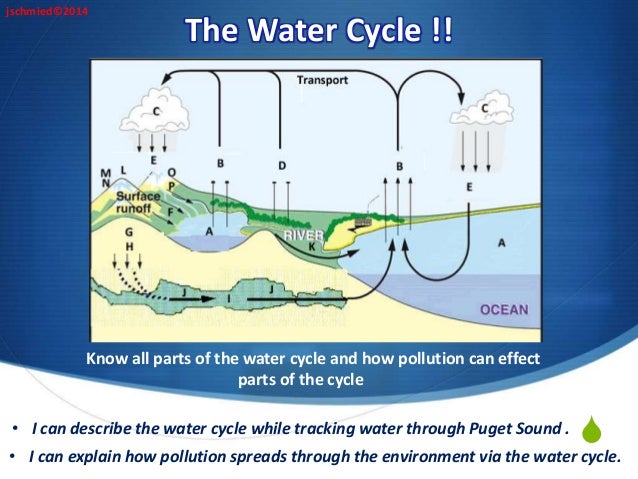
In urban areas the pollutants include gas, oil, pet waste, fertilizers, pesticides, salt and treated human waste from sewage treatment plants. Such waste when dumped into the water bodies contaminates the water bodies and in turn affects the water cycle.
What are the human impacts of the hydrologic cycle?
Human Impact. Human impacts are often magnified because of the hydrologic cycle. This is due to the fact that pollutants often follow the path of the water Withdrawal of Water Humans remove water out of the system to irrigate crops, to provide us with drinking water and to carry out many of our industrial processes.
What are the causes of water waste?
This means that irrigation is needed, which, in turn, causes water wastage. When humans remove natural vegetation and replace those areas with infrastructure, it speeds up overflow which leads to evaporation and higher river levels. The overflow water that we’re left with is stormwater, which cannot be consumed.
How do humans change the water cycle?
We change the flow of water using irrigation. We dam lakes and rivers for electricity and to create manmade lakes and ponds. The Colorado River in the US no longer reaches the ocean at times because humans have altered it so much. Groundwater usage in India: Climate change is causing numerous changes to the water cycle.
What are the factors that affect the water cycle?
Humans and the water cycle 1 Hydroelectricity. This involves changing the stored gravitational energy of water held behind the dam into electrical energy that can be used. 2 Irrigation. We need more food, and to make food, we need water. ... 3 Deforestation. ... 4 Greenhouse effect. ...

How does human waste affect water?
Raw sewage contains a variety of dissolved and suspended impurities. The organic materials are food and vegetable waste. When that waste hits the water, microorganisms begin to decompose the materials. That uses up some of the dissolved oxygen in the water because those microorganisms use it in their metabolism.
What human activities have impacted the water cycle?
Human activities such as deforestation, agriculture, construction of dams, urbanization, removal of groundwater from wells, and water abstraction from rivers and lakes has affected the water cycle significantly.
What human activities cause water pollution?
Causes of Water PollutionRapid Urban Development.Improper Sewage Disposal.Fertilizer Run-Off.Oil Spills.Chemical Waste Dumping.Radioactive Waste Discharge.
How do humans affect water quality?
How do human activities affect water quality? Urban and industrial development, farming, mining, combustion of fossil fuels, stream-channel alteration, animal-feeding operations, and other human activities can change the quality of natural waters.
How do humans impact the water cycle positively?
Purposefully changing water cycle : We pull water out of the ground in order to use it. We change the flow of water using irrigation. We dam lakes and rivers for electricity and to create manmade lakes and ponds. The Colorado River in the US no longer reaches the ocean at times because humans have altered it so much.
Which activities do you think has the greatest impact on water quality and availability?
Agriculture. Agriculture is a huge contributor to water pollution, from fertilizers used for row crops to the manure created by large-scale animal agriculture.
How does agriculture affect the water cycle?
Agricultural practices may also have negative impacts on water quality. Improper agricultural methods may elevate concentrations of nutrients, fecal coliforms, and sediment loads. Increased nutrient loading from animal waste can lead to eutrophication of water bodies which may eventually damage aquatic ecosystems.
How does burning fossil fuels affect the water cycle?
The tiny aerosol particles — pollutants from burning fossil fuel and vegetation — cut down the amount of heat reaching the ocean, which initiates the cycling of water vapour. The researchers think the aerosols may be 'spinning down' the hydrological cycle of the planet.
How do humans affect the water cycle?
Humans affect the water cycle in numerous ways. Some of our actions purposefully affect the water cycle and other human activities have unintentional consequences on the water cycle. The image above shows some examples of how we manipulate various sources of water on earth. We pull water out of the ground in order to use it.
Why do we dam lakes and rivers?
We dam lakes and rivers for electricity and to create manmade lakes and ponds. The Colorado River in the US no longer reaches the ocean at times because humans have altered it so much. Groundwater usage in India: Climate change is causing numerous changes to the water cycle.
Why can't the water cycle work in urban areas?
This happens when the natural water cycle cannot function properly in urban areas due to buildings, concrete and other surfaces that are preventing the water from reaching the ground, allowing it to soak into the soil .
How do artificial reservoirs affect the water cycle?
Artificial reservoirs. As much as artificial reservoirs are great sources for water conservation, they have a negative effect on the water cycle. These artificial water sources, often referred to as man-made reservoirs, can be formed by building a dam across a valley, diverting river flow into the reservoir.
How does land use change?
Land-use changes can be anything from evolving economic and social to biophysical conditions, and land-cover changes are seen as the global wind patterns and topography, which both play a major role in the moisture recycling and distribution patterns. Although we cannot control these elements, we can control land-use factors (like irrigations, artificial dams and deforestation) which all increase evaporation patterns, affecting runoff water, the yearly streamflow and the vegetation from the land.
Why are water storage units important?
Although they help to save water, they cause more environmental stress on land and have a big impact on time concentration of watersheds because of the evaporation caused. Because these water storage units are used for drinking water, stormwater lands in these reservoirs which causes the water to be contaminated.
What happens when you remove vegetation and replace with infrastructure?
When humans remove natural vegetation and replace those areas with infrastructure, it speeds up overflow which leads to evaporation and higher river levels. The overflow water that we’re left with is stormwater, which cannot be consumed. Stormwater contains pollutants such as sediment, nutrients, bacteria and chemicals that can threaten human and animal health.
How will land development affect stormwater?
Infrastructure and building will cause conventional methods of land development to collect and convey stormwater quickly into a series of drains and pipes that will flow directly into the closest waterbody or man-made artificial reservoir , with little or no water quality treatment.
How does the use of toxic chemicals affect agriculture?
Along with that, the increased use of toxic chemicals in the agriculture, automotive and manufacturing industries, as well as the runoff from chemical fertilisers and pesticides, is only continuing to pollute our surface water and contaminate our ground soil, making production growth impossible. Here are a few of the biggest effects on ...
What happens to water vapour in the atmosphere?
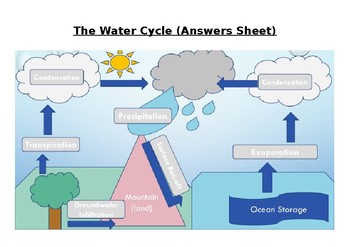
Water vapour in the atmosphere condenses into clouds and falls as precipitation (rain, hail or snow). The distribution of rainfall across the planet is very uneven, with some regions receiving rain all year round and some receiving none at all ( Figure 4 41 ).
Where is human waste collected?
Water-borne human waste is collected in sewers, treated in sewage plants and returned, as cleaner water, to the water cycle, into rivers or the sea. The primary function of sewage treatment is to break down faeces and remove harmful microbes from the water.
How do plants take in carbon dioxide?
To maintain a flow of nutrients through their stems and leaves they take up water in their roots and release it as water vapour through tiny holes in their leaves, called stomata, through which they also take in carbon dioxide.
How does pollution affect water resources?
These disposal practices leave most wastes inadequately treated, thereby causing pollution. This in turn affects precipitation (Box 4.2), surface waters (Box 4.3), and groundwater (Box 4.4), as well as degrading ecosystems (see Chapter 5). The sources of pollution that impact our water resources can develop at different scales (local, regional and global) but can generally be categorized (Table 4.5) according to nine types. Identification of source types and level of pollution is a prerequisite to assessing the risk of the pollution being created to both the aquatic systems and, through that system, to humans and the environment. With the knowledge of the principal sources of the pollution, the appropriate mitigation strategy can be identified to reduce the impact on the water resources.
How do sediments affect water?
Sediments occur in water bodies both naturally and as a result of various human actions. When they occur excessively, they can dramatically change our water resources. Sediments occur in water mainly as a direct response to land-use changes and agricultural practices, although sediment loads can occur naturally in poorly vegetated terrains and most commonly in arid and semi-arid climates following high intensity rainfall. Table 4.4 summarizes the principal sources of excessive sediment loads and identifies the major impacts that this degree of sediment loading can have on aquatic systems and the services that water resources can provide. A recently documented and increasing source of high sediment loads is the construction of new roads in developing countries where little consideration is given to the impacts of such actions on aquatic systems and downstream water supplies. Globally, the effects of excessive sedimentation commonly extend beyond our freshwater systems and threaten coastal habitats, wetlands, fish and coral reefs in marine environments (see Chapter 5). The importance of sediment control should be an integral consideration in any water resources development and protection strategy. UNESCO’s International Sediment Initiative (ISI) project will attempt to improve the understanding of sediment phenomena, and provide better protection of the aquatic and terrestrial environments.
Why is water quality important?
Assessing water quality enables the natural characteristics of the water to be documented and the extent of the pollution to be determined; however, today monitoring is a more holistic process relating to health and other socio-economic issues. The international compilation of surface water and groundwater quality data sets at a global scale is still in its relative infancy as compared to precipitation or surface water runoff data. Although some facilities have existed for several decades to collect and disseminate this type of data, it has been historically difficult to collect. This is attributable to several reasons. National centres have not always been linked to institutional networks. Most nations are simply not used to providing this information to anyone other than their immediate institutions and users for either national or specific project purposes. In addition, data in many developing countries is not extensive and even where it has been collected, making it publicly available as a data set is frequently not a priority for the already overloaded and meagrely resourced national and subnational water resource institutions. However, progress has been made in the past three years in this area. The GEMS/Water international water quality database 4 went online in March 2005 and now has begun to work with a broad range of agencies, NGOs and data quality groups to harmonize the reporting of water data and information. They have established a QA/QC (quality assurance/quality control) programme that includes laboratory evaluations based on a freely available published set of methods that are used by most of the laboratories that report their data to GEMS/Water. GEMS/Water (2005) reports that data is now received from about 1,500 stations globally, including about 100 for lakes and groundwater.
What are the causes of overuse of water?
Among the most prominent are the highly inefficient water supply provisioning practices for agriculture and municipal use, deforestation, and the basic lack of control over exploitation of the actual surface and groundwater sources. Inappropriate development of reservoirs and diversions combined with inadequate considerations of alternatives in conservation and use minimization (demand management) have further complicated and increased the impacts on existing water resources. While there are some hopeful signs of change emerging in selected local actions (see Chapters 5 and 7), these are few in comparison to the broad-based and fundamental modifications needed in national, regional and subnational practices to reverse and counteract these ongoing substantive impacts.
How do pharmaceuticals affect the environment?
A variety of pharmaceuticals including painkillers, tranquilizers, anti-depressants, antibiotics, birth control pills, estrogen replacement therapies, chemotherapy agents, anti-seizure medications, etc., are finding their way into the environment via human and animal excreta from disposal into the sewage system and from landfill leachate that may impact groundwater supplies. Agricultural practices are a major source and 40 percent of antibiotics manufactured are fed to livestock as growth enhancers. Manure, containing traces of pharmaceuticals, is often spread on land as fertilizer from which it can leach into local streams and rivers.
Why is it important to identify source types and level of pollution?
Identification of source types and level of pollution is a prerequisite to assessing the risk of the pollution being created to both the aquatic systems and, through that system, to humans and the environment.
What causes acidic conditions in water?
Atmospheric contamination from industrial plants and vehicle emissions leads to dry and wet deposition. This causes acidic conditions to develop in surface water and groundwater sources and at the same time leads to the destruction of ecosystems.
How does rain affect the environment?
When rain, snow or sleet falls from clouds and flow through the contaminated areas or when water flows through streams that are contaminated, pollutants are dispersed. These contaminants may infect plant or animal life, including human beings, and reduce their ability to grow and reproduce. When water is removed from the environment to supply our growing needs, the reduced flow of water affect the local water supply and it may eventually change the local environment and alter the plant and animal species that are found here.
What are the pollutants in water?
Humans add substances to the water that cause its properties to change. As precipitation falls on the ground and moves into rivers and creeks, it picks up pollutants that range from dirt sediments to toxic chemicals. In rural areas, pollutants include farm pesticides, herbicides and fertilizers as well as wastes from septic systems. In urban areas, the pollutants include gas, oil, pet waste, fertilizers, pesticides, salt and treated human waste from sewage treatment plants. Pollutants often cause the
Why are human impacts magnified?
Human impacts are often magnified because of the hydrologic cycle. This is due to the fact that pollutants often follow the path of the water. Humans remove water out of the system to irrigate crops, to provide us with drinking water and to carry out many of our industrial processes. Water also provides energy for many households ...
What are the pollutants in urban areas?
In urban areas, the pollutants include gas, oil, pet waste, fertilizers, pesticides, salt and treated human waste from sewage treatment plants. Pollutants often cause the. degradation and eutrophication of the water supplies. Overall Impact. When rain, snow or sleet falls from clouds and flow through the contaminated areas or when water flows ...
Quotes
Behavior
- One of the most concerning human activities that affects the entire water cycle is urbanisation. This happens when the natural water cycle cannot function properly in urban areas due to buildings, concrete and other surfaces that are preventing the water from reaching the ground, allowing it to soak into the soil.
Summary
- Land-cover changes are changes that are directly influenced by local, regional or global climate processes, whereas land-use changes are changes that are affected by humans.
Conservation
- As much as artificial reservoirs are great sources for water conservation, they have a negative effect on the water cycle. These artificial water sources, often referred to as man-made reservoirs, can be formed by building a dam across a valley, diverting river flow into the reservoir. Although they help to save water, they cause more environmental stress on land and have a big impact o…
Mechanism
- When we remove trees from forests that have been growing for years, it reduces evapotranspiration, which is the sum of evaporation and plant transpiration from land and ocean surface to the atmosphere, leading to a possible reduction in precipitation. This then leads to an increase in water eutrophication, which then cannot be consumed by humans.
Overview
- Cloud seeding is a weather modification, where you change the amount or type of precipitation that falls from clouds through the usage of harmful substances. During this process, the substances that fall from the clouds are dispersed into the air, causing cloud condensation which further affects climate conditions.