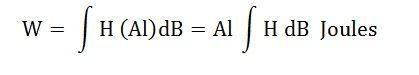
Does hysteresis loss depend on voltage and frequency?
Does hysteresis loss depend on voltage and frequency? Powerful .NET APIs to manipulate 100+ different file formats. Process DOCX, PDF, XLSX, PPTX, HTML, barcodes, raster & vector images, OCR features, financial reports. Yes, indeed. In the mathematical formula of hysteresis loss, the loss is directly proportional to the flux and voltage as well.
What is hysteresis loss and where does it occur?
Let us understand this concept by taking an example of electrical machines, as the hysteresis loss occurs mainly where there is a reversal of magnetism, as in the magnetic parts of the electrical machines.
How do you calculate hysteresis loss?
Steinmetz method: Steinmetz’s equation, a kind of empirical relationship established by Steinmetz in 1892, is used for calculate the hysteresis loss, which was obtained by experimental results for values of Bm in the range of 0.2 T and 1.5 T, is expressed as: where η and α are both obtained based on experimental results.
What is hysteresis loss in magnetic materials?
Hysteresis loss is associated with the phenomenon of hysteresis and is an expression of the fact when ferromagnetic material is involved. In ferromagnetic materials, not all the energy of the magnetic field is returned to the circuit when the external field is removed.

How does frequency affect hysteresis loss?
Indeed, an increase of the frequency involves a swelling-up of the hysteresis loop at constant magnetic flux density and so an increase of iron losses. The more accurate that swelling-up is measured, the more precise the dependency between frequency and iron losses is quantifiable.
How do hysteresis and eddy current losses depend on frequency?
Hysteresis losses are proportional to the electrical frequency and the eddy current losses are proportional to the square of the electrical frequency.
What is hysteresis loss and how it is dependent on supply voltage and frequency?
Eddy current loss and hysteresis loss are almost independent of load, significantly depending on supply voltage and frequency. As the flux density or flux is constant for a given voltage and frequency, eddy current loss and hysteresis loss remain constant at any load. Therefore, these losses are called constant losses.
What is hysteresis loss proportional to?
The energy loss associated with hysteresis is proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop. As the area of the hysteresis loop for a specimen is found to be large, the hysteresis loss in this specimen is also large. Hysteresis loss occurring in a material is, W h = η × B m 1.6 × f × V.
What are the factors on which hysteresis loss depends?
Hysteresis loss is directly proportional to the frequency of the field, magnetic flux intensity, and volume of the material.
Do eddy currents increase with frequency?
The eddy current field decreases with further increase of the frequency.
Which loss in transformer varies with frequency?
Depending on the frequency value in the range of 50-60 Hz, the change in eddy current loss has been observed while the transformer winding is excitation at 1.74 T magnetic flux density. It has been observed that increasing the frequency causes an increase in the no load loss in the 3-phase transformer.
What happens to the hysteresis losses and eddy current losses if the frequency of a transformer is increased keeping the supply voltage constant *?
hysteresis loss will decrease but eddy current will remain unchanged.
What is the formula of hysteresis loss?
The hysteresis loss per second is given by the equation[20]: Hysteresis loss, Ph= (Bmax)1.6f V joules per second (or) watts. Where, f: supply frequency in Hz, V: volume of core in cubic meters, η‟: hysteresis coefficient, Bmax: peak value of flux density in the core.
What will happen to hysteresis loss if voltage is doubled load is doubled and frequency is halved?
It is load independent. Thus by doing voltage twice and frequency half of the original value we will get same hysteresis loss.
How can you reduce the hysteresis loss?
How do we Reduce Hysteresis Losses? Hysteresis losses can be reduced by using material that has less area of the hysteresis loop. Hence, high grade or silica steel can be used for designing the core within a transformer because it has extremely less area of the hysteresis loop.
How can we minimize hysteresis loss the magnetic material?
In order to minimise loss due to hysteresis, the magnetic material should have. large B-H loop area.
How does hysteresis loss occur?
Hysteresis losses are the consequence of the fact that on the microscopic scale the magnetization process proceeds through sudden jumps of the magnetic domain walls that are unpinned from defects or other obstacles by the pressure of the external field ( see also Magnetic Hysteres is). The local eddy currents induced by the induction change accompanying the wall jump dissipate a finite amount of energy through the Joule effect.The sum over all jumps gives the hysteresis loss associated with the jump sequence. The jumps are so short (of the order of 10−8 –10 −9 s) that the external field is unable to influence the internal jump dynamics. The only effect of the field is to compress or expand the time interval between subsequent jumps in inverse proportion to the field rate of change, which yields a number of jumps per unit time and an amount of energy dissipated per unit time proportional to the magnetization frequency. Therefore, for the hysteresis loss in a loop of peak induction B, one obtains the typical expression
What is hysteresis loss?
Hysteresis loss is associated with the phenomenon of hysteresis and is an expression of the fact when ferromagnetic material is involved. In ferromagnetic materials, not all the energy of the magnetic field is returned to the circuit when the external field is removed. A hysteresis loop shows the relationship between the induced magnetic flux ...
What causes hysteresis loss in an electromagnetic circuit?
A hysteresis loss in an electromagnetic circuit will occur due to molecular magnetic friction (magnetostriction), as discussed in Section 1.6.2 (A-iv). This causes a distortion in voltage and current by distorting their natural sinusoidal waveforms. This distortion in the natural waveforms, in terms of magnetizing current Im, induced e.m.f. e and magnetic flux ϕ of the magnetic circuit is the source of generating triple harmonic quantities, the magnitude of which will depend upon the shape of the hysteresis loop, which is a function of the core material. A fluctuation in the system voltage which causes a change in the flux density B ( equation (1.5)) also adds to the triple harmonic quantities. Permeability μ of the magnetic core is different at different flux densities B. This results in giving rise to triple harmonics due to magnetic friction (magnetostriction). Wherever the switching of a capacitor bank is more frequent, the generation of triple harmonic voltages is more severe.
How to measure hysteresis loss?
For the hysteresis loss measurement, it is generally obtained by using DC- or low-ramp-rate magnetometry. This will be performed using either a superconducting quantum interference device (SQUID magnetometer) or a vibrating-sample magnetometer (VSM).
Why is the magnetic field changing?
Because AC is used, the direction of current is constantly changing through the coil, and therefore its magnetic field is constantly changing direction. Therefore, the molecules in the core are constantly moving to align in the proper direction. In their movement, they bump into each other, causing friction and heat.
What is the difference between extensive and intensive properties?
From the view point of the physics, an intensive property is a physical property of a system that does not depend on the system size or the amount of material in the system , while the extensive property is directly proportional to the size or amount.
What causes hysteresis losses?
Hysteresis losses are caused by continuous reversals in the alignment of the magnetic domains in the magnetic core . Energy is wasted in aligning the magnetic domains, every x sec it reverses direction so take energy to do this. The reversal is because that our current is AC, so if its frequency increases this means that we have more reversals and this means more wasted energy in aligning the magnetic domains.
How to reduce eddy current loss?
To reduce the Eddy current loss we use lamination of thin plate. Thin plate results in lower cross sectional area which increase the core resistance and hence Eddy current reduce.
What are the factors that affect hysteresis?
Factors Affecting Hysteresis Loss 1 The loop of the hysteresis is narrow; the material will be magnetized very easily. 2 Similarly, if the material doesn’t get magnetized simply, then the hysteresis loop will be large. 3 At different values of ‘B’, different materials can saturate, so the loop height will be affected. 4 This loop mainly depends on the material nature. 5 The loop size, as well as shape, mainly depends on the first position of the specimen.
What are some examples of hysteresis loss?
Some of the examples of hysteresis loss include permanent magnets, electromagnets, and the core of the transformer. These are used in ferromagnets. Hysteresis loops are significant in the designing of numerous electrical devices. Thus, this is all about an overview of hysteresis loss which includes formula, factors, and applications.
What is the benefit of a hysteresis loop?
The main benefit of the hysteresis loop mainly includes; the area of the hysteresis loop represents low hysteresis loss. This loop gives the retentivity & coercivity value of a material. Therefore the way to select ideal material to build a permanent magnet, then the core of the machine will become easier.
What happens if the loop of a hysteresis is narrow?
The loop of the hysteresis is narrow; the material will be magnetized very easily. Similarly, if the material doesn’t get magnetized simply, then the hysteresis loop will be large. At different values of ‘B’, different materials can saturate, so the loop height will be affected.
What are the two types of magnetic losses?
So magnetic losses are two types namely hysteresis & eddy current. This article discusses an overview of hysteresis loss and its affecting factors.
What are the losses in rotational motors?
Generally, these losses are classified into different losses like magnetic, mechanical, copper, brush otherwise stray losses based on the fundamental cause as well as mechanism.
What is the relationship between the H and B?
The main relationship among the ‘H’ (magnetizing force), ‘ B’ (the flux density) is illustrated in the following hysteresis curve. The hysteresis loop area shows the required energy to complete a complete cycle of magnetizing as well as de-magnetizing. The loop area mainly represents the lost energy throughout this process.
MAGNETISATION CURVE OR B-H CURVE
The curve drawn giving the relationship between magnetic flux density (B) and the magnetizing force (H)is known as the magnetization curve or B-H curve.
MAGNETIC HYSTERESIS
When a magnetic material is magnetized first in one direction and then in another direction then it is found that the flux density ‘B’ in the magnetic material lags behind the applied magnetizing force ‘H’.
HYSTERESIS LOSS
It is defined as the loss that occurred to neutralize the residual or remanent magnetism by the process of magnetization and demagnetization.
What is hysteresis loss?
Hysteresis loss is associated with the phenomena of hysteresis and is an expression of the fact when ferromagnetic material is involved, not all the energy of the magnetic field is returned to the circuit when mmf is removed. It is known as hysteresis loss.
What happens to the tip of a hysteresis loop?
The tip of hysteresis loop can be joined to obtain the magnetization characteristics. Hysteresis loss results in a dissipation of energy which appears as a heating of the magnetic material. The energy loss associated with hysteresis is proportional to the area of the hysteresis loop.
What is the lagging effect of flux density B?
Hysteresis is the ‘lagging’ effect of flux density B whenever there are changes in the magnetic field strength H. When an initially unmagnetized ferromagnetic material is subjected to a varying magnetic field strength H, the flux density B produced in the material varies.
What is the sum of hysteresis loss and eddy current loss?
Core Losses. The sum of hysteresis loss and eddy current losses is called core loss as both the losses occur within the core (magnetic material). For a given magnetic circuit with a core of ferromagnetic material, volume and thickness of the plates are constant and the total core loss can be expressed as follows.
Why is the magnetic field produced by the winding not linked to the secondary winding?
Stray Losses: All the magnetic field produced by the winding is not linked to the secondary winding due to the leakage of flux primary current It may induce eddy currents within nearby conductive objects, such as the transformer’s support and get converted to heat which is lost to the surroundings structure.
What is eddy current loss?
Eddy Current Losses: An eddy current is an electric current set up by an alternating magnetic field. These losses arise from the fact that the core itself is composed of conducting material, so that the voltage induced in it by the varying flux produces circulating currents in the material. Eddy current loss depends upon the rate of change ...
What are the losses of winding resistance?
Copper Losses in Winding resistance: Windings are made up of copper wire which get heated due to Joule heating when current flows through them. effect When working at higher frequencies, skin effect and proximity effect add to the losses due to winding resistance. Eddy Current Losses: An eddy current is an electric current set up by an alternating ...
What causes hysteresis loss?
Hysteresis loss is caused by the magnetization and demagnetization of the core as current flows in the forward and reverse directions. As the magnetizing force (current) increases, the magnetic flux increases.
What are the losses in electric motors?
These losses are generally categorized as magnetic losses, mechanical losses, copper losses, brush losses, or stray losses, depending on the underlying cause and mechanism.
What is the power loss caused by a motor core?
This induced EMF causes circulating currents to flow, referred to as eddy currents. The power loss caused by these currents is known as eddy current loss .
What is eddy current loss?
Eddy current losses are the result of Farady’s law, which states that, “Any change in the environment of a coil of wire will cause a voltage to be induced in the coil, regardless of how the magnetic change is produced.” Thus, when a motor core is rotated in a magnetic field, a voltage, or EMF, is induced in the coils. This induced EMF causes circulating currents to flow, referred to as eddy currents. The power loss caused by these currents is known as eddy current loss.
