What does the movement of the mantle affect?
The movement of materials within the Earth’s mantle is thought to drive plate tectonic movements on the surface, ultimately leading to earthquakes and volcanoes. The mantle is also the Earth’s ...
What are the two main factors in the mantle that?
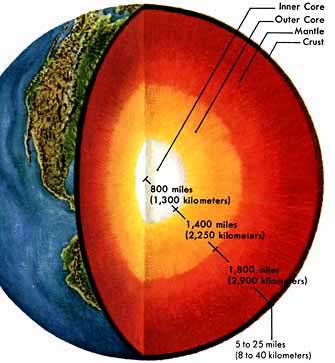
The two most important things about the mantle are as follows: It is made of semi-solid rock. It is hot. Figure 1. Peridotite is formed of crystals of olivine (green) and pyroxene (black). Scientists know that the mantle is made of rock based on evidence from seismic waves, heat flow, and meteorites.
What causes the mantle to heat up?
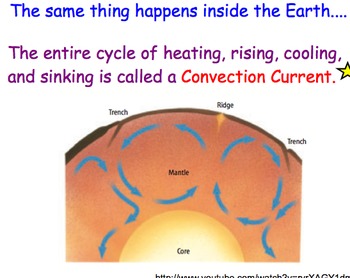
convection currents are a process in which the materials inside the mantle heat up and rise to the surface whilst the cooler liquid sinks; as it sinks it then heats up and rises again. This continuous cycle is established: hot liquid rising, cold liquid descending. These currents cause the tectonic plates to move.
What are some interesting facts about the Earth's mantle?
What are 4 facts about the Earth's mantle?
- The mantle makes up 84% of Earth's volume.
- The mantle extends from 35-2980 kilometers below Earth's surface.
- The mantle is mostly solid rock. ...
- The mantle ranges in temperatures from 200 to 4000 degrees Celsius.
- Convection currents in the mantle drive plate tectonics.
Is the mantle able to flow?
Although solid, the mantle can flow under enormous pressure and temperature as individual grains are stretched. Where the surface plates meet, they may rub alongside each other or one may dive under the other and sink into the mantle, creating a subduction zone.
How does heat flow through the mantle?
When the mantle convects, heat is transferred through the mantle by physically moving hot rocks. Mantle convection is the result of heat transfer from the core to the base of the lower mantle.
What is the part of the mantle that flows?
The Asthenosphere (weak sphere) is part of the Mantle that flows, a characteristic called plastic behavior. It might seem strange that a solid material can flow. A good example of a solid that flows is the movement of toothpaste in a tube.
What makes the mantle hot?
There are three main sources of heat in the deep earth: (1) heat from when the planet formed and accreted, which has not yet been lost; (2) frictional heating, caused by denser core material sinking to the center of the planet; and (3) heat from the decay of radioactive elements.
Is the mantle solid or liquid?
The Earth's mantle is mostly solid from the liquid outer core to the crust, but it can creep on the long-term, which surely strengthens the misconception of a liquid mantle. Courtesy of the U.S. Geological Society.
How fast does the mantle flow?
Estimates of the speed with which Earth's mantle moves range from 1 to 20 cm/year with an average of about 5 cm/year in the case of plate motions to as much as 50 cm/year in hotspots such as the Hawaiian Islands (see Plates, Plumes, And Paradigms (2005) edited by Gillian R.
How does the mantle behave as a viscous fluid?
The mantle is composed of denser rocks, on which the rocks of the crust float. On geologic timescales, the mantle behaves as a very viscous fluid and responds to stress by flowing. Together the uppermost mantle and the crust act mechanically as a single…
How does water get from the surface to the middle of the mantle?
In the modern deep water cycle, partial melting of the mantle extracts water from it. As buoyant magma rises, the water outgasses into oceans and other surface reservoirs through volcanoes. The water is returned to the mantle by subduction, as pictured in figure 1.
How does heat travel through Earth's layers?
Energy is transferred between the Earth's surface and the atmosphere in a variety of ways, including radiation, conduction, and convection. Conduction is one of the three main ways that heat energy moves from place to place. The other two ways heat moves around are radiation and convection.
How does convection work in the mantle?
The mantle is heated from below (the core), and in areas that are hotter it rises upwards (it is buoyant), whereas in areas that are cooler it sink down. This results in convection cells in the mantle, and produces horizontal motion of mantle material close to the Earth surface.
How convection currents occur in the mantle?
Convection currents are the result of differential heating. Lighter (less dense), warm material rises while heavier (more dense) cool material sinks. It is this movement that creates circulation patterns known as convection currents in the atmosphere, in water, and in the mantle of Earth.
How does heat from the lower mantle which the upper mantle?
The mantle is heated from below, cooled from above, and its overall temperature decreases over long periods of time. All these elements contribute to mantle convection. Convection currents transfer hot, buoyant magma to the lithosphere at plate boundaries and hot spots.
What is the mantle responsible for?
Artist’s view of the Earth’s interior showing, under the crust, the mantle’s movements responsible for plate tectonics. By analyzing microscopic defects in the mineral that makes up 60% of the Earth’s mantle, researchers have uncovered what makes this solid rock flow. “Humans have walked on the Moon.
How fast does the mantle move?
This level of viscosity means that the mantle moves at a speed of several centimeters per year. It is on a microscopic scale inside mantle material that the Earth’s major deformations are played out.
How deep is the mantle?
Geological activity on the Earth’s surface is a result of deep convection movements, which stir the mantle as far as 3000 kilometers below our feet. At such depths and in such extreme conditions, studying and understanding the continual flow of solid mantle rocks is a real scientific challenge. But even if the mantle remains largely inaccessible, its dynamics are slowly being unearthed.
What mineral makes up 60% of the upper mantle?
Using this approach, the team was able to tackle a longstanding mystery surrounding the deformation of olivine, a mineral that makes up to 60% of the upper mantle.
How do we see rock deformation?
To put things simply, we can see rock as a cluster of mineral grains. Any rock deformation results from a modification, either in the atomic structure of the grains making up the rock, or in the boundary between these grains. The geologists started off by identifying the crystal defects in olivine. “Without crystal defects, we would live in an incredibly hard world where metallurgy would be impossible, where the only metals would be brittle ones. Crystal defects endow materials with a capacity to be shaped, deformed or forged,” explains Cordier. “What we had to find out, regarding olivine in a 3D space, was how it was able to make shear movements in all directions.”
Why does the mantle get less viscous?
As stress increases, the mantle gets much less viscous and flows more easily. The model raises questions about how movements in the mantle are connected to the movements of plates at the surface. One prediction is that there is more energy available in subduction zones to cause earthquakes than previously thought.
What is the Earth's surface made of?
The Earth's surface is made of rocky plates floating on the mantle. Although solid, the mantle can flow under enormous pressure and temperature as individual grains are stretched. Where the surface plates meet, they may rub alongside each other or one may dive under the other and sink into the mantle, creating a subduction zone.
Where is the Pacific plate subduction zone?
Billen and graduate student Margarete Jadamec, now a postdoctoral researcher at Monash University in Australia, studied the Alaskan subduction zone, where the Pacific plate is diving beneath Alaska and pushing up Mt. McKinley.
Does the mantle flow faster?
Earth's mantle flows fast. by UC Davis. (PhysOrg.com) -- The Earth's mantle flows far more rapidly around a sinking tectonic plate than previously thought, according to new computer modeling by UC Davis geologists. The findings could change the way that we think about plate tectonics and the amount of energy available for earthquakes.
What is the process of convection of the mantle?
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface. The Earth's surface lithosphere rides atop the asthenosphere and the two form the components of the upper mantle. The lithosphere is divided into a number ...
Where is whole mantle convection?
Currently, whole mantle convection is thought to include broad-scale downwelling beneath the Americas and the Western Pacific, both regions with a long history of subduction, and upwelling flow beneath the central Pacific and Africa, both of which exhibit dynamic topography consistent with upwelling.
How long does it take for a convection cycle to occur?
A single shallow convection cycle takes on the order of 50 million years, though deeper convection can be closer to 200 million years. Currently, whole mantle convection is ...
What causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface?
Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface. It seems to have been much more active during the Hadean period, resulting in gravitational sorting of heavier molten iron, nickel, and sulphides to the core and lighter silicate minerals to the mantle.
What is the slow moving motion of Earth's solid mantle caused by?
Jump to navigation Jump to search. The slow moving motion of Earth's solid mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the planet's interior to its surface. Whole-mantle convection. Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by ...
How does accretion occur in the lithosphere?
Accretion occurs as mantle is added to the growing edges of a plate, associated with seafloor spreading. This hot added material cools down by conduction and convection of heat. At the consumption edges of the plate, the ...
What causes surface volcanism?
Secondary convection may cause surface volcanism as a consequence of intraplate extension and mantle plumes. In 1993 it was suggested that inhomogeneities in D" layer have some impact on mantle convection. Mantle convection causes tectonic plates to move around the Earth's surface.
How does the mantle flow?
Mantle convection is the very slow creeping motion of Earth's solid silicate mantle caused by convection currents carrying heat from the interior to the planet's surface. ... This hot added material cools down by conduction and convection of heat.
How can the mantle flow by convection if it is a solid?
The mantle is heated from below (the core), and in areas that are hotter it rises upwards (it is buoyant), whereas in areas that are cooler it sink down. ... This convection takes place in mantle rock (a mixture of silicate minerals) that at any given time would appear solid to us.
What is the process of convection currents in the mantle?
Convection currents are identified in Earth's mantle. Heated mantle material is shown rising from deep inside the mantle, while cooler mantle material sinks, creating a convection current. It is thought that this type of current is responsible for the movements of the plates of Earth's crust.
What causes convection currents in Earth mantle?
It has long been known that throughout the mantle there are convection currents circulating, caused by the difference in temperature at the earth's interior and surface. Hot material from the earth's outer core rises very slowly (over millions of years) throughout the mantle.
