How does lime reduce the acidity of the soil?
Lime (calcium carbonate) and other liming sources such as dolomite (magnesium carbonate) reduces soil acidity by neutralizing acid reactions in the soil. The carbonate component reacts with hydrogen ions in the soil solution and in doing so raises the soil pH.
What is the purpose of liming acidic soils?
Liming improves soil pH, Ca, and Mg contents and reduces Al concentrations in the soil solution. In addition, liming improves beneficial microbe populations in the soil. Furthermore, liming improves P concentration in the soil solution by reducing P immobilization by Fe and Al in acid soils (Fageria and Baligar, 2008).
How do you reduce acidity in soil?
How is soil acidity corrected? Soil acidity can be corrected easily by liming the soil, or adding basic materials to neutralize the acid present. The most commonly used liming material is agricultural limestone, the most economical and relatively easy to manage source.
Is liming used to counteract soil acidity?
Soil acidity is ameliorated by applying lime or other acid‐neutralizing materials. 'Liming' also reduces N2O emissions, but this is more than offset by CO 2 emissions from the lime as it neutralizes acidity.
What is the main purpose of liming?
There are three main purposes for liming ponds: 1) to increase the availability of nutrients, 2) to increase pH and to buffer against daily pH fluctuations and 3) to sterilize ponds prior to stocking. While these practices use lime, they involve different chemical compounds.
What is liming and its importance?
Liming is a traditional procedure in preparing soil for planting. It is the application of calcium- and magnesium-rich materials to soil in various forms, including marl, chalk, limestone, or hydrated lime. Lime used on farm land is also called agricultural lime.
How can acidity be neutralized?
Adding a base decreases the concentration of H3O+ ions in the solution. An acid and a base are like chemical opposites. If a base is added to an acidic solution, the solution becomes less acidic and moves toward the middle of the pH scale. This is called neutralizing the acid.
Which chemical is used to reduce the acidity of soil?
Solution : Gypsum is used to reduce the acidity of the soil.
Which base is used to neutralize the acidity in soils?
Calcium hydroxide is a strong base and rapidly ionizes to Ca⁺⁺ and OH⁻ ions. The calcium ions replace absorbed H ions on the soil colloid and thereby neutralize soil acidity.
How do you apply lime to acidic soil?
Working lime into the soil in the fall gives it several months to dissolve before spring planting. To add lime to the soil, first prepare the bed by tilling or digging to a depth of 8 to 12 inches (20-30 cm.). Spread the lime evenly over the soil, and then rake it in to a depth of 2 inches (5 cm.).
How does the addition of lime reduce the acidification of water?
The lime reacts with CO2 dissolved in the water, converting it into bicarbonate ions, thereby decreasing the acidity of the water and enabling the oceans to absorb more CO2 from the air, so reducing global warming.
What is liming as applied to soil?
Definition. Liming is the application of mineral calcium and magnesium compounds, mainly carbonates, oxides, hydroxides, or a mixture of them and, more rarely, silicates into acidic soils to decrease the concentration of protons (McLean, 1971; Miller et al., 1995).
How does liming acid soils improve their productivity?
Soil pH is an excellent chemical indicator of soil quality. Farmers can improve the soil quality of acid soils by liming to adjust pH to the levels needed by the crop to be grown. Benefits of liming include increased nutrient availability, improved soil structure, and increased rates of infiltration.
What are the effects of soil acidity?
Acidity has the following effects on soil: It decreases the availability of plant nutrients, such as phosphorus and molybdenum, and increases the availability of some elements to toxic levels, particularly aluminium and manganese. Essential plant nutrients can also be leached below the rooting zone.
What is meant by liming the soil?
Definition. Liming is the application of mineral calcium and magnesium compounds, mainly carbonates, oxides, hydroxides, or a mixture of them and, more rarely, silicates into acidic soils to decrease the concentration of protons (McLean, 1971; Miller et al., 1995).
What is the process of liming?
Liming is a process used for parchment or leather processing, in which hides are soaked in an alkali solution. It is performed using a drum and paddle or a pit. Its objectives are: Removal of interfibrillary proteins.
How does lime neutralize acid?
Liming materials neutralize acidity by dissolving and releasing a base (HCO 3- , OH -) into the soil solution, which reacts with acid (H +, Al 3+ ). The chemical reaction of dolomitic lime with soil acidity is as follows:
How does lime affect crop yields?
Although response to lime is frequently subtle (in contrast to the quick greenup that a nitrogen application gives to corn), ignoring its regular use limits crop yields. Proper use of lime, in combination with other sound agronomic and pest control practices, should increase crop income in North Carolina. Using conservative estimates based on 2001 North Carolina Agricultural Statistics, a 5 percent yield increase from proper lime use on crops that are sensitive to low pH (cotton, soybeans, peanuts) would increase gross farm income by about $31 million. In addition, a 1 percent yield increase from proper lime use on crops less sensitive to low pH (tobacco, corn, commercial vegetables, wheat, fruits/nuts) would increase gross farm income by about $15 million.
What are some examples of liming materials?
If the neutralizing value is known and the material is ground finely enough to react in the soil, these can be economical substitutes. Wood ash, steel mill slag, lime- stabilized biosolids, and poultry litter are examples. Often such materials contain other plant nutrients; however, most wood ash products are known to contain little if any magnesium. Magnesium is an important consideration if used on coarse-textured, low CEC soils where leaching occurs. These products must meet the legal standards noted above to be sold as liming materials in North Carolina. Even if they do not meet all of the standards, they still may be useful as soil amendments capable of reducing soil acidity and supplying a variety of nutrients, including calcium, magnesium, potassium, phosphorus, and micronutrients. If a product does not meet all the specifications of the lime law, the supplier will not be able to make claims about liming effectiveness. Then it will be up to the purchaser to have the material tested. Each lot of such materials should be analyzed, as considerable variation in CCE and fineness may occur. As with conventional lime, the ENV needs to be known in order to determine the appropriate application rate. The NCDA&CS Agronomic Division waste laboratory can analyze these materials for CCE. From the CCE determination, an ag lime equivalent (ALE) is reported. The ALE does not take into account particle size or fineness. The ALE is a numerical value expressed as the amount of waste in tons per acre that equals one ton of standard agricultural lime. In addition to ALE, the waste analysis provides nutrient value of the waste.
What is the most common liming material in North Carolina?
The most commonly used liming material in North Carolina is finely ground dolomitic rock, but calcitic lime is also widely used. Additional liming materials include burnt lime or hydrated lime, pelleted lime, liquid lime, wood ash, and industrial slags. North Carolina has few good natural lime sources. Calcitic marl liming materials (soft marine shell deposits) are available in the coastal plain, but there are no dolomitic lime deposits in the east. Dolomitic lime is commonly obtained from the mountains of Virginia or Tennessee.
What is the pH of organic soil in North Carolina?
In North Carolina, very little aluminum is left in solution at pH 6 in mineral (MIN) soils, at pH 5.5 in mineral-organic (M-O) soils, and at pH 5 in organic (ORG) soils. Organic matter also has a relatively high CEC, meaning a greater quantity of lime is needed to raise pH than when dealing with mineral soils.
Why does soil clay have a negative charge?
This negative charge is due to the chemical makeup of the soil clay and organic matter and means that it can attract positively charged ions. The larger the percentage of exchange sites occupied by aluminum, the greater the amount of hydrogen formed, thus the lower the pH and the higher the acidity of the soil.
What is the pH range of North Carolina soil?
Nutrient solubility and availability are improved by higher soil pH. The optimal pH range for most nutrients in North Carolina mineral soils is between 5.8 and 6.2. Manganese is an example of a micronutrient required by plants that becomes less soluble as pH increases.
What is lime used for in soil testing?
Most soil-testing labs will analyze lime to determine its neutralizing value and particle size distribution.
How long does it take for lime to react with soil?
Lime will react completely with the soil in two to three years after it has been applied; although, benefits from lime may occur within the first few months after application. How long the effects of lime last will depend on the kind of lime used, total soil acidity, amount of organic matter, kind and amount of clay, and cropping and management systems used. A soil test three to four years after lime application will help provide the answer.
What is lime used for?
In agriculture, lime is usually defined as calcium or calcium-magnesium containing compounds capable of reducing harmful effects of an acid soil by neutralizing soil acidity and raising the soil pH.
How much calcium carbonate is in a yard of lime?
If a source of marl has a calcium carbonate equivalent of 1,200 pounds, this means one cubic yard is as effective as 1,200 pounds of pure calcium carbonate.
What is reserve acidity?
Reserve acidity is the acidity that is adsorbed on the surfaces of soil and organic matter particles. This portion of the soil acidity accounts for more than 99 percent of the total acidity. An accurate determination of lime need requires measuring this reserve acidity.
When to use dolomitic lime?
Use dolomitic lime when the soil test indicates the magnesium level is low to marginal. When the soil magnesium level is adequate, use either calcitic or dolomitic lime. There is no evidence that dolomitic lime has any harmful effects.
How to determine the amount of lime needed?
Use a soil test to determine the amount of lime needed. A soil pH measurement alone is not sufficient to determine lime requirement. Most soiltesting laboratories use a special buffer pH method to determine the amount of lime needed. Michigan State University uses the SMP buffer method.
How does acidification affect soil?
Research has shown the process of soil acidification within the soil profile results in a stratification of soil pH. This means that the topmost surface of the soil profile (0-5cm) will often have a higher pH than those layers below. But it is these deeper layers that are important for plants to achieve their productive potential, as it is where most plant roots grow. When acidification is not managed it becomes more and more difficult to remediate. The greater the depth of the acidic layer, the greater the effect on plant growth and the more difficult it is to correct. Untreated subsurface soil acidity results long term degradation of the soil.
Why is it important to manage acid soils?
Managing acid soils is most important for the long term sustainability of farming systems and the soil resource.
How does acidic soil affect crops?
Sometimes the effect of acidic soils on the growth and production of crops and pastures is not direct, but rather through the effect on soil micro-organisms, that in turn affect plant growth. Soil organisms are influenced by soil pH.
Why are acid tolerant plants important?
It is important to remember that acid-tolerant plants can also be responsive to increases in soil pH. In the case of legumes it is important to consider not only plant impacts but also the possible effects of soil pH on nitrogen fixation.
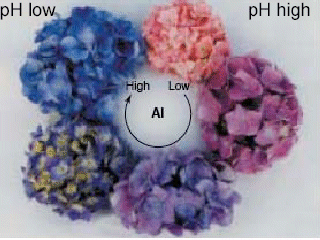
What does increased aluminium do to soil?
Increased aluminium (Al 3+) in the soil solution causing stunted root development in crops and pastures. Stunted roots result in reduced capability to access soil moisture and reduced nutrient uptake. In legumes resulting in reduced nodulation and nitrogen fixation, which may also reduce survival.
What is the pH of acidic soil?
Technically an acidic soil is one with a soil pH (CaCl2) below 4.8 in the root zone (0-20cm).
How long does it take for soil pH to change?
Changes in soil pH under agricultural use are measured in tens of years rather than thousands of years as in the natural environment.
What are the factors that affect soil pH?
Along with rainfall, there are other factors that will affect soil pH. Removal of grass clippings that contain alkaline elements, instead of allowing them to decompose into soil, will promote acidity. Leaves, pine needles, and other plant matter can create more acidic soil conditions as they decompose, and living plants will feed on alkaline elements (potassium, calcium, and magnesium). For these reasons, areas under dense tree cover or anywhere grass and tree roots compete for soil nutrients tend to have more acidic soil.
Why do trees have acidic soil?
For these reasons, areas under dense tree cover or anywhere grass and tree roots compete for soil nutrients tend to have more acidic soil.
Why does the soil pH matter?
Knowing the soil pH is crucial because it strongly effects grass growth. Soil pH dictates nutrient availability, elemental toxicity, and microbial activity.
What is pH?
Soil pH is the measure of its acidity or alkalinity and is rated on a simple logarithmic scale. The scale represents hydrogen ion concentration and ranges from 0.0-14.0, with 0 being the most acidic and 14 being the most alkaline. The halfway point on the scale, 7.0, is neutral. Soil acidity increases as values decrease from 7.0 to 0.0, and soil alkalinity increases as pH values increase from 7.0-14.
How can the pH be corrected?
Acidic soil pH can be corrected by applying lime. The most common liming materials are calcitic or dolomitic agricultural limestone. These are natural products made by finely grinding natural limestone. Since natural limestone is relatively water insoluble, agricultural limestone must be very finely ground so that it can mix with the soil particles and react with other nutrients to change soil acidity. The more finely ground the limestone is, the faster it will react in the soil. Both calcitic, and dolomitic lime contain calcium carbonate. Dolomitic lime however, also contains magnesium in the form of magnesium carbonate and should be used when soil tests indicate a magnesium deficiency.
What is the best pH level for lawns?
The chart clearly illustrates that between a pH of 6.0-7.0, availability is at its peak for most of the critical lawn nutrients. The other thing to observe is that at about 5.5, nutrient availability becomes problematic and only gets worse as the soil becomes more acidic. Likewise, as the soil becomes more alkaline than 7.0, nutrient availability will also begin to suffer. However, soils with a pH of 7.0 or more are very rare in New Jersey, so the concern is normally in keeping lawn soil as alkaline as possible. The chart is not specific to our grass types, for typical cool season grasses found in New Jersey, the recommend pH level for optimal nutrient availability is between 6.3 and 6.5.
Why use pelletized limestone?
Because high quality, finely ground limestone is very dusty and difficult to spread, some companies market a prilled or pelletized limestone for commercial and residential use. A small amount of clay or a polymer is added to the ground limestone so small prills are formed instead of dust. This makes it easier to apply out of a fertilizer spreader. Once applied, soil moisture will cause the granules to dissociate and disperse the limestone particles. Furthermore, newer pelletized lime products can be manufactured with reactants such as organic acids. These reactants speed up the chemical process by which lime changes soil pH, allowing for lawn applicators to produce quicker results, while using less product.
What Does Lime Do for Soil?
Both types of lime contain calcium, and dolomite lime also contains magnesium. Lime adds these two essential elements to the soil, but it is more commonly used to correct the soil pH.
Why does lime help plants?
They develop symptoms of nutrient deficiency, such as pale leaves and stunted growth. Using lime for acidic soil raises the pH so that plant roots can absorb the necessary nutrients from the soil.
How to know how much lime to use in soil?
The amount of lime your soil needs depends on the initial pH and the consistency of the soil. Without a good soil test, judging the amount of lime is a process of trial and error. A home pH test kit can tell you the acidity of the soil, but it doesn’t take the type of soil into consideration. The results of a soil analysis performed by a professional soil testing laboratory includes specific recommendations tailored to meet your soil’s needs.
How long does it take for lime to dissolve in soil?
You’ll begin to see a measurable difference in the soil pH about four weeks after adding lime, but it can take six to twelve months for the lime to dissolve completely. You won’t see the full effect of adding lime to the soil until it is completely dissolved and incorporated into the soil. For most gardeners, fall is a good time to add lime.
Why is liming important?
There are many benefits of proper liming. Nutrient availability is improved for plants when the correct pH is achieved. Phosphorus is tied up by low soil pH ; conversely, manganese is less available to plants if the soil pH is too high, and may be toxic if levels are too low.
What is the pH of soil?
Soil pH is a way to express soil acidity, which refers to the number of hydrogen and aluminum ions in a soil. On a scale of 1 to 14, pH below 7 is acidic and above 7 is basic or alkaline; 7 is neutral.
What is the best mesh size for liming?
Factors to consider when choosing a liming material include the fineness of particles, indicated by mesh size (smaller particles are better: 40-50 mesh works better than 8-20 mesh) and the purity of material, called Calcium Carbonate Equivalent (CCE).
What is the pH of soil in North Carolina?
Centipedegrass likes a lower pH, around 5.5, but other turfgrasses perform better around 6.5. Most other garden plants including fruits and vegetables prefer 6.0- 6.5 soil pH. With the exception of those plants adapted to low soil pH, such as blueberries, plants are unable to access nutrients in the soil if the pH is too low, and a plant’s failure to thrive is often related to low soil pH.
When is the best time to plant lime?
Fall is the best time of year to lime, but to paraphrase the old saying about the best time to plant a tree, if you didn’t lime in the fall the next best time is now. So, if icy winter weather has got you dreaming of your summer garden, plan to soil sample and lime according to recommendations to get the best start possible.
Is NC soil acidic?
Generally speaking, soil in NC is acid, due to the age of the soil (very old) and the natural weathering process (calcium, magnesium and other nutrients leach from the soil). In the Sandhills, our native soils pH can be quite low, in the 4s; blueberries like acidic soil, around this level, and plants like azaleas and rhodendrons also like ...
Is 5 pH more acidic than 6?
It is a logarithmic scale, meaning that soil with a pH of 5 is ten times more acidic than soil with a pH of 6, and 100 times more acidic than soil with a pH of 7. Aluminum and hydrogen are acidifying to the soil and by applying limestone (“liming”), aluminum ions are knocked off the soil and allowing basic ions such as calcium, potassium, ...
What are enzymes in soil called?
Enzymes, called phosphatases, are also known to influence the amount of phosphorus available to plants. Margenot's study looked at liming and soil management history to see if it influenced the activity of soil enzymes.
How long after liming did they measure phosphatase activity?
Twenty-seven days after liming, the researchers measured phosphatase activity. They also measured how much phosphorus was available to plants. They found no clear relationships between soil acidity levels changed by liming and phosphatase activity. This was unexpected.
How to make more phosphorus available to plants?
There are ways to make more phosphorus available to plants. For example, adding lime (calcium hydroxide) reduces soil acidity. That can unlock the phosphorus that was previously unavailable. This is a common practice. “Liming is a bread-and-butter tool for agriculture,” says Margenot.
Can plants take up phosphorus?
Plants can’t do without phosphorus. But there is often a ‘withdrawal limit’ on how much phosphorus they can get from the soil. That’s because phosphorus in soils is often in forms that plants can’t take up. That affects how healthy and productive the plants can be.
Do phosphatases react with soil acidity?
This was unexpected. “We know that phosphatases are sensitive to soil acidity levels,” says Margenot. “Our findings show that it is more complicated than just soil acidity when it comes to these enzymes.”
