalize the effects of expansionary policy. Tightening the money supply discourages business expansion and consumer spending and negatively impacts exporters, which can reduce aggregate demand .
How does fiscal policy affect aggregate demand?
Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. Those factors influence employment and household income, which then impact consumer spending and investment. Monetary policy impacts the money supply in an economy, which influences interest rates and the inflation rate.
Why is expansionary monetary policy important?
Expansionary monetary policy also typically makes consumption more attractive relative to savings. Exporters benefit from inflation as their products become relatively cheaper for consumers in other economies.
Why is contractionary fiscal policy used?
Similarly, the theory says that contractionary fiscal policy can be used to reduce government spending and sovereign debt or to correct out-of-control growth fueled by rapid inflation and asset bubbles .
How does fiscal policy affect GDP?
In the same way that fiscal and monetary policy impact GDP, they also impact aggregate demand. Fiscal policy impacts government spending and tax policy, while monetary policy influence s the money supply, interest rates, and inflation.
How does the money supply affect the economy?
Monetary policy impacts the money supply in an economy, which influences interest rates and the inflation rate. It also impacts business expansion, net exports, employment, the cost of debt, and the relative cost of consumption versus saving—all of which directly or indirectly impact aggregate demand.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy determines government spending and tax rates. Expansionary fiscal policy, usually enacted in response to recessions or employment shocks, increases government spending in areas such as infrastructure, education, and unemployment benefits.
What is expansionary fiscal policy?
Expansionary fiscal policy is the use of government spending, taxation and transfer payments to stimulate aggregate demand. Whenever the government is increasing its own purchases, lowering taxes or raising transfer payments, fiscal policy always influences at least one component of aggregate demand.
What is contractionary gap?
Illustration of a recessionary gap, also called a contractionary gap. During a recessionary gap, the economy is below the full employment level. In English, that just means that the job market is really slow and unemployment is higher than what it naturally is.
What policy did Larry and Natalie use to deal with the recession?
Let's watch Larry and Natalie as they experience firsthand the government's attempt to deal with this recession using expansionary fiscal policy.
What is the vertical line of the macroeconomic equilibrium?
So you can see here what it looks like. The vertical line is the economy's long-run potential. The macroeconomic equilibrium, seen here as the intersection of the aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve, is to the left of the economy's long-run potential, which is the vertical line. Right now, in this recession, aggregate demand is at Q1, which is less than Qp, the economy's potential. The price level, I want you to see, is at P1. As you'll see in a minute, after the government uses expansionary fiscal policy, both aggregate demand and the price level will rise. We'll be able to see the economy escape the recession and increase so that it returns to its long-run potential by watching Q1 go back to Qp, and P1 will rise to a higher level.
How does an increase in transfer payments affect aggregate demand?
Once again, economists would say it this way: 'An increase in transfer payments raises aggregate demand indirectly by increasing disposable income, which leads to higher consumption - and that leads to higher aggregate demand.' So this was very similar to the example of lowering taxes.
How do lower taxes affect aggregate demand?
Economists would say it this way: 'Lower taxes raise aggregate demand indirectly by increasing disposable income, which leads to higher consumption and therefore higher aggregate demand.'
Why is it important to reduce interest rates? Why does it matter? Why does it matter?
Why is this important; why does this matter? Because the economy depends on lower interest rates to create an incentive for consumers and businesses to borrow and invest. When interest rates go up, this leads to less investment, and less investment reduces economic output. At the end of the day, the fiscal policy actions that the government pursued in an effort to help the economy lost their effectiveness because of the crowding-out effect. Crowding out can reduce the effectiveness of expansionary fiscal policy. It doesn't always happen, but it's something that we need to be aware of that can happen.
What is the difference between the short run and long run?
The short run effect is a rise in savings, while the long run effect is a slowing in economic activity or lowering of prices. Monetary policy is how the central bank (the Federal Reserve in the United States) adjusts the size and rate of growth of the money supply.
What is the long run effect of expansionary monetary policy?
As a result, the demand goes up, and the prices for goods and services goes up as well. Thus, the long run effect of an expansionary monetary policy is inflation. The opposite effect is true for contractionary monetary policy. The short run effect is a rise in savings, while the long run effect is a slowing in economic activity or lowering ...
What is expansionary monetary policy?
An expansionary monetary policy is caused by a reduction in the interest rates, which then leads to increased borrowing. The short run effects include a rise in the number of investments.
What happens when interest rates are lower?
When interest rates are lower, the cost of borrowing money is less. This generally means that consumers will purchase more goods and will thus stimulate short-term demand. When interest rates are raised, on the other hand, the cost of borrowing is increased, which will generally tamp down aggregate demand in the short run.
How does expansionary monetary policy affect the economy?
Expansionary monetary policy increases the money supply to increase economic growth. In the short term, this will lower the interest rate, thus increasing borrowing and consumer spending. The demand of goods and services will increase. In the long run, this stimulated economy will increase job opportunities, thus lowering the unemployment rate.
What is monetary policy?
Monetary policy is related to increasing or decreasing the money supply. In the United States, this is done by the Federal Reserve, which implements monetary policy by either raising or lowering interest rates. (There are many different ways the Fed accomplishes this, but listing them is outside the scope of this question.)
Does monetary policy affect aggregate demand?
Monetary policy is more likely to have an impact on aggregate demand (AD) in the short run than in the long run. In the short run, monetary policy can have a relatively significant impact on AD. Let us look, for example, at what happens when the central bank engages in expansionary monetary policy.
Which direction does the aggregate demand curve shift?
1. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right
What is a CD in prison?
Small time Certificates of Deposit (CD's) Checkable deposits. If prisoners did not have dollars to use to purchase goods and services in prison but they had access to Top Ramen noodles that is then used as money by the prisoners, then Top Ramen becomes: A medium of exchange and a unit of account.
How does a fall in interest rates affect investment?
A fall in interest rates is likely to change investment, real GDP, prices, and employment in the short run in the following manners. Increase investment, real GDP, prices, and employment.
What will happen if unemployment is high?
With high unemployment, there will be a tendency for wages to fall, stimulating production, lowering prices, and increasing consumer spending. Compare two economies, A and B. Everything is the same except economy A is in recession and economy B is at full employment.
Why do people want to buy more Teslas?
People from around the world want to buy more Teslas as the price level in the U.S. falls. As spending increases, there will be upward pressure on the price of inputs including wages. As the marginal cost of production rises, businesses start to increase prices as they attempt to produce more.
Does expansionary fiscal policy affect real GDP?
False. While it is true that expansionary fiscal policy does not affect real GDP in the long run, it does raise interest rates, which lowers investment.
