How long does local anesthesia take to work?
You’ll be given local anesthesia shortly before your procedure to give it time to start working. This usually only takes a few minutes. While you shouldn’t feel any pain, you might still feel sensations of pressure. Tell your doctor right away if you start to feel any pain during the procedure. They may need to give you a higher dose.
What is the purpose of local anesthesia?
- Increase safety of the Local Anesthesia
- Prolong the duration of action of local anesthetic agents
- Helps in controlling bleeding
What are common side effects of local anaesthetic?
- history of adverse reactions to anesthesia
- sleep apnea
- seizures
- obesity
- high blood pressure
- diabetes
- heart disease
- lung disease
- kidney disease
- drug allergies
How long does local anesthetic take to wear off?
The effects of local anesthesia typically wear off within 30 to 60 minutes though they can last up to several hours. A few factors that contribute to the length of its active time are the dose, patient’s body, metabolism, and the presence of infection.
Are you awake under local anesthesia?
It is used for procedures such as performing a skin biopsy or breast biopsy, repairing a broken bone, or stitching a deep cut. You will be awake and alert, and you may feel some pressure, but you won't feel pain in the area being treated.
How quickly does local anaesthetic work?
Some local anaesthetic injections work after a few minutes. Others may take longer to work, up to around 30 minutes. An anaesthetic eye spray can take just a few seconds to work. A local anaesthetic cream can take up to 60 minutes to work.
How does local anesthetic work in the body?
Local anaesthetics stop the nerves in a part of your body sending signals to your brain. You won't be able to feel any pain after having a local anaesthetic, although you may still feel some pressure or movement. It normally only takes a few minutes to lose feeling in the area where a local anaesthetic is given.
How does local anesthesia work chemically?
Local anesthetics interrupt neural conduction by inhibiting the influx of sodium ions. In most cases, this follows their diffusion through the neural membrane into the axoplasm, where they enter sodium channels and prevent them from assuming an active or “open” state.
Does local anesthesia go into your bloodstream?
Local anesthetics are given for local numbing, but it's absorbed into your body and carried by blood all over the body. You may have both local and generalized side effects, including: Soreness at the injection site.
How do they wake you up from anesthesia?
Long recovery Currently, there are no drugs to bring people out of anesthesia. When surgeons finish an operation, the anesthesiologist turns off the drugs that put the patient under and waits for them to wake up and regain the ability to breathe on their own.
What should you not do before local anesthesia?
The doctor may instruct the person to refrain from eating during the few hours before surgery. It is also important not to drink any alcohol for 24 hours before receiving the anesthetic. An individual will often receive local anesthesia in the doctor's office.
What are the disadvantages of local anesthesia?
Cons of Local Anesthesia While local anesthesia will numb any sharp pain, some sensations of movement or pressure can remain. In addition, it is possible that you will see or hear parts of the procedure, which can make patients uncomfortable.
Can you sleep during local anesthesia?
In most cases, you'll be given a sedative through an intravenous (IV) line to relax you and make you a little sleepy, but you might still be aware and awake during the procedure. You can usually go home shortly after your procedure.
Is it normal to cry after local anesthesia?
He says for children, crying after anesthesia is very common – it happens in about 30 to 40 percent of the cases. For adults, the numbers are much lower – he estimates them to be around three percent – but crying is not even something that gets written down in the patient notes.
Why local anesthesia is given slowly?
Many studies compared slow and rapid injections and found that slow injections were associated with less discomfort than rapid injections. Slow injections are considered safer in cases of intravenous injections of anesthetic solutions, limiting cardiovascular alterations and anesthetic peak concentrations.
Can local anesthesia cause damage?
In clinical settings, most nerve damages induced by local anesthesia are transient sensory defects and permanent nerve damage rarely occurs. However, permanent nerve damage can be fatal in a minority of patients with local anesthetic-induced permanent nerve damage.
What is the fastest local anesthetic?
Benzocaine is the fastest (1 minute), followed by lidocaine = cocaine < pramoxine < tetracaine < dyclonine and < dibucaine. All of the topical products have a duration of action ranging from about 30 minutes to an hour.
How does anaesthetic work so quick?
General anesthesia works by interrupting nerve signals in your brain and body. It prevents your brain from processing pain and from remembering what happened during your surgery.
How do local anesthetics affect the duration of neural blockade?
This property is expressed as the percentage of circulating drug that is protein bound and has been found to correlate with an anesthetic's affinity for protein within sodium channels as well. The greater the tendency for protein binding, the longer the anesthetic will sustain neural blockade. For example, bupivacaine exhibits 95% protein binding compared to 55% for mepivacaine, and this is credited for the difference in their duration of neural blockade.
Why do local anesthetics cause seizures?
As local anesthetics are absorbed from the injection site, their concentration in the bloodstream rises and the peripheral nervous system and central nervous system (CNS) are depressed in a dose-dependent manner. (See Figure 3.) Low serum concentrations are used clinically for suppressing cardiac arrhythmias and status seizures, but ironically, higher concentrations induce seizure activity. Convulsive seizures are the initial life-threatening consequence of local anesthetic overdose. Presumably this is due to selective depression of central inhibitory tracts, which allow excitatory tracts to run amuck. As serum concentrations continue to rise further, all pathways are inhibited, resulting in coma, respiratory arrest, and eventually cardiovascular collapse. Evidence of lidocaine toxicity may commence at concentrations >5 µg/mL, but convulsive seizures generally require concentrations >10 µg/mL.
What is the intermediate chain of anesthetics?
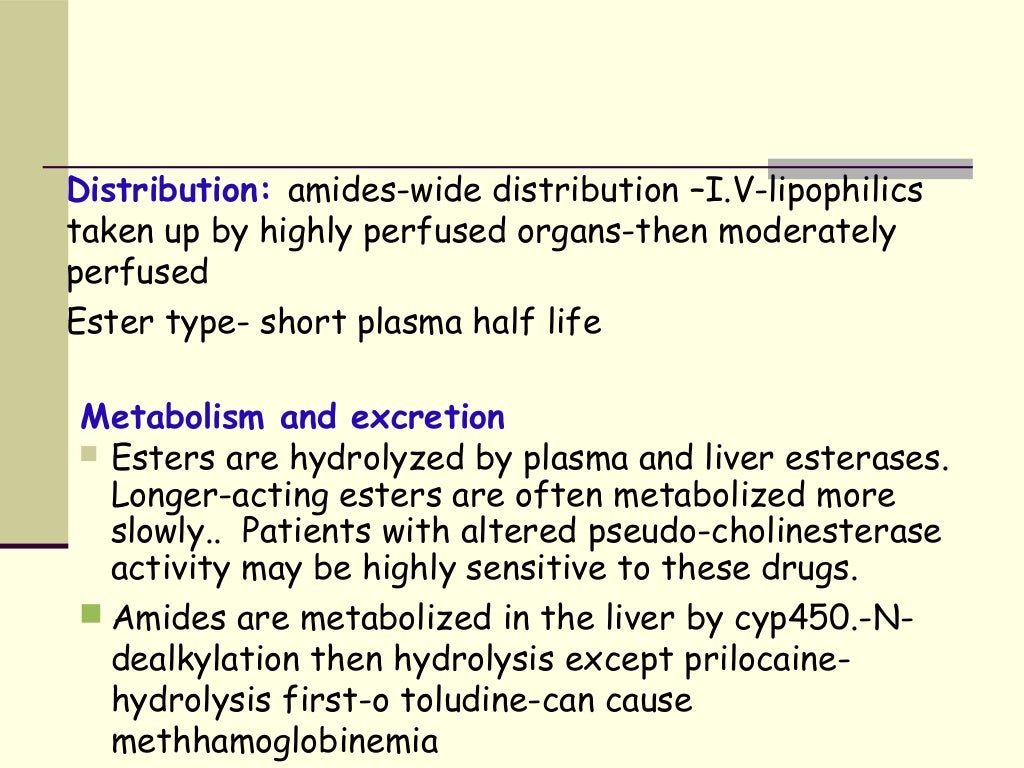
The intermediate chain or linkage provides a convenient basis for classification of local anesthetics, and also determines their pattern of elimination. Amides are biotransformed in the liver but esters are hydrolyzed in the bloodstream by plasma esterases. Ester local anesthetics are no longer packaged in dental cartridges and are used infrequently, with the exception of benzocaine, found in several topical anesthetic preparations. Articaine is unique in this regard. It is classified as an amide according to its intermediate linkage, but also contains an ester side chain on its aromatic ring. Hydrolysis of this side chain renders the molecule inactive, and it is therefore eliminated in a manner identical to ester anesthetics.
How does lipid solubility affect anesthesia?
Greater lipid solubility of a drug not only enhances potency but also enables more rapid diffusion through cell membranes. For local anesthetics, this hastens the onset for anesthesia in isolated fibers during in vitro studies, but it must be appreciated that other factors come into play clinically. For example, inherent vasodilating properties may promote systemic absorption before the anesthetic reaches the nerve membrane. High lipid solubility may impede dispersion throughout tissue fluids and also fosters sequestration in neighboring adipose tissues or myelin sheaths. In either case, fewer numbers of molecules reach the neuronal membrane and onset is delayed. Therefore, unlike in vitro studies of isolated fibers, greater lipid solubility generally slows the onset of anesthesia in the clinical setting. Injecting higher concentrations that allow a greater number of molecules to reach the membrane and hasten onset can offset this influence. Although bupivacaine and articaine are both highly lipid soluble, the 4% concentration of articaine provides for a much faster onset.
Why are neural fibers sensitive to local anesthesia?
Also, smaller fibers are generally more susceptible, because a given volume of local anesthetic solution can more readily block the requisite number of sodium channels for impulse transmission to be entirely interrupted. For these reasons the tiny, rapid-firing autonomic fibers are most sensitive, followed by sensory fibers and finally somatic motor fibers.1,2The anesthesiologist blocking mixed spinal nerves is acutely aware of these differential sensitivities. As patients recover from spinal anesthesia they first regain voluntary motor function, then sensation returns, and finally they can micturate (autonomic control). The dentist is generally spared this consideration because the trigeminal nerve branches anesthetized for dental procedures are comprised only of small, rapid-firing sensory fibers. However, the many classes of sensory fibers also vary in their diameters and firing rates. For example, pain fibers are more sensitive than those carrying pressure and proprioception. A patient may remain disturbed by a sense of pressure despite complete anesthesia of pain fibers.
How do local anesthetics interrupt neural conduction?
Local anesthetics interrupt neural conduction by inhibiting the influx of sodium ions through channels or ionophores within neuronal membranes. Normally these channels exist in a resting state, during which sodium ions are denied entry. When the neuron is stimulated, the channel assumes an activated or open state, in which sodium ions diffuse into the cell, initiating depolarization. Following this sudden change in membrane voltage, the sodium channel assumes an inactivated state, during which further influx is denied while active transport mechanisms return sodium ions to the exterior. Following this repolarization, the channel assumes its normal resting state. An appreciation of these sodium channel states helps to explain the preferential sensitivity of local anesthetics for various classes of neuronal fibers.
How are allergic reactions triggered?
Allergic reactions are triggered by immune mechanisms whereby lymphocytes are sensitized to antigen and, upon subsequent exposure, mediate a series of pathophysiologic changes. Gell and Coombs first categorized hypersensitivity (allergic) reactions as Type I through IV, based on distinct immunologic mechanisms.8Type I reactions occur within minutes of provocation and are mediated by antibodies or immunoglobulin E (IgE) produced by B lymphocytes. This is the type most commonly provoked by components of local anesthetic formulations. Type 4 reactions are delayed for several days following provocation and are mediated by sensitized T lymphocytes. This type of reaction to local anesthetics has been implicated only rarely.
What are the different types of local anaesthetic?
A local anaesthetic is usually the choice for surgery on small areas of your body, such as minor skin surgery or the extraction of a wisdom tooth. It may also be used with a general anaesthetic to improve pain relief after surgery.
How do I prepare for a local anaesthetic?
All anaesthetics have risks so talk to your doctor beforehand about your options. Discuss any medical conditions or allergies you have. You can also ask about how to manage the pain after the local anaesthetic has worn off.
How does an epidural work?
How does an epidural work?With an epidural, a small plastic tube is inserted between the bones of your spine, into the space around your spinal cord. A combination of drugs is given through the tube. A local anaesthetic blocks nerves in the spinal cord that transmit pain signals and an opiate provides further pain relief.
What is the purpose of spinal anaesthetic?
Epidural and spinal anaesthetics are often used to stop pain during labour or caesarean sections. An epidural block and a spinal block both involve the injection of local anaesthetic into the spine.
What is the best local anaesthetic for lower back pain?
Epidural is highly effective local anaesthetic procedure includes injectind anaesthetic around the spinal nerves in your lower back.
What is nerve block?
A nerve block involves injecting local anaesthetic around a cluster of nerves that supply a particular part of the body, such as the arm or the leg. These numb a large area. Nerve blocks may be used during and after surgery, for example on the hip or knee.
What is local anaesthesia?
Listen. A local anaesthetic is a type of medicine used to temporarily numb a part of your body. Unlike a general anaesthetic, local anaesthetics do not cause the loss of consciousness. When a local anaesthetic takes effect, you will feel no pain, but may still sense pressure or movement.
What is the name of the drug that was first used in dentistry?
One of the original synthetic compounds was called Novocaine, short for “the new cocaine” and many patients believe they’re being given Novocaine in the dentist’s chair. However, the most commonly used local anesthetic today is Lidocaine, which was discovered in the late 1940s.
How does anesthetic affect the brain?
When a nerve senses a painful stimulus to the body it sends a signal to the brain to register the sensation. As your brain processes the pain, it alerts you to stop the action or avoid similar situations in the future. Local anesthetic prevents nerves from sending this message. Anesthetic is applied as close to the treatment area as possible, to ensure that the right signal channels are blocked.
Why is local anesthesia used in dentistry?
One of the greatest advancements in modern dentistry is the use of local anesthetic to keep patients comfortable and treatment painless. If you’re curious about how it works, here’s a short explanation of the science behind local anesthetic and how it keeps dental procedures and oral surgery safe and pain-free.
What is the benefit of local anesthetic?
A benefit of local anesthetic is that your body can process the medication naturally and gradually return to its normal state without any intervention. As the anesthetic is broken down, you will slowly regain feeling in the affected area.
Where did local anesthetics originate?
The earliest form of local anesthetic was derived from the coca plant. Known as cocaine, this is the only natural-based anesthetic discovered to date and all future synthetic versions of the compound are based on the original formula.
Is local anesthesia better than general anesthesia?
Using local anesthesia over general anesthesia comes with several benefits: Faster recovery time. Less postoperative discom fort. Easier to monitor the patient during the procedure. If you have any questions or concerns related to local anesthetic, be sure to ask your oral surgeon during your initial consultation.
How Does It Work?
Medication used as a local anesthetic numbs the nerves in the area that will be subjected to treatment. It blocks the signals the nerve would normally send to the brain so that you don’t feel any pain. Local anesthetic can be administered topically in the form of a gel or injected directly into the treatment area.
What to Expect During the Procedure
Before you undergo certain dental treatments, like a tooth extraction or a root canal, the dentist will numb the area. Before proceeding, they will make sure the site is completely numb before starting.
After Getting Local Anesthetic
After a procedure needing local anesthesia, it’s recommended to take a rest and not do any strenuous activities. This helps you metabolize the anesthetic more slowly and not have it fade away too soon after the treatment. You will get a prescription for painkillers for the period following the anesthetic’s effect when the pain comes back.
Side Effects of Local Anesthesia
One of the side effects of local anesthetics is accidental injuries caused by the numbness. In other words, you could potentially bite your tongue, lips, or the inside of your cheeks without realizing it, causing potentially serious injuries.
Get a Beautiful Smile with Smillie Dental
If you have any questions about local anesthetics used in dentistry, or the procedures where they might be needed, don’t hesitate to contact Dr. Joseph Smillie or Dr. Helen Smillie at Smillie Dental.
What is the best way to administer local anesthesia?
Local anesthetics can be applied topically and subcutaneously to anesthetize local tissues. Topical use for some agents (e.g., viscous lidocaine) can include oral ingestion with swish and spit, as well as gargling and swallowing for pharyngeal anesthesia effects. Oral applications can also include agents such as benzocaine applied to the gums or aphthous stomatitis. These local anesthetic agents can also be administered around peripheral nerves and in the neuraxial space to anesthetize larger nerves or dermatomal distributions. Lidocaine is also administered intravenously to provide surgical anesthesia for an extremity, such as Bier block, or as a cardiac antiarrhythmic. [7][8]
How does local anesthesia work?
This causes membrane depolarization and propagation of the impulse. Local anesthetics block nerve impulse transmission in the peripheral and central nervous system without causing central nervous system depression or altered mental status. The block generally occurs in a stepwise sequence depending on the concentration and volume of the local anesthetic, with autonomic impulses blocked first, then sensory impulses, and finally, motor impulses. Local anesthetics are used to anesthetize skin, subcutaneous tissue, and peripheral nerves for invasive or surgical procedures. This activity outlines the indications, mechanism of action, administration methods, significant adverse effects, contraindications, toxicity, and monitoring, of topical, local, and regional anesthetic agents so providers can direct patient therapy when indicated as part of the interprofessional team.
How long does it take for a local anesthetic to work?
The duration of action of local anesthetics can range from 30 minutes to 12 hours or more. The range depends on the location of the block (high blood supply equals shorter duration), the local anesthetic used, and its preparation (liposomal preparations create extended-release drugs).
What is the sequence of anesthesia block?
The block generally occurs in a stepwise sequence depending on the concentration and volume of the local anesthetic, with autonomic impulses blocked first, then sensory impulses, and finally , motor impulses. Local anesthetics are used to anesthetize skin, subcutaneous tissue, and peripheral nerves for invasive or surgical procedures.
Why do you dictate the anesthesia agent used?
Because of the variable pharmacodynamics, pharmacokinetics, and toxicity profile of the various local anesthesia agents, the intended procedure will dictate the agent used.
How does anesthetic block nerve impulses?
Local anesthetics block nerve impulse transmission in the peripheral and central nervous systems without causing central nervous system depression or altered mental status. The block generally occurs in a stepwise sequence depending on the concentration and volume of the local anesthetic, with autonomic impulses blocked first, then sensory impulses, and finally, motor impulses.
Why do you add sodium bicarbonate to local anesthetic?
Thus, many clinicians add sodium bicarbonate to overcome the acidity and increase the efficacy of the local anesthetic. Epinephrine is often added to a local anesthetic solution, which allows the clinician to use a lower dose of the anesthetic and improve safety.
What is the best treatment for sore throat?
Slightly painful conditions, such as mouth ulcers and sore throats, can sometimes be treated with over-the-counter gels and sprays that contain a local anaesthetic. Injections of a local anaesthetic and steroid medication may be used to treat more severe conditions, such as long-term joint pain .
How long does it take to lose feeling after a local anaesthetic?
You won't be able to feel any pain after having a local anaesthetic, although you may still feel some pressure or movement. It normally only takes a few minutes to lose feeling in the area where a local anaesthetic is given.
What is local anaesthesia?
Local anaesthesia involves numbing an area of the body using a type of medication called a local anaesthetic.
What is the best way to prevent pain after wisdom tooth removal?
Preventing pain during and after surgery. A local anaesthetic, usually given by injection, may be used along with a sedative medication to keep you relaxed while an operation or procedure is carried out. Local anaesthetics are mainly used for relatively minor procedures, such as: a filling or wisdom tooth removal.
How long should you wait to move after anaesthesia?
You should move carefully until the anaesthetic has worn off as you may not notice if you injure yourself.
Why do you use a syringe during childbirth?
They're often used during childbirth to ease the pain of labour or if a caesarean section is needed. They can also be used to reduce the amount of general anaesthesia needed during some operations and can provide pain relief afterwards.
Why is a syringe used for surgery?
It may be used so an operation can be carried out without needing a general anaesthetic, or to prevent pain afterwards.
What is general anesthesia?
1. General anesthesia is used to render a patient unconscious and is administered for invasive operations like a laparoscopic hernia repair. Dr. Ma further adds that the anesthesiologist controls the patient’s breathing. 2. Sedation anesthesia is used for minimally invasive procedures like colonoscopies.
Why do you use an epidural before stitches?
4. Regional anesthesia numbs a large area of the body while the patient remains awake. Perhaps the most widely recognized use is an epidural to make childbirth more comfortable for women.
What is anesthesia in medical terms?
In the simplest sense, anesthesia is medication that helps alleviate pain or discomfort during a procedure. There are numerous types and delivery methods. Additionally, different drugs can be used in combinations as appropriate for the patient and the procedure.
Why do you need a nerve block before surgery?
It would require general anesthesia and a nerve block (regional anesthesia) may also be placed prior to surgery to help minimize pain and aid in the recovery process . If it all sounds like a careful balancing act, that’s because it is. This is why any provider who administers anesthesia must be highly trained.
Does propofol cause unconsciousness?
“A drug such as propofol can induce unconsciousness, but has no analgesic effects,” Dr. Ma points out.#N#It’s essential that she knows what each medication does as well as the appropriate combination at each stage of a procedure. Anesthesia is not a matter of flipping a switch and walking away. It requires constant monitoring and adjustment, particularly for complex surgeries.#N#“When administering anesthesia for an ‘awake craniotomy,’ the patient will need to be completely motionless,” Dr. Ma says. “However, during part of the surgery, the patient will need to be awake and talking.”#N#Another example Dr. Ma offers is for a shoulder surgery where the patient would be sitting. It would require general anesthesia and a nerve block (regional anesthesia) may also be placed prior to surgery to help minimize pain and aid in the recovery process.#N#If it all sounds like a careful balancing act, that’s because it is. This is why any provider who administers anesthesia must be highly trained. These medical professionals include anesthesiologists, nurse anesthetists, oral surgeons, dentists, and anesthesiologist assistants.
Does propofol inhibit communication?
A 2018 study focused specifically on propofol to dig into what mechanisms are at play. The research found this type of anesthesia restricts movement of a type of protein in a way that inhibits communication between neurons. But the study’s authors also note there’s still a lot yet to learn.
Is anesthesia a matter of flipping a switch?
Anesthesia is not a matter of flipping a switch and walking away. It requires constant monitoring and adjustment, particularly for complex surgeries. “When administering anesthesia for an ‘awake craniotomy,’ the patient will need to be completely motionless,” Dr. Ma says.
What is local anesthesia?
Local anesthesia prevents pain during medical procedures by numbing a specific part of the body. Its effects are short-lived, so healthcare teams primarily use it for minor outpatient procedures. Anesthetists or doctors only apply local anesthetic to the part of the body that the medical procedure involves.
What is the purpose of sedation and anesthesia?
Together, anesthesia and sedation enable the doctor or surgeon to carry out the procedure without causing pain or distress.
How long before surgery can you drink alcohol?
The doctor may instruct the person to refrain from eating during the few hours before surgery. It is also important not to drink any alcohol for 24 hours before receiving the anesthetic. A person will often receive local anesthesia in the doctor’s office.
Which is better for anesthesia: Lidocaine or Bupivacaine?
Lidocaine is the most widely used local anesthetic, but doctors and anesthetists use different drugs for different purposes. For longer procedures, bupivacaine is more suitable. Trusted Source. , but it can be more painful than other drugs during administration.
How does a drug block pain?
Healthcare professionals use various drugs to block the pain, which they can deliver in the form of an injection or a spray or ointment. The drug works by acting on certain nerve pathways to prevent the nerves in the area of application from sending signals to the brain.
Can a doctor do a numbing procedure?
The doctor will not proceed with the procedure if the person does not feel the numbing effect. The anesthetic will prevent the person from experiencing pain during the procedure, but they may still feel pressure.
What happens if you have a CNS depression?
In very care cases, the person may experience central nervous system (CNS) depression, in which the body’s neurological functions slow down too much, leading to a decreased heart rate and breathing rate. This state can lead to cardiac arrest if the blood stops pumping to the heart.

Blocking The Signal from Nerve to Brain
A Short History of Local Anesthetic
- The earliest form of local anesthetic was derived from the coca plant. Known as cocaine, this is the only natural-based anesthetic discovered to date and all future synthetic versions of the compound are based on the original formula. One of the original synthetic compounds was called Novocaine, short for “the new cocaine” and many patients believe they’re being given Novocaine …
A Temporary Solution
- A benefit of local anesthetic is that your body can process the medication naturally and gradually return to its normal state without any intervention. As the anesthetic is broken down, you will slowly regain feeling in the affected area. Duration of effect is determined by the amount and type of anesthetic administered. There are different compounds for short, intermediate and long-acti…
Added Benefits of Local Anesthesia
- Using local anesthesia over general anesthesia comes with several benefits: 1. Faster recovery time 2. Less postoperative discomfort 3. Easier to monitor the patient during the procedure If you have any questions or concerns related to local anesthetic, be sure to ask your oral surgeon during your initial consultation.