How does intermolecular forces influence viscosity?
Higher the intermolecular forces, higher will be the viscosity. When there is a strong intermolecular force, the molecules of the liquids are strongly bonded to each other. This induces a resistance to move. The liquids whose molecules are polar or capable of forming hydrogen bonds are more viscous.
Does viscosity increase with increased intermolecular forces?
Viscosity increases as intermolecular interactions or molecular size increases.
How do intermolecular forces affect the properties of surface tension and viscosity?
As the intermolecular forces increase, the area of space becomes less, and the surface tension increases. So, as the intermolecular forces increase both the viscosity and surface tension also increases.
How do intermolecular forces affect the properties of liquid?
Intermolecular forces determine bulk properties, such as the melting points of solids and the boiling points of liquids. Liquids boil when the molecules have enough thermal energy to overcome the intermolecular attractive forces that hold them together, thereby forming bubbles of vapor within the liquid.
What is the relationship between viscosity and intermolecular forces quizlet?
Viscosity is defined as a liquid's resistance to flowing, so compounds with weaker intermolecular forces will have lower viscosities. Of these options, only having a compact molecular shape results in weaker intermolecular forces, so this will result in the lowest viscosity. You just studied 8 terms!
How does viscosity depend on intermolecular forces quizlet?
Viscosity is greater in substances with stronger intermolecular forces because molecules are more strongly attracted to each other., preventing them from flowing around each other as freely.
How temperature and intermolecular forces affect viscosity?
As the temperature of a liquid increases, kinetic energy of the molecules increases which can overcome intermolecular forces. So, the liquid can flow more easily, this results in decrease in viscosity of the liquid.
What are the effects of intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular forces are the forces that bind two molecules together. Physical properties are affected by the strength of intermolecular forces. Melting, boiling, and freezing points increase as intermolecular forces increase. Vapor pressure decreases as intermolecular forces increase.
How does intermolecular forces affect the surface tension?
The surface tension of a liquid results from an imbalance of intermolecular attractive forces, the cohesive forces between molecules: A molecule in the bulk liquid experiences cohesive forces with other molecules in all directions. A molecule at the surface of a liquid experiences only net inward cohesive forces.
Why water has low viscosity when it has high intermolecular forces?
Water has very strong intermolecular forces, hence the low vapor pressure, but it's even lower compared to larger molecules with low vapor pressures. Viscosity is the property of fluid having high resistance to flow.
How is viscosity affected by hydrogen bonding?
In liquids, the ability of neighboring molecules to rearrange and jostle past each other is directly related to viscosity, the property which describes the propensity to flow. The presence of hydrogen bonds (H-bonds) complicates the molecular scale picture of viscosity.
What is the effect in viscosity of the compound has weak intermolecular forces?
The stronger the intermolecular forces of attraction for the molecule, the higher the viscosity of the liquid. The liquid with stronger intermolecular forces of attraction will have a higher resistance to flow due to stronger interactions among molecules, which means that it will have higher viscosity.
What causes viscosity to increase?
Viscosity generally increases as the temperature decreases. The viscosity of a liquid is related to the ease with which the molecules can move with respect to one another. Thus the viscosity of a liquid depends on the: strength of attractive forces between molecules, which depend on their composition, size, and shape.
Does high viscosity mean weak intermolecular forces?
The stronger the intermolecular forces of attraction for the molecule, the higher the viscosity of the liquid. The liquid with stronger intermolecular forces of attraction will have a higher resistance to flow due to stronger interactions among molecules, which means that it will have higher viscosity.
Do weak intermolecular forces have high viscosity?
Substances with stronger intermolecular forces are more viscous than substances with weaker intermolecular forces.
Why Water has low viscosity when it has high intermolecular forces?
Water has very strong intermolecular forces, hence the low vapor pressure, but it's even lower compared to larger molecules with low vapor pressures. Viscosity is the property of fluid having high resistance to flow.
What is the bond between honey and oxygen?
The bonds in honey are hydrogen and oxygen form hydrogen bonding, which are one of the strongest bonds, and this causes strong cohesion forces between them and it causes the flow of honey to be slow/viscous. Cohesion is the attraction in a molecule of liquid to each other due to intermolecular forces.
What is the attraction in a molecule of liquid to each other due to intermolecular forces?
Cohesion is the attraction in a molecule of liquid to each other due to intermolecular forces.
What is the difference between capillary action and surfactant action?
The stronger the intermolecular interactions, the greater the surface tension. Surfactants are molecules, such as soaps and detergents, that reduce the surface tension of polar liquids like water. Capillary action is the phenomenon in which liquids rise up into a narrow tube called a capillary. It results when cohesive forces, ...
What forces bind a substance to a surface?
Adhesive forces bind a substance to a surface. Capillary action is the net result of two opposing sets of forces: cohesive forces, which are the intermolecular forces that hold a liquid together, and adhesive forces, which are the attractive forces between a liquid and the substance that composes the capillary.
What causes a liquid to rise against gravity?
Intermolecular forces also cause a phenomenon called capillary action, which is the tendency of a polar liquid to rise against gravity into a small-diameter tube (a capillary ), as shown in Figure 11.4. 3. When a glass capillary is is placed in liquid water, water rises up into the capillary. The height to which the water rises depends on the diameter of the tube and the temperature of the water but not on the angle at which the tube enters the water. The smaller the diameter, the higher the liquid rises.
What are the properties of intermolecular interactions?
Although you have been introduced to some of the interactions that hold molecules together in a liquid, we have not yet discussed the consequences of those interactions for the bulk properties of liquids. We now turn our attention to three unique properties of liquids that intimately depend on the nature of intermolecular interactions: 1 surface tension, 2 capillary action, and 3 viscosity.
What action pulls ethylene glycol up into the capillary?
Capillary action will pull the ethylene glycol up into the capillary. The meniscus will be concave.
Why do water molecules have a spherical shape?
Because a sphere has the smallest possible surface area for a given volume, intermolecular attractive interactions between water molecules cause the droplet to adopt a spherical shape. This maximizes the number of attractive interactions and minimizes the number of water molecules at the surface.
How are nutrients transported to the trunk of a tree?
Fluids and nutrients are transported up the stems of plants or the trunks of trees by capillary action. Plants contain tiny rigid tubes composed of cellulose, to which water has strong adhesion. Because of the strong adhesive forces, nutrients can be transported from the roots to the tops of trees that are more than 50 m tall. Cotton towels are also made of cellulose; they absorb water because the tiny tubes act like capillaries and “wick” the water away from your skin. The moisture is absorbed by the entire fabric, not just the layer in contact with your body.
What is the difference between capillary action and surfactant action?
The stronger the intermolecular interactions, the greater the surface tension. Surfactants are molecules, such as soaps and detergents, that reduce the surface tension of polar liquids like water. Capillary action is the phenomenon in which liquids rise up into a narrow tube called a capillary. It results when cohesive forces, ...
What are the properties of liquids that depend on intermolecular interactions?
Surface tension, capillary action , and viscosity are unique properties of liquids that depend on the nature of intermolecular interactions. Surface tension is the energy required to increase the surface area of a liquid by a given amount. The stronger the intermolecular interactions, the greater the surface tension.
What forces bind a substance to a surface?
Adhesive forces bind a substance to a surface. Capillary action is the net result of two opposing sets of forces: cohesive forces, which are the intermolecular forces that hold a liquid together, and adhesive forces, which are the attractive forces between a liquid and the substance that composes the capillary.
What is the tendency of a polar liquid to rise against gravity into a small-diameter tube?
Intermolecular forces also cause a phenomenon called capillary action, which is the tendency of a polar liquid to rise against gravity into a small-diameter tube (a capillary ), as shown in Figure 11.4. 3. When a glass capillary is is placed in liquid water, water rises up into the capillary.
What action pulls ethylene glycol up into the capillary?
Capillary action will pull the ethylene glycol up into the capillary. The meniscus will be concave.
Why do water molecules have a spherical shape?
Because a sphere has the smallest possible surface area for a given volume, intermolecular attractive interactions between water molecules cause the droplet to adopt a spherical shape. This maximizes the number of attractive interactions and minimizes the number of water molecules at the surface.
How are nutrients transported to the trunk of a tree?
Fluids and nutrients are transported up the stems of plants or the trunks of trees by capillary action. Plants contain tiny rigid tubes composed of cellulose, to which water has strong adhesion. Because of the strong adhesive forces, nutrients can be transported from the roots to the tops of trees that are more than 50 m tall. Cotton towels are also made of cellulose; they absorb water because the tiny tubes act like capillaries and “wick” the water away from your skin. The moisture is absorbed by the entire fabric, not just the layer in contact with your body.
What are the intermolecular forces present in water?
The intermolecular forces present in a sample of water are hydrogen bonds . The high surface tension of water allows a paper clip to "float" on the surface of the water. It's not actually floating, it's resting on top of the hydrogen bonds that exist between the water molecules at the surface. See the video below which shows a paper clip resting on the surface of water in a beaker.
What happens to surface tension when hydrogen bonds are removed?
If the hydrogen bonds are removed or disrupted, the surface tension will decrease. Watch what happens to the paper clip in the video when detergent
How do molecules move?
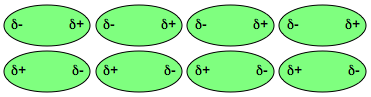
Molecules are free to move among other molecules unless there is a chemical bond that holds them together. But even in the absence of a chemical bond, molecules will exhibit a sort of friction force between them. This may be purely mechanical, such as a highly crosslinked polyment with a large physical size. But it is also very dependent of the surface properties of the molecules. Polar molecules have a lopsided charge distribution on the structure. This creates areas that may be either more positive or negative, despite the molecule having an overall neutral charge. As molecules are attraced by these forces, they will lose some of their freedom of movement. A classic example is water. Water’s unique structure leads to polarization of its bonds. One side will have a greater negative charge than the other and the watrer molecules will form a well-organized tertiary structure that obstructs their free movement. So thihgt, that one can place a metal papercilp on top with it sinking. The addition of modifiers, such as surfactnats, may disrupt that type of attraction.
What are intermolecular forces?
Intermolecular Forces are the forces which act at atomic level. These forces keep the molecules and atoms bound together. Without these forces no molecule would be possible. These Forces mediate interaction between molecules, including forces of attraction or repulsion which act between molecules and other types of neighboring particles, .
Why does methane only have London forces?
something like methane only has London forces because it’s nonpolar and has a symmetrical geometry
Which forces most definitely influence viscosity?
Intermolecular forces most definitely influence viscosity. Viscosity is more related to IM forces than collisions.
Do polar molecules have a lopsided charge distribution?
Molecules are free to move among other molecules unless there is a chemical bond that holds them together. But even in the absence of a chemical bond, molecules will exhibit a sort of friction force between them. This may be purely mechanical, such as a highly crosslinked polyment with a large physical size. But it is also very dependent of the surface properties of the molecules. Polar molecules have a lopsided charge distribution on the structure. This creates areas that may be either more positive or negative, despite the molecule having an overall neutral charge. As molecules are attraced