What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis occurs when high levels of carbon dioxide disrupt the blood’s acid-base balance. It often occurs in people who experience rapid, uncontrollable breathing (hyperventilation). Treatment includes supplemental oxygen and therapies to reduce the risk of hyperventilation.
What is hyper hyperventilation in respiratory alkalosis?
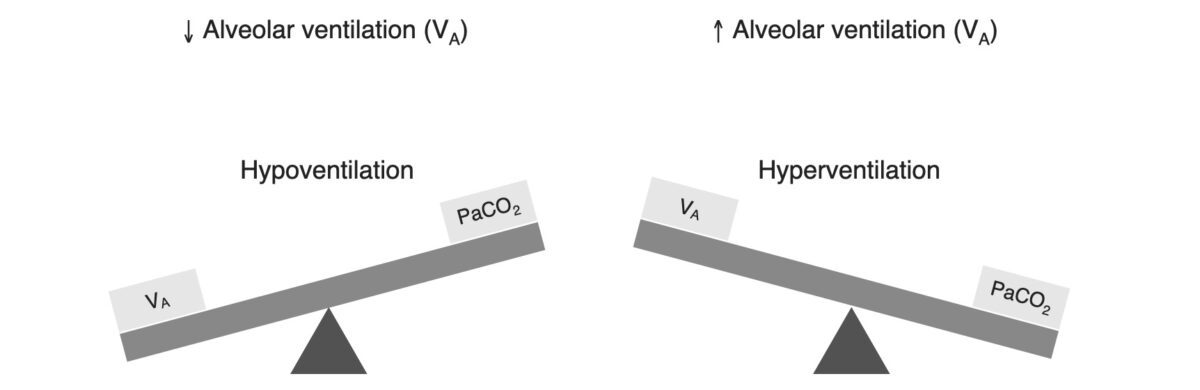
hyperventilation (ie increased alveolar ventilation) is the mechanism responsible for the lowered arterial pCO2 in ALL cases of respiratory alkalosis. this low arterial pCO2 will be sensed by the central and peripheral chemoreceptors and the hyperventilation will be inhibited unless the patient’s ventilation is controlled.
What causes respiratory alkalosis in sepsis?
Respiratory alkalosis may be an early sign of sepsis, preceding hypoxemia or hypotension. (Remember, one of the classic features of systemic inflammatory response syndrome is tachypnea ). The cause of respiratory alkalosis will often be evident from the history and physical examination.
How to treat respiratory alkalosis caused by overbreathing due to panic and anxiety?
The following strategies and tips are useful for respiratory alkalosis caused by overbreathing due to panic and anxiety. Fill the paper bag with carbon dioxide by exhaling into it.
Does hypoxemia cause alkalosis?
a Causes of Respiratory Alkalosis Respiratory alkalosis is due to hyperventilation, which may be stimulated by hypoxemia associated with pulmonary disease, congestive heart failure, or severe anemia.
How does hypoxemia cause respiratory acidosis?
Abstract: Most causes of respiratory acidosis are due to hypoventilation, not increased CO2 production. Respiratory insufficiency causes hypoxemia, which can lead to a secondary metabolic acidosis. The early phase of respiratory acidosis is associated with severe acidemia in acute respiratory failure.
Does hypoxia cause acidosis or alkalosis?
Hypoxia, depending upon its magnitude and circumstances, evokes a spectrum of mild to severe acid-base changes ranging from alkalosis to acidosis, which can alter many responses to hypoxia at both non-genomic and genomic levels, in part via altered hypoxia-inducible factor (HIF) metabolism.
What can cause respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory alkalosis is a condition marked by a low level of carbon dioxide in the blood due to breathing excessively....Common causes include:Anxiety or panic.Fever.Overbreathing (hyperventilation)Pregnancy (this is normal)Pain.Tumor.Trauma.Severe anemia.More items...•
How does hypoxia affect acid-base balance?
Hypoxia can lead to anaerobiosis and metabolic acidosis and, in animals that are apneic, to respiratory acidosis. A fall in blood and tissue pH is a major limiting factor in hypoxic tolerance and a variety of strategies occur in vertebrates, in concert with hypometabolism, to respond to this acid-base challenge.
What happens to pH levels during hypoxia?
Hypoxia and steady-state pH It is well established that hypoxia/ischemia leads to a decrease in both pHi and pHo in vivo (Tombaugh and Sapolsky, 1993).
Why does hyperventilation cause respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory Alkalosis When a person hyperventilates they exhale more carbon dioxide than normal. As a result the carbon dioxide concentration in the blood is reduced and the bicarbonate/carbonic acid equilibrium shifts to the left. The corresponding drop in H3O+ concentration causes an increase in pH.
What causes hypoxemia hypercapnia and acidosis?
Hypercapnia and respiratory acidosis ensue when impairment in ventilation occurs and the removal of carbon dioxide by the respiratory system is less than the production of carbon dioxide in the tissues. Lung diseases that cause abnormalities in alveolar gas exchange do not typically result in alveolar hypoventilation.
How does the body compensate for respiratory alkalosis?
The kidney compensates in response to respiratory alkalosis by reducing the amount of new HCO3− generated and by excreting HCO3−. The process of renal compensation occurs within 24 to 48 hours. The stimulus for the renal compensatory mechanism is not pH, but rather Pco2.
What are the two types of respiratory alkalosis?
Classification. There are two types of respiratory alkalosis: chronic and acute as a result of the 3–5 day delay in kidney compensation of the abnormality. Acute respiratory alkalosis occurs rapidly, have a high pH because the response of the kidneys is slow.
Which of the following can cause respiratory alkalosis quizlet?
Anxiety with hyperventilation is the most common cause of respiratory alkalosis; therefore anxiety disorders increase the risk for this acid-base imbalance.
What is the difference between metabolic and respiratory alkalosis?
Metabolic alkalosis: Metabolic alkalosis may be caused by losing too much acid from the body, or by having too much bicarbonate. Respiratory alkalosis: Respiratory alkalosis can happen when there is too little carbon dioxide in the blood due to the lungs breathing out too much carbon dioxide.
What causes hypoxemia hypercapnia and acidosis?
Hypercapnia and respiratory acidosis ensue when impairment in ventilation occurs and the removal of carbon dioxide by the respiratory system is less than the production of carbon dioxide in the tissues. Lung diseases that cause abnormalities in alveolar gas exchange do not typically result in alveolar hypoventilation.
How does respiratory acidosis occur?
Respiratory acidosis is a condition that occurs when the lungs cannot remove all of the carbon dioxide the body produces. This causes body fluids, especially the blood, to become too acidic.
How does excess CO2 lead to respiratory acidosis?
Respiratory acidosis occurs when the lungs can't remove enough of the carbon dioxide (CO2) that the body produces. Excess CO2 causes the pH of your blood and other bodily fluids to decrease, making them too acidic. Usually, the body is able to balance the ions that control acidity.
How does hyperventilation lead to respiratory acidosis?
Abstract. Deviations of the alveolar ventilation rate from normality induce respiratory acid-base disturbances. Alveolar hyperventilation leads to hypocapnia and thus respiratory alkalosis whereas alveolar hypoventilation induces hypercapnia leading to respiratory acidosis.
What is the difference between acidosis and hypotenstion?
Acidosis = body cells laking enough oxygen. hungry for O2 the vasculature opens up demanding more O2 = hypotenstion. hypotenstion = increased lack of O2 to brain =confusion, headache, blurred vision. heart cells hungry for O2 can't pump as fast and need to slow down =bradycardia.
Why is serum osmolality low?
that means the serum osmolality is low because the salt is diluted in all that excess water.
Can pulmonary emboli go with acidosis?
Howcome in Alkalosis you have "pulmonary emboli" but in acidosis have alot of respiratory things like "pneumonia", "COPD" it kind of sounds like "p emboli" can go with acidosis
Where is metabolic acidosis based?
Metabolic acidosi/alkalosis is based in the kidneys - by absorption/excretion of bicarb/hydrogen ions.
Can heart cells pump faster than O2?
heart cells hungry for O2 can't pump as fast and need to slow down =bradycardia
Is alkalosis associated with hyperventilation?
If so, consider that respiratory alkalosis is always associated wtih hyperventilation and that a patient with pulmonary emboli is often found in respiratory distress with an elevated respiratory rate.
What are the mechanisms of hypoxemia?
There are various mechanisms of hypoxemia. These are V/Q mismatch, right-to-left shunt, diffusion impairment, hypoventilation, and low inspired PO2.
What is the mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction?
The mechanism of hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Hypoxia causes closure of voltage-gated potassium channel, leading to K+accumulation intracellularly. It leads to depolarization of the cells, opening of voltage-gated calcium channel and calcium-mediated pulmonary vasoconstriction
What is a high V/Q ratio?
High V/Q ratios develop when ventilation is excess in proportion to perfusion. Figure 3is showing an example of high V/Q ratio in pulmonary embolism (PE). It can produce a dead space like effect.[14] Since perfusion is less; removal of CO2by high V/Q unit is low. Although the impact of high V/Q unit on blood oxygenation is minimal, it can cause hypoxemia if the compensatory rise in total ventilation is absent. Since the high V/Q unit receiving less perfusion, blood from this area is diverted to other areas leading to the development of low V/Q in other areas of the lungs. It results in the development of hypoxemia unless the compensatory rise in total ventilation is impaired. The compensatory rise in ventilation can lead to normalization of V/Q ratio of the low V/Q areas.
How does the A-A oxygen difference increase with age?
In young person, the A-a oxygen difference is <10 mmHg. The A-a oxygen difference increases with age. It is primarily due to age-induced decrease in the PaO2level because of the rise in V/Q mismatch. The drop in PaO2after 70 years is about 0.43 mmHg per year.[3] High FiO2by increasing both the alveolar and arterial oxygen level widens the gradient. The rise in gradient is due to disproportionate increase in alveolar oxygen level. The arterial blood oxygen level does not rise to the same proportion as the alveolar oxygen level due to its admixing with unoxygenated blood coming from bronchial veins, mediastinal veins, and thebesian veins.[1]
What is the difference between hypoxia and hypoxia?
Hypoxemia is defined as a decrease in the partial pressure of oxygen in the blood whereas hypoxia is defined by reduced level of tissue oxygenation. It can be due to either defective delivery or defective utilization of oxygen by the tissues. Hypoxemia and hypoxia do not always coexist.
What is the fractional concentration of inspired oxygen?
FiO2is the fractional concentration of inspired oxygen. It is 0.21 at room air.
Why is oxygen important?
Oxygen is an essential element for life and without oxygen humans can survive for few minutes only. There should be a balance between oxygen demand and delivery in order to maintain homeostasis within the body.
What is hypoxemia in the body?
Your blood carries oxygen to the organs and tissues of your body. Hypoxemia is when you have low levels of oxygen in your blood. Hypoxemia can be caused by a variety of conditions, including asthma, pneumonia, and chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD). It’s a serious medical situation and requires prompt medical attention.
How to treat hypoxemia?
Treatment. Since hypoxemia involves low blood oxygen levels, the aim of treatment is to try to raise blood oxygen levels back to normal. Oxygen therapy can be utilized to treat hypoxemia. This may involve using an oxygen mask or a small tube clipped to your nose to receive supplemental oxygen.
Why is there a mismatch in ventilation?
There are two causes of ventilation perfusion mismatch: The lungs are getting enough oxygen, but there’s not enough blood flow (increased V/Q ratio). There is blood flow to the lungs, but not enough oxygen (decreased V/Q ratio).
What is the difference between perfusion and ventilation?
Ventilation refers to the oxygen supply in the lungs, while perfusion refers to the blood supply to the lungs. Ventilation and perfusion are measured in a ratio, called V/Q ratio. Normally, there’s a small degree of mismatch in this ratio, however if the mismatch becomes too great, problems can occur. There are two causes of ventilation perfusion ...
What is it called when you have low oxygen levels?
Hypoxemia is when you have low levels of oxygen in your blood. There are several different types of hypoxemia and many different conditions can cause it. Hypoxemia is a serious condition and can lead to organ damage or even death if left untreated.
What happens when oxygen enters the lungs?
Diffusion impairment. When oxygen enters the lungs, it fills small sacs called alveoli. Tiny blood vessels called capillaries surround the alveoli. Oxygen diffuses from the alveoli into the blood running through the capillaries. In this type of hypoxemia, the diffusion of oxygen into the bloodstream is impaired.
What is the condition where there isn't enough oxygen in the blood?
Anemia is a condition in which there aren’t enough red blood cells to effectively carry oxygen. Because of this, a person with anemia may have low levels of oxygen in their blood. Additionally, hypoxemia can be a symptom of another condition such as respiratory failure.
What causes respiratory alkalosis?
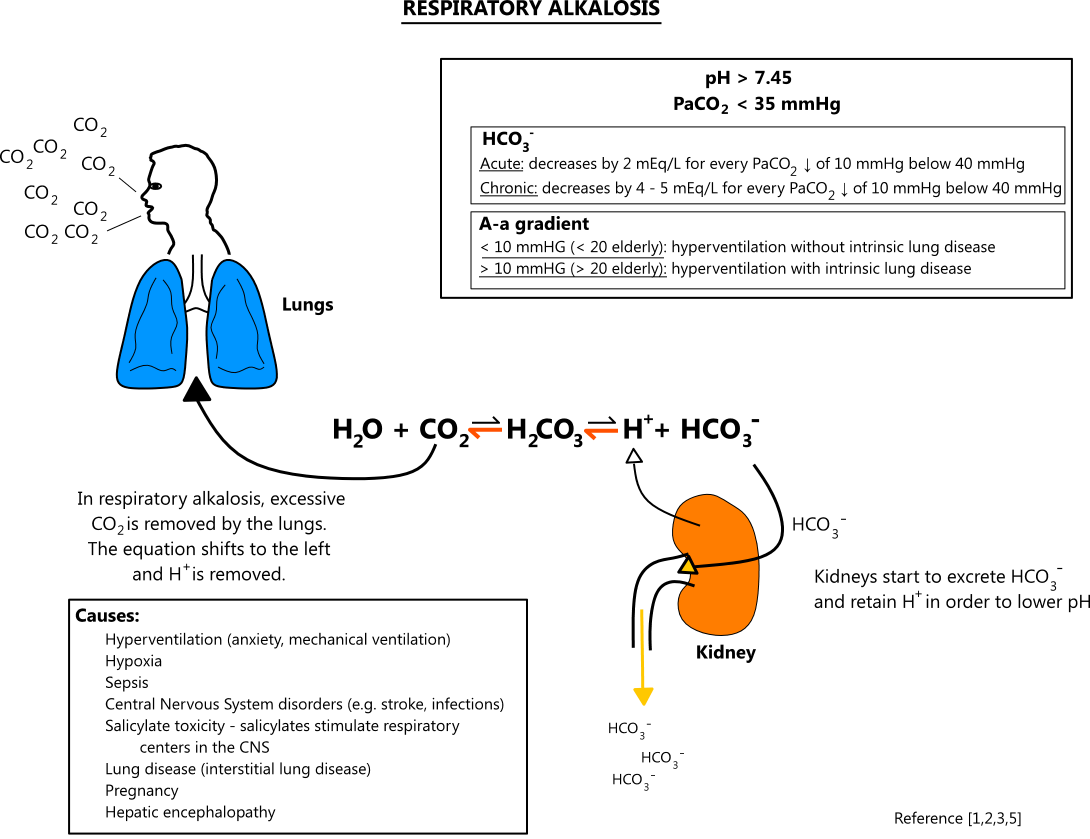
These include central causes, hypoxemic causes, pulmonary causes, and iatrogenic causes. Central sources are a head injury, stroke, hyperthyroidism, anxiety-hyperventilation, pain, fear, stress, drugs, medications such as salicylates, and various toxins. Hypoxic stimulation leads to hyperventilation in an attempt to correct hypoxia at the expense of a CO2 loss. Pulmonary causes include pulmonary embolisms, pneumothorax, pneumonia, and acute asthma or COPD exacerbations. Iatrogenic causes are primarily due to hyperventilation in intubated patients on mechanical ventilation. [6][7]
How to treat metabolic alkalosis?
Treatment of metabolic alkalosis is targeted at treating the underlying pathology. In anxious patients, anxiolytics may be necessary. In infectious disease, antibiotics targeting sputum or blood cultures are appropriate. In embolic disease, anticoagulation is necessary. Ventilator support may be necessary for patients with acute respiratory failure, acute asthma, or acute, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) exacerbation if they show signs of respiratory fatigue. In ventilator controlled patients, it may be necessary to reevaluate their ventilator settings to reduce respiratory rate. If hyperventilation is intentional, monitor the arterial or venous blood gas values closely. In severe cases, pH may be directly reduced using acidic agents. However, this is not routinely done. [14][15][16]
How does HCO3 affect alkalosis?
HCO3 functions as an alkalotic substance. CO2 (carbon dioxide) functions as an acidic substance. Therefore, Increases in HCO3 (bicarbonate) or decreases in CO2 will make blood more alkalotic . The opposite is also true where decreases in HCO3 or an increase in CO2 will make blood more acidic. CO2 levels are physiologically regulated by the pulmonary system through respiration, whereas the HCO3 levels are regulated through the renal system with reabsorption rates. Therefore, respiratory alkalosis is a decrease in serum CO2. While it is theoretically possible to have decreased CO2 production, in every scenario this illness is a result of hyperventilation where CO2 is breathed away. [2][3][4]
What is the normal pH of the blood?
Respiratory alkalosis is 1 of the 4 basic classifications of blood pH imbalances. Normal human physiological pH is 7.35 to 7.45. A decrease in pH below this range is acidosis, an increase above this range is alkalosis. Respiratory alkalosis is by definition a disease state where the body’s pH is elevated to greater than 7.45 secondary to some respiratory or pulmonary process.[1]
What is the primary pH buffer system in the human body?
The primary pH buffer system in the human body is the HCO3/CO2 chemical equilibrium system. Where:
Is respiratory alkalosis an acute or chronic process?
Respiratory alkalosis may be an acute process or a chronic process. These are determined based on the level of metabolic compensation for the respiratory disease. Excess HCO3 levels are buffered to reduce levels and maintain a physiological pH through the renal decrease of H secretion and increasing HCO3 secretion; however, this metabolic process occurs over the course of days whereas respiratory disease can adjust CO2 levels in minutes to hours. Therefore, acute respiratory alkalosis is associated with high bicarbonate levels since there has not been sufficient time to lower the HCO3 levels and chronic respiratory alkalosis is associated with low to normal HCO3 levels. [8][1][9]
Is respiratory alkalosis a disease?
Respiratory alkalosis is the most common acid-base abnormality with no discrimination between genders. The exact frequency and distribution of disease are dependent upon the etiology. Likewise, the morbidity and mortality rates are dependent on the etiology of the disease. [5]
Why do some people have chronic respiratory alkalosis?
Some people, such as those with chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, may experience chronic respiratory alkalosis due to continuing hyperventilation. This is because these people frequently breathe faster than normal when trying to get more oxygen into the body.
What causes alkalosis in the lungs?
Numerous medical conditions can cause respiratory alkalosis. Some of these include: 1 atrial flutter 2 panic disorder 3 liver disease 4 pneumothorax, which occurs when air in the pleural cavity causes a collapsed lung 5 pulmonary embolism 6 overdose of salicylate medications, such as aspirin
Why does alkalosis have a pH of 7.45?
A person with respiratory alkalosis will have a pH higher than 7.45 and a lower arterial carbon dioxide level because they are breathing off excess carbon dioxide.
What does it mean when you breathe so fast?
At its simplest definition, respiratory alkalosis almost always means that a person is breathing so fast that they are getting rid of carbon dioxide in excess. Carbon dioxide is an acid.
Why does breathing too fast cause respiratory alkalosis?
Outlook. Breathing too fast can cause a person to go into respiratory alkalosis. This occurs when a person’s pH level is higher than 7.45. A person may breathe too fast due to anxiety, overdosing on certain medications, or using a ventilator. Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis may include muscle spasms, irritability, ...
How does the body correct alkaline pH?
The body may try to self-correct the pH imbalance that comes with respiratory alkalosis, such as by having the kidneys increase excretion of alkaline and reduce excretion of acid.
What is the pH level of respiratory alkalosis?
The human body normally works to maintain a pH level of around 7.35–7.45.
What is the net effect of global hypocapnia?
The net effect is an impairment in ventilation-perfusion matching, which may exacerbate hypoxemia. ( 12097540)
What is the most common acid-base disorder among critically ill patients?
Hypocapnia is the most common acid-base disorder among critically ill patients. ( 12097540) This shouldn't be surprising, since hypocapnia may be caused by almost any pulmonary disease, pain/anxiety, or sepsis – exceedingly common conditions among critically ill patients. In most cases, the cause of hypocapnia will be evident and this won't require further investigation or management. However, very rarely a patient may be discovered with unexplained, significant hypocapnia – which warrants additional evaluation.
What does low CO2 mean in end tidal?
End tidal CO2 revealing a substantially low CO2 measurement also suggests hypocapnia (e.g., etCO2 << 30 mm). However, this may also be caused by pulmonary dysfunction with an increase in dead space volume. Therefore, correlation between the end tidal CO2 and an ABG/VBG measurement is needed to confirm the diagnosis of hypocapnia.
Can sepsis cause hypocapnia?
Consider sepsis as a cause of hypocapnia, if other etiologies are unlikely or excluded.
Can alkalosis be seen on physical examination?
The cause of respiratory alkalosis will often be evident from the history and physical examination. If the cause remains unclear, the following evaluations might be considered.
Is respiratory alkalosis a compensatory response?
This chapter is about primary respiratory alkalosis, which is respiratory alkalosis (hypocapnia) that isn't a compensatory response to a metabolic acidosis.
Is respiratory alkalosis a sign of sepsis?
Respiratory alkalosis may be an early sign of sepsis, preceding hypoxemia or hypotension. (Remember, one of the classic features of systemic inflammatory response syndrome is tachypnea ).
What is the underlying cause of respiratory alkalosis?
Hyperventilation and respiratory alkalosis. Hyperventilation is typically the underlying cause of respiratory alkalosis. Hyperventilation is also known as overbreathing. Someone who is hyperventilating breathes very deeply or rapidly.
How to tell if you have respiratory alkalosis?
Symptoms of respiratory alkalosis. Overbreathing is a sign that respiratory alkalosis is likely to develop. However, low carbon dioxide levels in the blood also have a number of physical effects, including: dizziness. bloating. feeling lightheaded. numbness or muscle spasms in the hands and feet. discomfort in the chest area.
How to get carbon dioxide out of your lungs?
Breathe into a paper bag. Fill the paper bag with carbon dioxide by exhaling into it. Breathe the exhaled air from the bag back into the lungs. Repeat this several times. Doing this several times can give the body the carbon dioxide it needs and bring levels back up to where they should be.
How long does it take for alkalosis to go away?
Symptoms should disappear shortly after carbon dioxide levels in the blood are brought back to normal.
What happens if you overbreathe?
Overbreathing is a sign that respiratory alkalosis is likely to develop. However, low carbon dioxide levels in the blood also have a number of physical effects, including: 1 dizziness 2 bloating 3 feeling lightheaded 4 numbness or muscle spasms in the hands and feet 5 discomfort in the chest area 6 confusion 7 dry mouth 8 tingling in the arms 9 heart palpitations 10 feeling short of breath
What happens when you inhale oxygen?
Your body needs oxygen to function properly. When you inhale, you introduce oxygen into the lungs. When you exhale, you release carbon dioxide , which is a waste product.
What happens when you exhale?
When you exhale, you release carbon dioxide, which is a waste product. Normally, the respiratory system keeps these two gases in balance. Respiratory alkalosis occurs when you breathe too fast or too deep and carbon dioxide levels drop too low. This causes the pH of the blood to rise and become too alkaline. When the blood becomes too acidic, ...
What is respiratory alkalosis?
Respiratory Alkalosis = a primary acid-base disorder in which arterial pCO2 falls to a level lower than expected.
What is the mechanism responsible for the lowered arterial pCO2 in ALL cases of respiratory alkalosis?
hyperventilation (ie increased alveolar ventilation) is the mechanism responsible for the lowered arterial pCO2 in ALL cases of respiratory alkalosis.
What is the limit of bicarbonate in respiratory alkalosis?
limit: the lower limit of ‘compensation’ for this process is 18mmol/l – so bicarbonate levels below that in an acute respiratory alkalosis indicate a coexisting metabolic acidosis.
Does bicarbonate buffer have compensation?
mechanism: not really compensation but changes in the physicochemical equilibrium of the bicarbonate buffer system occur due to the lowered pCO2 and this results in a slight decrease in HCO3-.
Is pulmonary oedema a persistent disorder?
Pulmonary oedema (all types) Maintenance. required a persistent disorder. this is different to the situation with a metabolic alkalosis where maintenance of the disorder requires an abnormality to maintain it as well as the problem which initiated it.
Does a decrease in arterial pCO2 cause respiratory alkalosis?
MANAGEMENT. the decrease in arterial pCO2 inhibits the rise in ventilation -> the hypocapnic inhibition of ventilation (acting via the central chemoreceptors) may leave the patient with an impaired state of tissue oxygen delivery. in most cases correction of the underlying disorder will resolve respiratory alkalosis.
