What species are extinct?
One thing we do know: The western black rhinoceros, the Tasmanian tiger, and the woolly mammoth are among the creatures whose populations at one point dwindled to zero, and it’s possible that...
Are extinctions necessary?
Human populations depend on plants and animals for much of their food, medicines, clothing, and shelter. Even more important, intact ecosystems perform many vital functions, like purifying the air, filtering harmful substances out of water, turning decayed matter into nutrients, preventing erosion and flooding, and moderating climate. This is why extinction matters.
What are some examples of mass extinction?
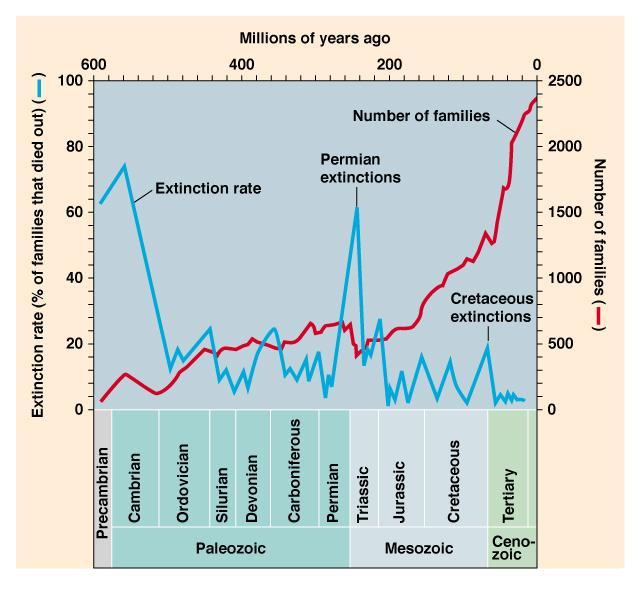
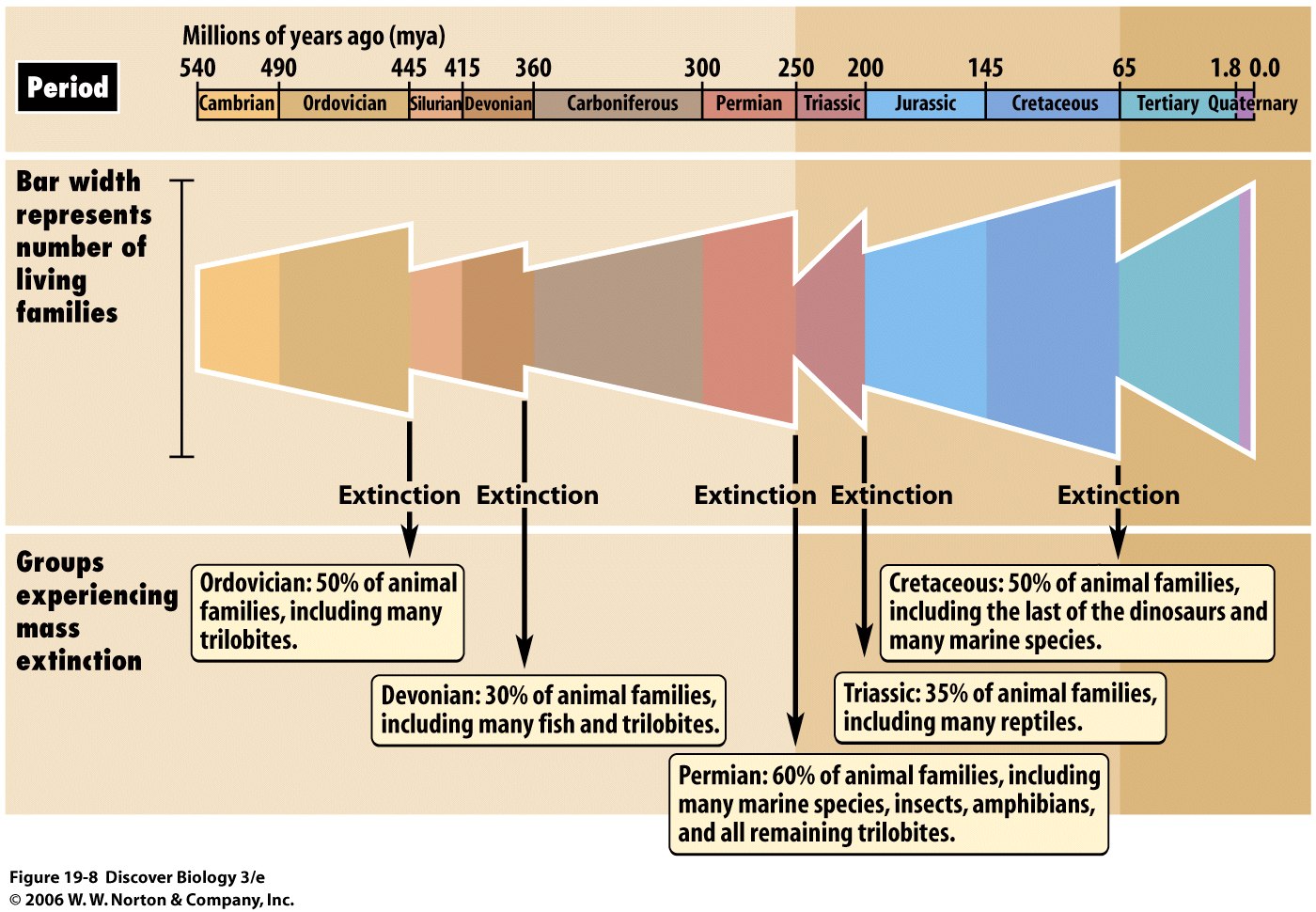
What are the 5 major mass extinctions?
- Ordovician-silurian Extinction: 440 million years ago.
- Devonian Extinction: 365 million years ago.
- Permian-triassic Extinction: 250 million years ago.
- Triassic-jurassic Extinction: 210 million years ago.
- Cretaceous-tertiary Extinction: 65 Million Years Ago.
What does extinction mean simple?
n. 1. the act of extinguishing. 2. the state of being extinguished or extinct. 3. the act or process of becoming extinct: the extinction of a species. 4. the reduction or loss of a conditioned response as a result of the absence or withdrawal of reinforcement.

How does extinction effect evolution?
At the most basic level, mass extinctions reduce diversity by killing off specific lineages, and with them, any descendent species they might have given rise to. In this way, mass extinction prunes whole branches off the tree of life.
Why extinction is an important part of evolution?
Extinction is the engine of evolution, the mechanism by which natural selection prunes the poorly adapted and allows the hardiest to flourish. Species constantly go extinct, and every species that is alive today will one day follow suit. There is no such thing as an “endangered species,” except for all species.
Does extinction promote evolution?
Extinction events exert a powerful influence on evolution [1–4]. For example, the Cretaceous-Paleogene extinction event is believed to have displaced non-avian dinosaurs with mammals in many ecological niches [1, 3], potentiating the later evolution of humans.
How did the dinosaur extinction affect evolution?
A few hundred thousand years after dinosaurs disappeared, there were much larger, cow-sized species. 'Mammals just took advantage of the opportunity and started to evolve really fast,' Dr Brusatte said.
What does extinction mean in evolution?
Extinction occurs when species are diminished because of environmental forces (habitat fragmentation, global change, natural disaster, overexploitation of species for human use) or because of evolutionary changes in their members (genetic inbreeding, poor reproduction, decline in population numbers).
Why does it matter if species go extinct?
Balance and Biodiversity Many endangered species are top predators whose numbers are dwindling due to conflicts with humans. 4 We kill predators all over the world because we fear for our own interests, we compete with them for prey and we destroy their habitats to expand our communities and agricultural operations.
Would humans evolve again if we went extinct?
But even if that common ancestor still existed, the fact that evolution is the result of both random mutation and a process of natural selection imposed by environmental conditions, means it's highly unlikely that it would ever retrace its steps in quite the same way.
Can extinct animals come back through evolution?
Unfortunately, DNA slowly degrades, and once it's gone completely, there's no way to recover it. Researchers believe DNA has a half-life of 521 years, so after 6.8 million years, it's believed to be completely gone. That's why species like dinosaurs have virtually no chance of de-extinction.
What are the positive effects of extinction?
In effect, a mass extinction cleans the slate, creating new evolutionary niches which promote a wide range of species, increasing biodiversity, competition and in some cases increasing complexity in organisms as they try to carve out their niche in the new world.
Would humans evolve if dinosaurs didn't go extinct?
They would still probably be small, scrawny, and very generalized. But instead, the mammals were able to evolve and diversify and, well, ultimately, millions of years later, become some humans. So perhaps we would not have been here if it weren't for this extinction event 65 million years ago.
What extinction led to the evolution of dinosaurs?
The first dinosaurs appear in the fossil record around 240 million years ago, in the Middle Triassic. Growing evidence suggests that dinosaur origins may have formed part of the long-term recovery of ecosystems from the Permo-Triassic (PT) mass extinction.
What mass extinction caused the evolution of dinosaurs?
Cretaceous-tertiary Extinction: 65 Million Years Ago Scientists refer to the major extinction that wiped out nonavian dinosaurs as the K-T extinction, because it happened at the end of the Cretaceous period and the beginning of the Tertiary period.
Why extinction is an important concern of humans?
Each time a species goes extinct, the world around us unravels a bit. The consequences are profound, not just in those places and for those species but for all of us. These are tangible consequential losses, such as crop pollination and water purification, but also spiritual and cultural ones.
What is the most important cause of extinction?
The main modern causes of extinction are the loss and degradation of habitat (mainly deforestation), over exploitation (hunting, overfishing), invasive species, climate change, and nitrogen pollution.
What are the positive effects of extinction?
In effect, a mass extinction cleans the slate, creating new evolutionary niches which promote a wide range of species, increasing biodiversity, competition and in some cases increasing complexity in organisms as they try to carve out their niche in the new world.
What is the importance of evolution?
Evolution is important because it explains how life developed on Earth and how different species are connected. The evolutionary linkages aid in the addressing of biological challenges, as well as the diversity of life.
What are the causes of background extinction?
Background extinctions result from ordinary biological processes, such as competition between species, predation, and parasitism. When two species compete for very similar resources—say, the same kinds of seeds or fruits—one may become extinct, although often they will displace one another by dividing the territory or by specializing in slightly different foods, such as seeds of a different size or kind. Ordinary physical and climatic changes also account for background extinctions—for example, when a lake dries out or a mountain range rises or erodes.
What caused the mass extinction of the dinosaurs?
Most scientists believe that the Cretaceous mass extinction was provoked by the impact of an asteroid or comet on the tip of the Yucatán Peninsula in southeastern Mexico 65 million years ago. The object’s impact caused an enormous dust cloud, which greatly reduced the Sun’s radiation reaching Earth, with a consequent drastic drop in temperature and other adverse conditions. Among animals, about 76 percent of species, 47 percent of genera, and 16 percent of families became extinct. Although the dinosaurs vanished, turtles, snakes, lizards, crocodiles, and other reptiles, as well as some mammals and birds, survived. Mammal s that lived prior to the event were small and mostly nocturnal, but during the ensuing Paleogene and Neogene periods they experienced an explosive diversification in size and morphology, occupying ecological niches vacated by the dinosaurs. Most of the orders and families of mammals now in existence originated in the first 10 million–20 million years after the dinosaurs’ extinction. Bird s also greatly diversified at that time.
Why do immediate descendants differ little?
Because of the gradualness of evolution, immediate descendants differ little, and then mostly quantitatively, from their ancestors. But gradual evolution may amount to large differences over time. The forelimbs of mammals are normally adapted for walking, but they are adapted for shoveling earth in moles and other mammals that live mostly underground, for climbing and grasping in arboreal monkeys and apes, for swimming in dolphins and whales, and for flying in bats. The forelimbs of reptiles became wings in their bird descendants. Feathers appear to have served first for regulating temperature but eventually were co-opted for flying and became incorporated into wings.
How do new species come about?
New species come about by the processes discussed in previous sections. These processes are largely gradual, yet the history of life shows major transitions in which one kind of organism becomes a very different kind. The earliest organisms were prokaryote s, or bacteria- like cells, whose hereditary material is not segregated into a nucleus. Eukaryote s have their DNA organized into chromosome s that are membrane-bound in the nucleus, have other organelles inside their cells, and reproduce sexually. Eventually, eukaryotic multicellular organisms appeared, in which there is a division of function among cells—some specializing in reproduction, others becoming leaves, trunks, and roots in plants or different organs and tissues such as muscle, nerve, and bone in animals. Social organization of individuals in a population is another way of achieving functional division, which may be quite fixed, as in ants and bees, or more flexible, as in cattle herds or primate groups.
When did the most catastrophic extinctions occur?
The most catastrophic extinction took place at the end of the Permian Period. Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc. Several other mass extinctions have occurred since the Cambrian. The most catastrophic happened at the end of the Permian Period , about 251 million years ago, when 95 percent of marine species, 82 percent of genera, ...
How have eyes evolved?
Eyes, which serve as another example, also evolved gradually and achieved very different configurations, all serving the function of seeing. Eyes have evolved independently at least 40 times. Because sunlight is a pervasive feature of Earth’s environment, it is not surprising that organs have evolved that take advantage of it. The simplest “organ” of vision occurs in some single-celled organisms that have enzymes or spots sensitive to light ( see eyespot ), which helps them move toward the surface of their pond, where they feed on the algae growing there by photosynthesis. Some multicellular animals exhibit light-sensitive spots on their epidermis. Further steps—deposition of pigment around the spot, configuration of cells into a cuplike shape, thickening of the epidermis leading to the development of a lens, development of muscles to move the eyes and nerves to transmit optical signals to the brain—all led to the highly developed eyes of vertebrates ( see eye, human) and cephalopods (octopuses and squids) and to the compound eyes of insects.
Why do mass extinctions occur?
Mass extinctions occur for many reasons, some of which are completely beyond the influence of biological processes. Volcanism, asteroid impacts and even a near-Earth supernovae and consequent gamma ray bursts have all been credited with mass dying and destruction.
What is the best example of a species' success?
Perhaps the best example of all was the Oxygen Catastrophe of 2.3 billion years ago, when photosynthesising cyanobacteria became so prolific that it transformed the Earth’s atmosphere , making it inhospitable to anaerobic organisms.
How does extinction affect evolution?
Extinction plays a vital role in evolution to the extent that it’s the driving force between the success (or failure) of any species that has lived, does live and ever will live. Sometimes, it only takes a very minor catalyst to irrevocably change the course of Earth’s history. For example, had the Chicxulub impactor, which is widely believed to have been responsible for the extinction of the non-avian dinosaurs, had just a very slightly different trajectory, it would have safely flown right past the planet.
What event altered the course of evolution?
Mass extinction events like the one that wiped out the non-avian dinosaurs, profoundly alter the course of evolution.
What are the causes of extinction?
Until modern times, human-driven extinctions were caused by two things: habitat destruction and over-hunting. Today, however, we have climate change to contend with as well.
What are the two choices that species face in the world of evolution?
In the harsh and unforgiving world that is evolution, species are faced with two choices: adapt or die. From global warming to relentless habitat encroachment, we are shaping the future of life on Earth in many different ways. But does this mean that nature will be able to keep up with us, and what can we do to help stem the tide of destruction that we continue to cause? Let me know what you think in the comments below.
What is the Holocene epoch?
Right now, we’re living in an interglacial period that we call the Holocene Epoch, which is part of the Quaternary Ice Age. These periods of glaciation are driven by the Milankovitch cycles, which are in turn controlled by the movements of the Earth around the Sun. However, our impact on the environment appears to be even greater, meaning that we might have even staved off the next glacial period by as much as 100,000 years.