Heat Pump in Air Conditioning Mode
- Warm air from the inside of your house is pulled into ductwork by a motorized fan.
- A compressor circulates refrigerant between the indoor evaporator and outdoor condensing units.
- The warm air indoor air then travels to the air handler while refrigerant is pumped from the exterior condenser coil to...
Is a heat pump the same as an AC unit?
So, from a cooling perspective, minus a few technical details, heat pumps and air conditioners are essentially the same when operating in cooling mode, with no significant difference in operation, efficiency, or energy costs. While essentially identical in cooling mode, heating mode is a completely different story.
What are the worst heat pumps?
- Trane and American Standard: 9.0 / 10
- Carrier, Bryant, and Payne: 8.5 / 10
- Lennox: 8.5 / 10
- Armstrong Air, Ducane and AirEase: 8.5 / 10
- Rheem and Ruud: 8.0 / 10
- Daikin, Goodman, and Amana: 7.5 / 10
- Heil, Arcoaire, Keeprite, Comfortmaker, Tempstar and Day & Night: 7.5 / 10
- Maytag, Frigidaire, Broan, Gibson and Miller: 6.5 / 10
What should I do when my heat pump runs constantly?
Heat pump itself runs constantly; Check Correct Fan Settings. A common reason a blower fan keeps running is it’s simply set to the wrong mode. There is a setting or toggle on your thermostat that controls how the fan operates – the AUTO setting allows the fan to only run when your heat pump cycles, while the ON setting keeps the fan in operation all the time.
What to do if heat pump ices up in the winter?
Method 1 Method 1 of 2: Allowing the Pump's Defrost to Run Inspect the heat pump coils for ice buildup daily during cold weather. ... Let the heat pump defrost itself if it's only covered with thin ice. ... Turn the fan on to engage the defrost function. Some models of heat pump may not be able to defrost themselves while the fan is off. Contact an HVAC repair specialist if the pump doesn't defrost itself. ...
Does a heat pump cool as well as an air conditioner?
Though the name seems to suggest otherwise, heat pumps don't just heat—they cool too! In fact, a heat pump can cool your home just as well as an air conditioner. A heat pump with a 16 SEER rating works just as efficiently as an air conditioner with a 16 SEER rating.
How does a heat pump work in summer?
During the summer months, heat pumps work by transferring heat from the inside of your home to the outside. Heat pumps use a coil and fan, where the coil functions as a condenser. It uses refrigerant, which absorbs heat and pushes it outside, making your home cooler.
What are the disadvantages of a heat pump?
7 Disadvantages of Heat Pumps are:High upfront cost.Difficult to install.Questionable Sustainability.Requires significant work.Issues in cold weather.Not entirely carbon neutral.Planning permissions required.
How do heat pumps work for dummies?
To provide heat, a heat pump works by extracting heat from the air outside of your home and transferring it to refrigeration coolant – the coolant is then compressed, which increases the temperature significantly; the coolant is then moved to the indoor unit of the heat pump, which then passes air over the hot coolant, ...
What temperature is a heat pump not effective?
between 25 and 40 degrees FahrenheitHeat pumps do not operate as efficiently when temperatures drop to between 25 and 40 degrees Fahrenheit for most systems. A heat pump works best when the temperature is above 40. Once outdoor temperatures drop to 40 degrees, heat pumps start losing efficiency, and they consume more energy to do their jobs.
Can a heat pump cool a house in 100 degree weather?
While heat pumps may cool a home just as efficiently as any other conditioner, they also won't be any more efficient. Some homeowners assume that heat pumps help save money. While there's no difference between air conditioners and heat pumps with regard to efficiency, there are differences between models.
Why heat pumps may not be the future?
They don't work well in poorly insulated homes Homes need to be well insulated for heat pumps to be effective because the devices work at lower temperatures and so will struggle to get the house warm and keep it to temperature. They work better with lower temperature heating systems, such as underfloor heating.
What is the major problem of heat pump?
Other common causes of your heat pump not cooling include low refrigerant levels, dirty air filters or coils, or a faulty thermostat. Also, check your outdoor unit for blockage as leaves and debris can get stuck in the system and prevent it from functioning properly.
Do heat pumps use a lot of electricity?
Heat pumps require some electricity to run, but it's a relatively small amount. Modern heat pump systems can transfer three or four times more thermal energy in the form of heat than they consume in electrical energy to do this work – and that the homeowner pays for.
How long do heat pumps last?
15 yearsThe life expectancy of a heat pump depends on several factors, such as the type of heat pump, your location, and how well the heat pump is maintained. Heat pumps normally last an average of 15 years, though some can wear out after a decade. Some of the newer units being manufactured today can last a bit longer.
How much electricity does a heat pump use per month?
What exactly is a heat pump?Heat pump BTU ratingAvg. monthly bill increaseAnnual kWh increase9,000$261,950 kWh12,000$372,775 kWh15,000$473,525 kWh18,000$634,725 kWhMar 2, 2020
How long should a heat pump run per day?
Typically, a heat pump should cycle two to three times an hour. The heat pump should stay on for 10 to 20 minutes during the cycle. However, during cold outside temperatures (below 30-40 degrees), a heat pump will constantly run to maintain the home temperature.
Does a heat pump run all the time in the summer?
Heat Pump Issues During Summer If the temperature outside is above 100°, you can most likely expect your heat pump to run constantly in order to keep your home cool. If it continues to run all the time even when the temperature outside drops, however, then you may be in need of heat pump maintenance.
Will a heat pump work in hot weather?
Heat pumps are highly energy-efficient and cost-effective when used in place of air conditioners in hot weather. However, heat pumps are much less efficient when used in colder temperatures, making them best to use in warmer climates.
Should I turn off my heat pump in the summer?
If your home does not require air conditioning, simply shut off your heat pump. As heat pumps still use electricity, use it only when needed for cooling and try other ways to keep your home cool (like closing windows and curtains during the hottest parts of the day, or planting leafy trees in front of windows).
How long does a heat pump run in summer?
A heat pump typically has two to three cycles an hour. The system will stay on for 10 to 20 minutes during the cycle. This time frame is sufficient to deliver your surplus energy (the difference between inside and outside temperature) throughout your home. What is this?
What is a heat pump?
What is a heat pump? This is a very common question for HVAC professionals, as heat pumps are an often misunderstood marvel of engineering and desi...
What does a heat pump do?
A heat pump is both a heating and cooling system, extracting heat from the air and moving it via an air handler to another location. In the summer...
Where do heat pumps work best?
Heat pumps work best in moderate climates, where the outside temperature during colder months does not drop near or below freezing on a regular bas...
How does a heat pump work in the winter?
A heat pump absorbs heat from outside air and blows it inside to warm your home up. They are much less expensive to run than a gas furnace because...
Does a heat pump cool as well as an air conditioner?
Heat pumps can heat AND cool the air unlike air conditioners. Even when it comes to cooling your house down, heat pumps are more efficient compared...
What temperature is a heat pump not effective?
Although heat pumps are more efficient than A/C normally, they aren't able to retain their efficiency between 25 and 40 degrees Fahrenheit. Heat pu...
How do you reset your heat pump?
To reset your heat pump, turn the thermostat and the pump off first. Turn off any associated breakers and let the refrigerant settle for at least t...
What is the average life expectancy of a heat pump?
On average, heat pumps last for 10 to 15 years depending on your use and maintenance. Some have also reported their systems remaining operational f...
What is a heat pump?
A heat pump is part of a heating and cooling system and is installed outside your home. Like an air conditioner, it can cool your home, but it’s also capable of providing heat. In cooler months, a heat pump pulls heat from the cold outdoor air and transfers it indoors, and in warmer months, it pulls heat out of indoor air to cool your home.
Where Do Heat Pumps Work Best?
Heat pumps are more common in milder climates, where the temperature does not typically drop below freezing. In colder regions, they can also be combined with furnaces for energy-efficient heating on all but the coldest days. When the temperature outside drops too low for the heat pump to operate effectively, the system will instead use the furnace to generate heat. This kind of system is often called a dual fuel system – it is very energy efficient and cost effective.
What Types of Heat Pumps Are There?
The two most common types of heat pumps are air-source and ground-source. Air-source heat pumps transfer heat between indoor air and outdoor air, and are more popular for residential heating and cooling.
What is a dual fuel heat pump?
When the temperature outside drops too low for the heat pump to operate effectively, the system will instead use the furnace to generate heat. This kind of system is often called a dual fuel system – it is very energy efficient and cost effective.
Do heat pumps burn fossil fuel?
In colder climates, an electric heat strip can be added to the indoor fan coil for additional capabilities. Heat pumps do not burn fossil fuel like furnaces do, making them more environmentally friendly.
Do heat pumps create heat?
Heat pumps do not create heat. They redistribute heat from the air or ground and use a refrigerant that circulates between the indoor fan coil (air handler) unit and the outdoor compressor to transfer the heat. In cooling mode, a heat pump absorbs heat inside your home and releases it outdoors.
How does a heat pump work?
What a heat pump does is use a small amount of energy to switch that process into reverse, pulling heat out of a relatively low-temperature area, and pumping it into a higher temperature area. So heat is transferred from a "heat source," like the ground or air, into a "heat sink," like your home.
Why do heat pumps and air conditioners work in the same way?
One of the biggest advantages of a heat pump over a standard heating ventilating and air conditioning (HVAC) unit is that there's no need to install separate systems to heat and cool your home.
Why do you need a backup burner in an air source heat pump?
In a typical air-source heat pump, there's the need for a backup burner to supply temporary heat when the system switches into reverse to defrost the coils . This backup burner prevents the system from blowing cold air through the registers while the coils defrost, which is key if your goal is to stay warm.
Why are heat pumps ineffective?
This is because moving heat from a very cold area to a hotter one takes more energy than moving heat between two areas with a more moderate temperature difference. There's also more heat available outside in a moderate climate than in a cold climate. It's important to note that even in a cold climate, there's still heat in the outside air to be pumped indoors, but the unit needs to work harder to extract the heat that's available. Supplemental energy may be required to make the heat pump produce enough warmth to comfortably heat your home when the temperature falls below freezing, and that's no good.
What is the most common type of heat pump?
One of the most common types of heat pumps is the air-source heat pump . This marvel of modern technology takes heat from the air outside your home and pumps it inside through refrigerant-filled coils, not too different from what's on the back of your fridge.
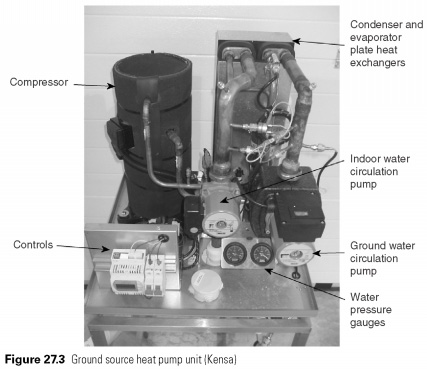
How does a ground source heat pump work?
The most common type of ground-source heat pump transfers heat directly from the ground by absorbing it through buried pipes filled with water or a refrigerant.
What is an absorption heat pump?
More water is then pumped from the well to extract more heat in a continuous open loop . Advertisement. If that's not enough to blow your mind, consider the absorptionheat pump -- air-source pumps that are powered by natural gas, solar power, propane or geothermal-heated water, rather than by electricity.
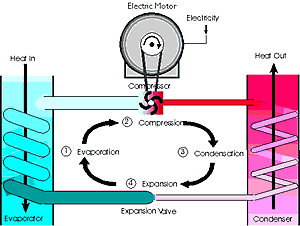
How does a heat pump work?
Heat Pump in Heat Mode 1 A heat pump can switch from air condition mode to heat mode by reversing the refrigeration cycle, making the outside coil function as the evaporator and the indoor coil as the condenser. 2 The refrigerant flows through a closed system of refrigeration lines between the outdoor and the indoor unit. 3 Although outdoor temperatures are cold, enough heat energy is absorbed from the outside air by the condenser coil and release inside by the evaporator coil. 4 Air from the inside of your house is pulled into ductwork by a motorized fan. 5 The refrigerant is pumped from the interior coil to the exterior coil, where it absorbs the heat from the air. 6 This warmed air is then pushed through connecting ducts to air vents throughout the home, increasing the interior temperature. 7 The refrigeration cycle continues again, providing a consistent method to keep you warm.
How does a heat pump switch from air conditioning to heat mode?
A heat pump can switch from air condition mode to heat mode by reversing the refrigeration cycle , making the outside coil function as the evaporator and the indoor coil as the condenser.
How does a condenser coil absorb heat?
Although outdoor temperatures are cold, enough heat energy is absorbed from the outside air by the condenser coil and release inside by the evaporator coil. Air from the inside of your house is pulled into ductwork by a motorized fan. The refrigerant is pumped from the interior coil to the exterior coil, where it absorbs the heat from the air.
How does refrigerant work?
The refrigerant absorbs the heat as it passes over the indoor air. This cooled and dehumidified air is then pushed through connecting indoor ducts to air vents throughout the home , lowering the interior temperature. The refrigeration cycle continues again, providing a consistent method to keep you cool.
What is a control board in a heat pump?
Control board: Controls whether the heat pump system should be in cooling, heating or defrost mode. Coils: The condenser and evaporating coil heat or cool the air depending on the directional flow of refrigerant. Refrigerant: The substance in the refrigeration lines that circulates through the indoor and outdoor unit.
How does a compressor work?
A compressor circulates refrigerant between the indoor evaporator and outdoor condensing units. The warm air indoor air then travels to the air handler while refrigerant is pumped from the exterior condenser coil to the interior evaporator coil. The refrigerant absorbs the heat as it passes over the indoor air.
What is refrigerant in refrigeration?
Refrigerant: The substance in the refrigeration lines that circulates through the indoor and outdoor unit.
A heat pump is a part of a heating and cooling system and is installed outside the home
Air conditioners, furnaces, and heat pumps are all HVAC systems. The heat pump, however, can act alone and perform both heating and cooling. In certain situations, it may be ideal for pairing it with a backup system like a furnace, but it does have enough electrical power to transfer heat and cool air into a home.
A heat pump is capable of using air to cool or heat your home by redistributing heat
No matter what the temperature is outside, a heat pump can gather heat located in the ground or air outside the home. The pump takes the heat into the system, compresses it to increase the temperature of a refrigerant, then pushes the hot air into the home.
The two most common types of heat pumps are air-source pumps and ground-source pumps
The main difference between an air-source pump and a ground-source (or geothermal) pump is the heat source. Air-source pumps have a unit outside the home and an internal piping system that extracts heat from the outside air and moves it indoors.
Heat pumps are most common in milder climates where temperatures rarely drop below freezing
While heat pumps can certainly keep your house warm during the winter, they may take longer in areas where the climate is colder and can drop below freezing. When a heat pump collects heat from outside, it becomes difficult once the air drops to a low enough temperature.
Like with any part of a heating and cooling system, heat pumps need regular maintenance
Dirty heat pump components, like coils, filters, and fans, can alter the air quality inside the home. It’s crucial to maintain a clean heat pump and ensure all parts are running correctly. If the pump does not get regular maintenance, the system can become damaged and eventually stop working properly, resulting in homeowners replacing it.
Always call a professional if you are experiencing issues with your heat pump
Sometimes an issue may arise inside piping, under the ground, or inside a unit that a homeowner may not be able to see or diagnose. It’s essential to contact a professional who knows the inside and out of the system to help find the issue.
What temperature should an A/C unit be?
Facts And Maintenance Tips 1 Most A/C Units are only capable of only a 15 to 20 temperature differential – In layman’s terms, if the outside temperature is 95°F, the best you can hope for inside the home is 75°F to 80°F. Therefore, any lack of maintenance will cause your system to be less effective and cost more than necessary. 2 According to the Department of Energy, 78° Fahrenheit is the sweet spot for air conditioners to balance energy savings and comfort when people are at home and need cooling. 3 An A/C system is a closed system. Meaning unless there is a leak somewhere, the fluid inside should always be present and will not dissipate.
What is the best temperature for an air conditioner?
According to the Department of Energy, 78° Fahrenheit is the sweet spot for air conditioners to balance energy savings and comfort when people are at home and need cooling.
How does R410A work?
The R410A refrigerant is in a gas state as it enters the outside unit. The gas enters into the compressor, which pressurizes the gas. The gas enters the compressor at about 50°F. As it exits the compressor it succumbs to a substantial pressure/temperature increase. The gas increases in temperature to approximately 150°F. If you’ve ever noticed all the very delicate air fins creating the walls of the Outside Unit, you’re looking at the condenser coil. The gas enters the coil and is snaked through the long winding coils throughout the outside of the unit. The fan on top of the Outside Unit draws outside ambient temperature air through the coils to remove heat, dispelling it through the top. Place your hand in the air stream of the fan output and you’ll experience just how much heat is being removed. By the time the gas makes its way through the coils, it has cooled to a liquid state. It is still under high pressure and still relatively hot… About 100°F. I’ll bet you’re wondering, how can it become a liquid when it’s 45°F above its boiling point… It converts to a liquid due to the high pressure exerted upon it at that time! The liquid travels through a tube from the Outside Unit to the Inside Unit.
How does a heat pump work?
But in a very practical sense, a heat pump works exactly like any air conditioner does – only the cycle can be reversed so that the cold air goes outside, and the hot air stays inside!
What is the purpose of a heat pump?
A heat pump, however, takes advantage of the natural properties of thermal dynamics to move heat from one place to another. The electricity used by the system is used only to power the compressor and the fans – not create heat – so far less energy is needed.
How much power does a NewAir AC-14100H use?
As evidence, let’s compare a couple NewAir products. The NewAir AC-14100H air conditioner heater uses less than 1000 watts to produce 10,000 BTUS of cooling, and it is only slightly less efficient during heating. In contrast, even a highly-efficient resistance heater like the NewAir AH uses 1500 watts to create only 5120 BTUs of heat. That’s an increase of 50% more energy used for only half the heating power.
What are the components of a compressor?
Four major components make this happen: 1 Compressor – The compressor squeezes the refrigerant (such as refrigerant, though refrigerant is used less frequently today then other more eco-friendly coolants), and turns it into a hot, high-pressured gas that gets pumped into the condenser. 2 Condenser – The condenser is a long coiled tube (like on the back of your refrigerator). As the refrigerant moves through it, heat is dissipated into the environment (usually helped by a fan). As it cools, it turns back into a liquid before being passed into the expansion valve. In a central AC, the condenser is located outside the house, so the heat stays outside. In a portable unit, the heat from the condenser coils is vented outdoors through the exhaust hose. 3 Expansion Valve – The expansion valve further lowers the pressure on the refrigerant, returning it to a liquid state before pumping it into the evaporator. 4 Evaporator – The evaporator is another long coil. Inside this coil, subjected to less pressure, the refrigerant begins to turn into a gas. As it evaporates, it pulls heat from the air to use as energy to power the transformation from liquid to gas. As the gas absorbs the heat, the cold air that is produced by the process is blown into the room by a fan.
What is the process of turning a refrigerant into a gas?
Evaporator – The evaporator is another long coil. Inside this coil, subjected to less pressure, the refrigerant begins to turn into a gas. As it evaporates, it pulls heat from the air to use as energy to power the transformation from liquid to gas. As the gas absorbs the heat, the cold air that is produced by the process is blown into the room by a fan.
How does an air conditioner work?
As the gas absorbs the heat, the cold air that is produced by the process is blown into the room by a fan. Then the cool, low-pressure gas from the evaporator is returned to the compressor, and the cycle begins again. So, in short, the air conditioner takes the heat from one side of the system ...
What is the job of a compressor?
Compressor – The compressor squeezes the refrigerant (such as refrigerant, though refrigerant is used less frequently today then other more eco-friendly coolants), and turns it into a hot, high-pressured gas that gets pumped into the condenser.