For each point of the root locus a value of can be calculated. This is known as the magnitude condition. The root locus only gives the location of closed loop poles as the gain
How do I find the gain of the root locus plot?
If you click on the root locus plot at s=-1.5+ j 0, MATLAB will calculate and display the gain K as is shown in the diagram at right (along with some information about the system behavior). You can also make use of MATLAB's rlocfind () function. You can try this yourself. We will use the same system as before, shown here to refresh your memory
What is the use of root locus method?
So, the root locus method helps to determine the movement of the poles in the s-plane with the variation in gain of the control system. Suppose we have a closed-loop system as represented below: For the above given closed-loop system, gain K is a variable parameter which is a part of the forward path of the system.
How to find how the roots move as the gain is varied?
For the very simple system of this problem, there were many ways to find how the roots varied as we varied the gain of the system. For a more complicated system this is not easy. The root locus plot gives us a graphical way to observe how the roots move as the gain, K, is varied.
What is the root locus of feedback system?
The root locus of a feedback system is the graphical representation in the complex s -plane of the possible locations of its closed-loop poles for varying values of a certain system parameter. The points that are part of the root locus satisfy the angle condition.

What is gain margin How is evaluated for a root locus?
The gain margin will be given by the point where the root locus crosses the imaginary axis in the complex plane. The phase margin is associated with the place where the root locus has a magnitude of one, and the damping ratio is equivalent to the cosine of the angle of the poles.
What is gain in root locus?
The root locus returns the closed-loop pole trajectories as a function of the feedback gain k (assuming negative feedback). Root loci are used to study the effects of varying feedback gains on closed-loop pole locations. In turn, these locations provide indirect information on the time and frequency responses.
What does the root locus plot imply about the effectiveness of a proportional gain controller?
The root locus plot indicates how the closed loop poles of a system vary with a system parameter (typically a gain, K). We can choose a value of 's' on this locus that will give us good results.
How does gain affect pole location?
DC gain can be lower and as the pole is shifted to the left the DC gain increases. DC gain=T(s) overall transfer function at s=0 for a unit step input. so as the closed loop poles are so far on the left HSP from the imaginary axis, the dc gain will be smaller and the transient response will be faster.
What is gain in control system?
Gain is a proportional value that shows the relationship between the magnitude of the input to the magnitude of the output signal at steady state. Many systems contain a method by which the gain can be altered, providing more or less "power" to the system.
What is phase and gain margin?
The phase margin is the number of degrees by which the phase angle is smaller than −180° at the gain crossover. The gain crossover is the frequency at which the open-loop gain first reaches the value 1 and so is 0.005 Hz. Thus, the phase margin is 180° − 120°=60°.
How root locus plots can be used to improve the performance of a control system?
Root locus is helping us to map graphically as graph all possible locations of the poles within the system on the s-plane. The different locations of the poles are obtained under the effect of gain changes (proportional gain).
How do you determine the stability of a root locus?
The root locus procedure should produce a graph of where the poles of the system are for all values of gain K. When any or all of the roots of D (denominator) are in the unstable region, the system is unstable. When any of the roots are in the marginally stable region, the system is marginally stable (oscillatory).
How do you interpret a root locus plot?
9:1013:09The Root Locus Method - Introduction - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipJust on how to interpret it and use it drawing a root locus by hand is useful. However most of theMoreJust on how to interpret it and use it drawing a root locus by hand is useful. However most of the time you'll just use a software package like MATLAB to draw the root locus for you.
How does gain affect transfer function?
Key TakeawaysTransfer function gain=Yssr(t), where Yss represents output y(t) at steady-state and r(t) is the input.The transfer function gain is the magnitude of the transfer function, putting s=0. ... If Ka is the given transfer function gain and Kc is the gain at which the system becomes marginally stable, then GM=KcKa.
How does gain affect step response?
Even though the difference between the step response and the steady state response gets bigger for all times when you use a bigger gain K, the percentage difference remains the same. That is why K does not affect settling time. The poles of your system are, p=ωn(−ζ±√ζ2−1).
What is the significance of the gain K?
The proportional gain K is usually a fixed property of the controller but, in some proportional controllers, K is manually adjustable. If K is increased, the sensitivity of the controller to error is increased but the stability is impaired.
How do you calculate gain from poles?
2:493:52Zeros and Poles of a Transfer Function - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipOn simplifying this we get this so the poles of this transfer function R. Minus 1 minus 2 and minusMoreOn simplifying this we get this so the poles of this transfer function R. Minus 1 minus 2 and minus 3 you have the 0 of the strands. Function is 0 the gain is 6.
How do you find the gain constant?
1:566:47DC Gain of a System - YouTubeYouTubeStart of suggested clipEnd of suggested clipForm we can say the value of k is 1 over 3 so we can write k is equal to 1 over 3 which is equal toMoreForm we can say the value of k is 1 over 3 so we can write k is equal to 1 over 3 which is equal to 0.33. And in the standard time constant. Form the k represents the dc gain of a system.
How do you find the gain of a transfer function?
Transfer function gain=Yssr(t), where Yss represents output y(t) at steady-state and r(t) is the input. The transfer function gain is the magnitude of the transfer function, putting s=0. Otherwise, it is also called the DC gain of the system, as s=0 when the input is constant DC.
How can you find out gain at specific point on the root locus?
* You can simply make characteristic equation 1+GH =0 and find K. * Use angle criteria Angle(GH) = +-180 ° * Or, Magnitude criteria |GH| = 1 * Having characteristic equation, obtain the intersection with jω axis by Routh-Hurwitz criteria. It will give you maximum gain.
Why is the root locus important?
The root locus also helps in finding the information related to the settling time of the system. Its implementation is quite easy.
What is the root locus method?
So, the root locus method helps to determine the movement of the poles in the s-plane with the variation in gain of the control system.
How to represent the characteristic equation of a closed loop system?
We are already aware of the fact the characteristic equation of the closed-loop system is represented by equating the denominator of the transfer function to 0.
What does the nature of the transient response of the system show?
This clearly signifies that the nature of the transient response of the system shows dependency on the location of the poles in the s-plane. However, we all must know how the location of poles in s-plane varies with the variation in parameters of the system.
What happens to gain K if it is varied from – to +?
So, this leads to taking us to the conclusion that if gain K is varied from – ∞ to + ∞ then every individual value of k within this range will provide a different set of locations of the poles in the s-plane.
When was root locus analysis proposed?
Root Locus Analysis was proposed by W R Evans in the year 1948.
Can we determine G (s)H (s)?
It is to be noted that with the unknown value of K, we will not be able to determine |G (s)H (s )| at any point in s-plane. However, if we get an idea regarding the existence of a point in s-plane on the root locus then it must also satisfy the magnitude condition.
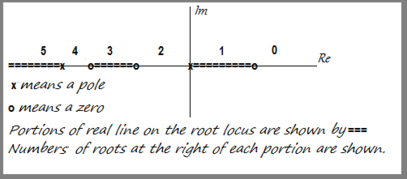
What is root locus plot?
A root locus plot is a variation on this kind of plot. It shows the path of the roots as K is varied, but does not show the actual values of K. This kind of plot is sufficiently important that Matlab has a command specifically for generating these plots.
What is a locus in math?
For our purposes, a locus is defined as the set of all points on a plane that satisfy a given requirement.
How to plot the path of the roots as K varies?
If we want to plot the path of the roots as K varies we can calculate the roots of the equation s 2 + 3s + K = 0, for many values of K by using the quadratic equation.
Where is the step response on a plot?
Finally the step response is displayed on the rightmost plot .
Do we have to set the magnitudes of the real and imaginary parts of the roots equal to each other?
we must set the magnitudes of the real and imaginary parts of the roots equal to each other.
Can we choose a value of s on a locus?
We can choose a value of 's' on this locus that will give us good results. The shape of the locus can also give us information on design of a more complex (lead/lag, PID controller) - though that wasn't discussed here.