In simple terms, electricity is supplied to the house on the hot wires. After it flows through the household system, it is fed back to the utility on the neutral wire, completing the electrical circuit. The service panel contains a large main breaker that is the switch controlling the power to the rest of the circuit breakers inside the panel.
How does electricity get from the power plant to the House?
Here's how electricity gets to your house:
- Electricity is made at a generating station by huge generators. ...
- The current is sent through transformers to increase the voltage to push the power long distances.
- The electrical charge goes through high-voltage transmission lines that stretch across the country.
Why is there no electricity in my house?
- Check if there are any lights or movement visible on your electricity meter. ...
- If you have a pre-payment meter, you may need to add credit.
- Check your consumer unit, sometimes known as the fuse box or the trip switches - has one of the switches tripped into the off position?
How is electricity brought into a house?
How Is Electricity Brought Into A House? The electric transmission of power is effected by employing the source of power to drive a machine called a dynamo, which generates an electric current. This current is conveyed by a copper conductor, insulated from the earth, to the distant station, where it passes through a machine called an ...
How much electric energy does a house use?
Electricity: Profile Class 1 (kWh) Electricity: Profile Class 2 (kW) Low - 1,800. Low - 2,400. Medium - 2,900. Medium - 4,200. High - 4,300. High - 7,100. From this, we can work out that in a house with medium electricity use, the average monthly electricity use is about 242kWh. (2,900kWh divided by 12 months).
/GettyImages-682151574-5a7a1b8eba617700368c53ff.jpg)
How does electricity enter a home?
Electricity enters your home through a service head from a series of outdoor power lines or an underground connection. A typical service head consists of two 120-volt wires and one neutral wire that deliver power to lights and appliances around the home.
Where are you most likely to interact with your home's electrical system on a daily basis?
Electrical outlets are the place where you are most likely to interact with your home’s electrical system on a daily basis.
What is a grounded outlet?
Grounded outlets have a round hole for the grounding conductor in addition to the two vertical slots. The circle slot is connected to a ground wire. Grounded outlets are required to be installed in all modern homes today. If your home does not have grounded outlets, then your electrical system is likely missing critical safety features. Consult an electrician about updating your home.
What is a circuit breaker?
Fuses and circuit breakers are safety devices that help prevent overloading of your home electrical system and prevent fires. They stop the electrical current if it exceeds the safe level for some portion of your home electrical system.
How many conductors does electricity have?
Electricity always seeks to return to its source and complete a continuous circuit. A typical circuit in your home has two conductors: hot and neutral. Electricity travels from the service panel to home appliances through the hot conductor, and returns the current to the main service panel through the neutral conductor. A third or “grounding” wire is also connected to all outlets and metal boxes in your home.
How to tell if a home has aluminum wiring?
The best way to determine whether a home has aluminum wiring is to hire a licensed, qualified electrician, but it may also be possible to identify an aluminum-wired system by checking the cables that run through the basement or attic to see if the cable is labeled “AL” or Aluminum.
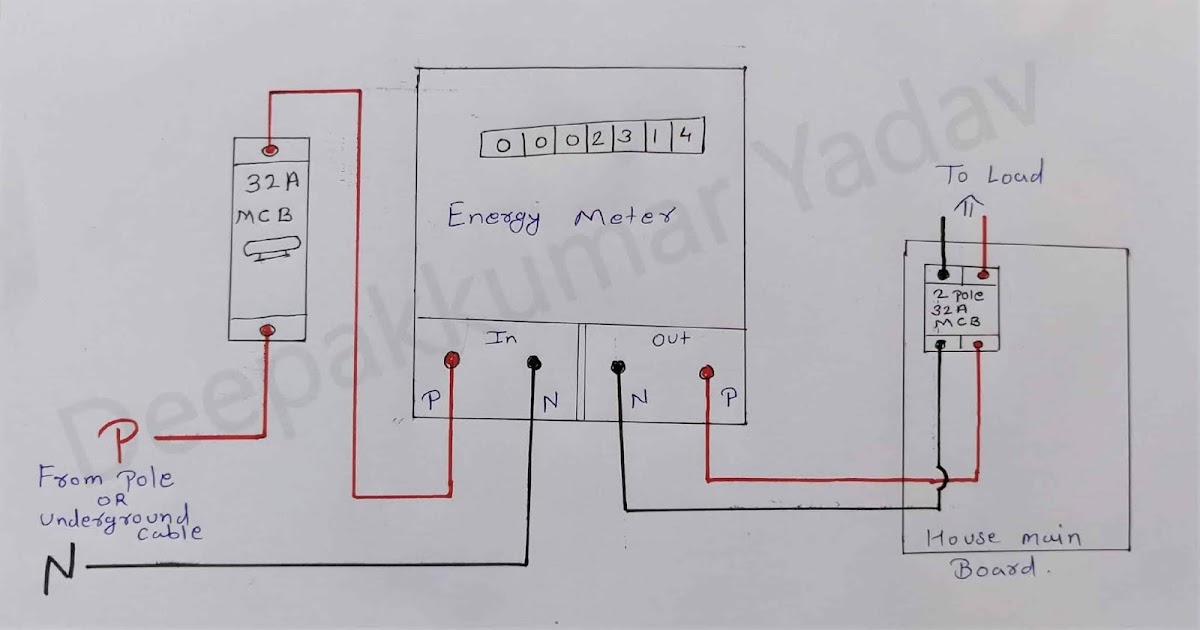
What is an electric meter?
The electric meter is mounted outdoors where electricity enters your home. This device is used to measure the amount of electricity that is consumed in your home. The meter is monitored by your electric utility company and is protected by law—tampering with it is both extremely dangerous and illegal.
How does electricity flow?
Electricity flows in from one of two 120-volt wires and backs out through a grounded neutral wire. Any flaw in the wire to and from these points will interrupt the current’s path and cause a fault in one of your circuits.
What is the purpose of an electrical panel?
This panel’s job is to distribute power throughout your home and disconnect power from the incoming feed .
Why disconnect power from utility company?
This allows the homeowner to disconnect the power from the utility company from the outside of the house without having to get to the electrical panel. A great reason for this would be a house fire. The fire department can kill the power from outside the home without entering the home.
How many amps does a breaker need?
The power comes into the main breaker and is usually 100 or 200 amps. Individual breakers then distribute individual circuits (called branch circuits) throughout your home. These breakers range in size from 15 to 100 amps.
Why do you tape wires together?
The reason is to make every connection accessible. For instance, if you splice the wires together and tape them within the wall cavities with no box and cover it with drywall, how will you get back to it to work on the splice if there’s a problem? You can open a box at any time.
Why do electrical boxes need to be spliced?
The National Electric Code requires that wires be spliced into boxes. The reason is to make every connection accessible.
What is a switch?
Switches. Switches come in many different styles. There are single-pole, three-way, four-way, dimmer, and motion-sensing switches. Their purpose is to turn on and off a circuit from different places in your home. Switches are used to control lighting, ceiling fans, receptacles, and appliances.
What happens if you have old electrical wiring?
If you have old wiring, you probably have a whole set of issues. One of the more common ones is frayed insulation because there was no grounding, and the wiring wasn’t made to handle today’s heavy-duty appliances. There are several other common electrical problems that are not restricted to old wiring: 1 Frequent surges caused by lighting, damaged power lines, or faulty appliances or wiring 2 Dips in power supply because of faulty devices (or those made of poor-quality materials) connected to the power grid 3 Light switches that don’t work correctly 4 A circuit breaker that trips frequently 5 An overloaded circuit breaker 6 Shocks 7 Lights that are too bright or too dim 8 High electrical bills 9 Lightbulbs that burn out too often 10 “Possessed” recessed lights that go out and then come back on
Why is my old wiring frayed?
One of the more common ones is frayed insulation because there was no grounding, and the wiring wasn’t made to handle today’s heavy-duty appliances.
What color wires are used for electrical wiring?
How to Connect electrical wires. When you’re doing wiring installation, you need to identify the parts of the wiring cable, the non-metallic electrical cable: the outer sheathing (the jacket) and the inner wires. The colored “wire” you see—the green, black, red, blue or white—is actually the sheathing that covers the inner copper wires.
What are the red wires on a smoke detector?
Red wires are also hot wires used to interconnect smoke detectors, so that if one alarm goes off, all the others do as well. White and gray wires are neutral wires that connect to the neutral bus bar, which attracts current and carries it throughout the house.
How to avoid electrical shock?
Familiarize yourself with the different wires. Make sure you know which colored wire goes where and their purpose to avoid electrical shock and to safely wire your home. Have more wire than you need. Make sure it stretches at least three inches outside of the electrical box. Patch drywall with big plates.
What is the NEC code for wiring?
NEC code identifies types of electrical wires and electrical cable types by color. When you remove a switch plate, you’ve probably noticed yellow, white, black, ...
Why does my power supply dip?
Dips in power supply because of faulty devices (or those made of poor-quality materials) connected to the power grid. Light switches that don’t work correctly. A circuit breaker that trips frequently. An overloaded circuit breaker. Shocks. Lights that are too bright or too dim. High electrical bills.
How does electricity start?
Your home's electricity starts with the power service and electric meter. The utility company's service cables (whether overhead or underground) extend to your house and connect to the utility's meter base. The electric meter plus into this meter base. The meter measures the amount of electricity your home uses and is the basis for the charges on your electric bill. The meter runs only when electricity is used in the house.
Why is it important to know the basic components of an electrical system?
People depend on electricity constantly, and when the power goes out in a storm or there's a tripped breaker or another problem in an electrical circuit, understanding the basic components of an electrical system can help you get things running again. It's also important to know who is responsible for what portion of your electrical service.
How many amps can a main breaker run?
A main breaker of 200 amps will allow a maximum of 200 amps to flow through it without tripping. In a tripped state, no current will flow to the panel. In systems without an external disconnect switch, the main breaker serves as the household disconnect.
What is a breaker in a house?
The breakers for the branch circuits fill the panel (usually below) the main breaker. Each of these breakers is a switch that controls the flow of electricity to a branch circuit in the house. Turning off a breaker shuts off the power to all of the devices and appliances on that circuit. If a circuit has a problem, such as an overload or a fault, the breaker automatically trips itself off.
Why does my breaker go off?
If a circuit has a problem, such as an overload or a fault, the breaker automatically trips itself off. The most common cause of a tripped breaker is a circuit overload. If you're running a high-demand appliance, such as a vacuum, toaster, or heater, and the power goes out, you've probably overloaded the circuit.
What are the devices in a house?
Devices are all the things in the house that are connected to electricity, including switches, receptacles (outlets), light fixtures, and appliances. Devices are connected to the individual branch circuits that start at the breakers in the main service panel.
What is the name of the wires that connect to the breaker box?
Two large "hot" wires connect to big screw terminals, called lugs, inside the service panel, providing all the power to the panel.
How does electricity enter a home?
Electricity enters every home by running through a power meter supplied by the local utility company, then, in most cases, through a master 200-amp circuit breaker, and then to the home’s breaker box, often still referred to as a fuse box .From the breaker box, this flow of electricity is spread over numerous circuits to different parts of the home by first passing through individual circuit breakers which serve as a safety mechanism to keep the system from being overloaded. A home’s electrical system is designed to work off 120 volts with the exception of certain major appliances, such as an electric clothes dryer, which runs off 240 volts.
How many volts does a house use?
A home’s electrical system is designed to work off 120 volts with the exception of certain major appliances, such as an electric clothes dryer, which runs off 240 volts. Electrical wiring comes in different gauges, or sizes. The heavier the gauge, i.e., the thicker the copper wire, the more electrical current it can carry without overheating.
What happens if you use too much wire with a low amp breaker?
On the other hand, if a too large of a gauge wire is used with a low amp breaker then the breaker may continuously trip, disrupting the circuit before the wire ever reaches its maximum electrical load. It is imperative to know exactly what gauge wire and what amp breaker have to be used for any given application.
Why are receptacles called duplex?
Modern receptacles are called “duplex receptacles” because they have two screws on both sides. As the name implies, they can bring electrical current into one set of screws and then send it out on the other “duplex” set of screws to another fixture.
What is the black wire called?
A black wire carries the electrical current and is therefore commonly known as the “hot” wire. There is a white wire that is the “neutral,” and, finally, a bare copper wire that is the ground wire. When electrical wires are joined together ...
How many wires are in a house?
Be sure to consult your local and state building codes before beginning any electrical work. Standard household electrical wire contains three wires: black (hot), white (neutral) and bare copper (ground). Typical electrical wire for home use comes in an insulated sleeve and consists of three wires. A black wire carries the electrical current ...
Where does the hot wire come from?
A “hot” wire will come from a circuit breaker or other “hot” junction box and lead to the first wall outlet. From there another wire is run from the first wall outlet to the second wall outlet.
How many hot wires does a house have?
Most homes in the United States have two hot wires and one neutral coming into them. Supplying a stated 240/120 volts. The actual voltage received is normally slightly less 230/115 volts. This type of power is commonly called single phased power. Most residential homes have this type of basic house wiring.
What determines how much current goes through a wire?
Additionally, the size of the wire will determine how much current can go through it. You will want to use the correct size wire whenever you are installing or replacing electrical devices.
How many volts does a hot wire and a neutral supply?
When you use one hot wire and the neutral you get 115 volt power. Most small electrical devices and lights run on this current. Heavy duty items like ranges, hot water tanks and dryers use both hot wires and the neutral to achieve 230 volts.
Why is wiring color coded?
Newer wiring is color coded, to let the installer know what the wire is for. However, colors are not an absolute indicator of how a wire is being used.
What are some pages related to residential wiring?
Some popular pages related to residential wiring are, ' Doorbell Wiring ', ' Phone Jack Wiring ', ' Installing Electrical Outlets ', ' Wiring a Light Switch ' and ' Wiring a Ceiling Fan '.
What is alternating current?
Most residential homes have this type of basic house wiring. The power coming into your home is also called alternating current. There are people in the world that can explain what that means exactly, but none of them are writing this article. Alternating current is used to allow electricity to be transported over long distances.
Is wiring a house dangerous?
The first rule to remember is that basic house wiring can be dangerous. Never attempt to do it without a good understanding of how it works and safe work practices. This article is intended to provide basic information and is not a comprehensive discussion of all aspects of house wiring. See the article on ' Electrical Safety Tips for Homeowners ' for more information.
Where does electricity come from in a house?
The Electrical Panel. If your house is "on the grid," your power comes from a generating station that works 24/7 to produce electricity for you and your neighbors. The power comes to your house on transmission lines and gets stepped down to 240 volts by a transformer before coming to your main electrical panel.
How does an electrical circuit work?
But whatever form of current being discussed, an electrical circuit is the wiring pathway that runs from the power source, through wires to the devices being powered, the back again to the power source. A circuit is essentially a completed loop of electrical current. Any time you turn a wall switch ON or OFF, or any time you plug in and turn on a lamp or other appliance, you are either completing, or interrupting, that circuit.
What is the color of the hot wire in a 120 volt circuit?
The hot wire for the circuit attaches to the circuit breaker and the return wire attaches to the neutral bus. In addition, each circuit has a ground wire that connects to the ground bus. The National Electric Code specifies white as the color for the neutral wire, and by convention, the hot wire is either black or red. In 120-volt circuits, the hot wire is almost always black. The ground wire is usually bare copper, but it can be a green insulated wire.
What color wires are used to connect a breaker?
Hot terminals are always brass, neutral terminals are chrome or silver colored and ground terminals are green. Because the wires are color-coded, you always know which wire to attach to which terminal in order to close the circuit and power the device. It's always white wire to chrome/silver, terminal bare copper to green terminal, and black or red wire to brass terminal.
How does a transformer work?
Inside the panel, a pair of hot wires coming from the transformer connect to a pair of brass bus bars, and a single neutral wire, connected to a chrome bus bar, completes the circuit by returning back to the transformer. The voltage of each hot bus relative to the return bus is 120 volts. All the 120-volt circuits in the house, which are the ones that power lights and outlets, connect to one of the brass bus bars and to the neutral bus. In addition, they connect to a third bus which is connected to a ground rod. Grounding provides a way to safely complete the circuit in case of a power surge or some other fault. It prevents electrical accidents and fires.
How does a 240V circuit work?
A 240-volt circuit is created by using a two-gang breaker, which contacts both bus bars at the same time. Since the voltage between each hot bus and the return wire is 120 volts, the voltage between the two hot bus bars is 240 volts.
What is the difference between 120 and 240 volts?
Note: The 120-volt and 240-volt ratings are averages. In practice, line voltages can vary. For the purposes of this discussion, 120-volts refers to devices with ratings between 110 and 125 volts, and 240-volt devices can refer to voltage ratings ranging from 230 to 250 volts.