
What are the negative effects of fiscal policy?
Jan 31, 2020 · Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. It also impacts business expansion, net exports, employment, the cost of debt and the relative cost of consumption versus saving—all of which directly or indirectly impact aggregate demand.
What is fiscal policy, its objectives, tools and types?
This value is often used as a measure of economic well-being or extension. Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in control spending and taxation. Government spending and taxation influence employment and household proceeds, which dictate consumer spending and investment. Monetary policy smashes the money supply in an economy, which influences …
How does fiscal policy affect economic growth?
May 16, 2019 · Fiscal Policy: Economic Effects Congressional Research Service 2 tax cuts indirectly increases aggregate demand in the economy. For example, an individual income tax cut increases the amount of disposable income available to individuals, enabling them to purchase more goods and services.
How does fiscal policy impact the budget deficit?
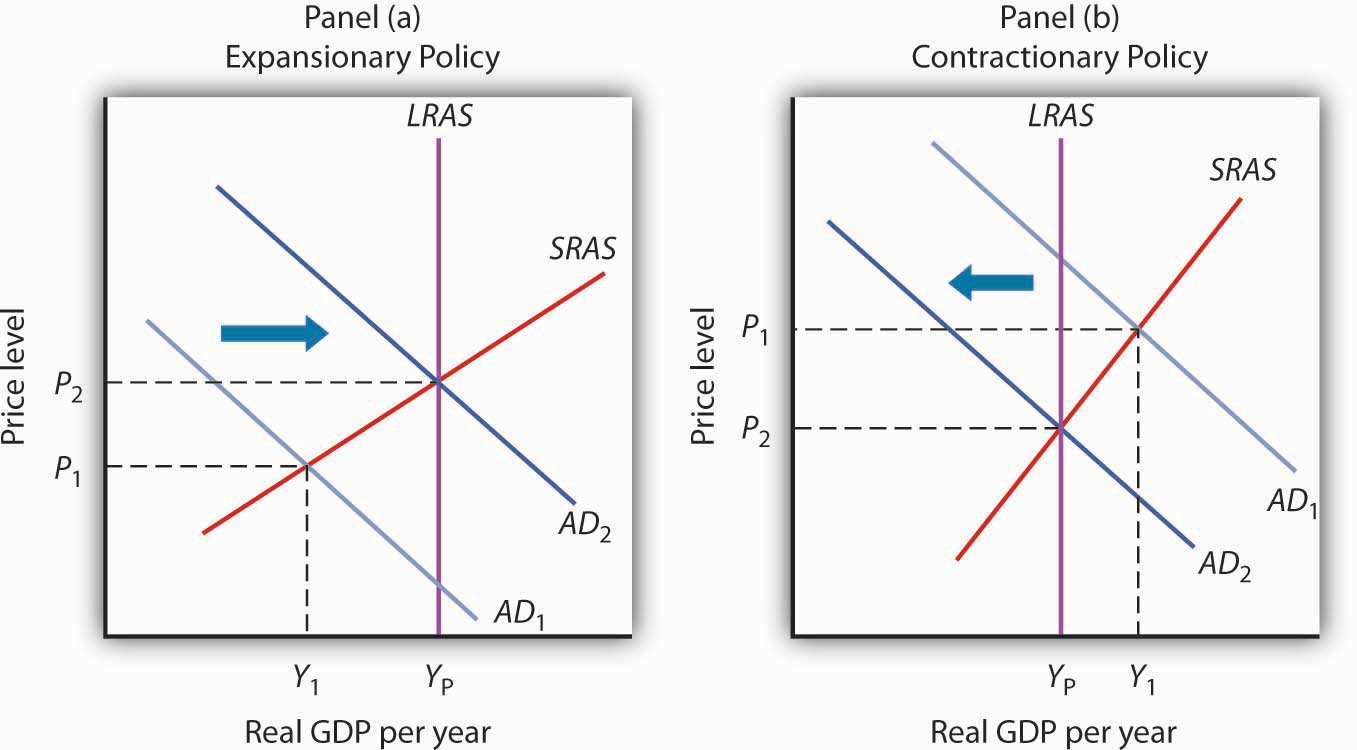
How does fiscal policy increases aggregate demand?
What Fiscal Policy Increases Aggregate Demand? Expansionary fiscal policy that is intended to increase aggregate demand includes cutting taxes and increasing government spending. Both provide more money to consumers and businesses, allowing them to purchase and invest.
What fiscal policy reduces aggregate demand?
Contractionary fiscal policy decreases the level of aggregate demand, either through cuts in government spending or increases in taxes. Contractionary fiscal policy is most appropriate when an economy is producing above its potential GDP.
How does fiscal policy affect aggregate demand quizlet?
Changes in fiscal policy that stimulate Aggregate Demand when the economy goes into recession, without policymakers having to take any deliberate action. The tax system: In recessions taxes fall automatically, which stimulates agg demand. In recession, more people apply for public assistance.
How does expansionary fiscal policy affect aggregate demand?
Expansionary fiscal policy tools include increasing government spending, decreasing taxes, or increasing government transfers. Doing any of these things will increase aggregate demand, leading to a higher output, higher employment, and a higher price level.
How does fiscal policy affect economic growth?
Fiscal policy is a government's decisions regarding spending and taxing. If a government wants to stimulate growth in the economy, it will increase spending for goods and services. This will increase demand for goods and services. Since demand goes up, production must go up.Sep 25, 2021
How does fiscal policy reduce inflation?
Fiscal Policy Fiscal policy involves the government changing tax and spending levels in order to influence the level of Aggregate Demand. To reduce inflationary pressures the government can increase tax and reduce government spending. This will reduce AD.Jul 12, 2019
Which changes in fiscal policy stimulate aggregate demand when the economy goes into recession without policymakers having to take any deliberate action?
Automatic Stabilizers and Fiscal Policy When an economy is in a recession, automatic stabilizers may by design result in higher budget deficits. This aspect of fiscal policy is a tool of Keynesian economics that uses government spending and taxes to support aggregate demand in the economy during economic downturns.
What fiscal policy would increase real GDP?
Increased government spending will result in increased aggregate demand, which then increases the real GDP, resulting in an rise in prices. This is known as expansionary fiscal policy.
What are the main ways in which government influences aggregate demand quizlet?
When an increase in government purchases increases aggregate demand, the increase in spending increases money demand, which increases the equilibrium interest rate, which in turn partially offsets the initial increase in aggregate demand.
What happens to aggregate demand during expansionary fiscal policy quizlet?
Expansionary fiscal policy increases the level of aggregate demand, thus, shifting it to the right. Both equilibrium price and real GDP increase.
How does fiscal policy affect investment?
To engage in fiscal stimulus by either increasing spending or decreasing tax revenue, the government must increase the size of its deficit and borrow money to finance that stimulus. This can lead to an increase in interest rates and subsequent decreases in investment and some consumer spending.Jan 21, 2021
How monetary policy influences aggregate demand and how these can be used to expand the economy?
Monetary policy affects interest rates and the available quantity of loanable funds, which in turn affects several components of aggregate demand. Tight or contractionary monetary policy that leads to higher interest rates and a reduced quantity of loanable funds will reduce two components of aggregate demand.
How does fiscal policy affect aggregate demand?
Fiscal policy affects aggregate demand through changes in government spending and taxation. Those factors influence employment and household income, which then impact consumer spending and investment. Monetary policy impacts the money supply in an economy, which influences interest rates and the inflation rate.
How does fiscal policy affect GDP?
In the same way that fiscal and monetary policy impact GDP, they also impact aggregate demand. Fiscal policy impacts government spending and tax policy, while monetary policy influence s the money supply, interest rates, and inflation.
How does the money supply affect the economy?
Monetary policy impacts the money supply in an economy, which influences interest rates and the inflation rate. It also impacts business expansion, net exports, employment, the cost of debt, and the relative cost of consumption versus saving—all of which directly or indirectly impact aggregate demand.
What is fiscal policy?
Fiscal policy determines government spending and tax rates. Expansionary fiscal policy, usually enacted in response to recessions or employment shocks, increases government spending in areas such as infrastructure, education, and unemployment benefits.
What is aggregate demand?
Aggregate demand is an economic measure of the total demand for all finished goods or services created in an economy. It represents the overall demand regardless of the price level, during a specific period of time. Aggregate demand and gross domestic product (GDP) are calculated the same way and move in tandem, ...
How is money policy enacted?
Monetary policy is enacted by central banks by manipulating the money supply in an economy. The money supply influences interest rates and inflation, both of which are major determinants of employment, cost of debt, and consumption levels.
What is expansionary monetary policy?
Expansionary monetary policy involves a central bank buying Treasury notes, decreasing interest rates on loans to banks, or reducing the reserve requirement. All of these actions increase the money supply and lead to lower interest rates. This creates incentives for banks to loan and businesses to borrow.
How does monetary policy work?
Monetary policy is enacted by central banks by negotiating the money supply in an economy. The money supply influences interest bawl outs and inflation, both of which are major determinants of employment, cost of indebted and consumption levels. Expansionary monetary policy entails a central bank either acquisition bargaining Treasury notes, decreasing interest rates on loans to banks or turn the reserve requirement. All of these actions increase the money supply and place to lower interest rates. This creates incentives for banks to lend and businesses to borrow. Debt-funded business expansion positively affects consumer splurge and investment through employment, thereby increasing aggregate demand. (For associated reading, see: What are some examples of expansionary monetary policy?)
What is aggregate exact?
Aggregate exact is a macro-economic concept representing the total demand for goods and services in an saving. This value is often used as a measure of economic well-being or extension.

The Formula For Aggregate Demand
Understanding Fiscal Policy and Aggregate Demand
- Fiscal policy determines government spending and tax rates. Expansionary fiscal policy, usually enacted in response to recessions or employment shocks, increases government spending in areas such as infrastructure, education, and unemployment benefits. According to Keynesian economics, these programs can prevent a negative shift in aggregate demand...
Understanding Monetary Policy and Aggregate Demand
- Monetary policy is enacted by central banks by manipulating the money supplyin an economy. The money supply influences interest rates and inflation, both of which are major determinants of employment, cost of debt, and consumption levels. Expansionary monetary policy involves a central bank buying Treasury notes, decreasing interest rates on loans to banks, or reducing the …