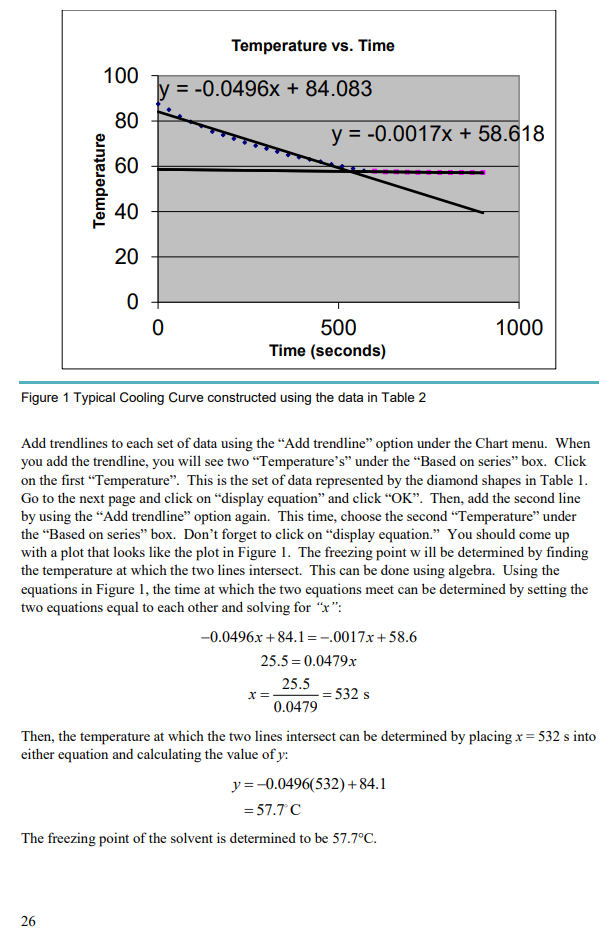
How does molar mass affect osmotic pressure? The osmotic pressure of a solution is the pressure difference needed to stop the flow of solvent across a semipermeable membrane. The osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the molar concentration of the solute particles in solution.
Full Answer
How to calculate osmotic pressure?
Osmotic Pressure given density of solution Solution
- Convert Input (s) to Base Unit
- Evaluate Formula
- Convert Result to Output's Unit
What is the formula for osmotic pressure?
Osmotic Pressure
- M = 7.65 atm / (1) (0.0820 L.atm/mol.K) (310)
- M = 0.301 mol / L. Step 4: Finding the amount of sucrose per liter.
- Mol = 0.301 mol/L x 1 L
- Mol = 0.301 mol. Finally, we should use 54.1 grams per liter of glucose for an intravenous solution to match the 7.65 atm at 37 degrees Celsius osmotic pressure of ...
What is the unit of osmotic pressure?
π = iMRT π is not equal to 3.14159 in this situation. π stands for the osmotic pressure and is usually expressed in the pressure unit of atmospheres. The definition of osmotic pressure: the amount of pressure required to stop the process of osmosis in your experimental set-up.
How does concentration affect osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is determined by solute concentration – water will “try harder” to diffuse into an area with a high concentration of a solute, such as a salt, than into an area with a low concentration. So in the case of osmosis, the solutes cannot move because they cannot pass through the membrane.
Does molar mass affect osmotic pressure?
The osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the molar concentration of the solute particles in solution.
What is the relation between osmotic pressure and molecular weight?
The flow of solvent that occurs due to a concentration gradient across the membrane is called osmosis. According to Equation 5, the molecular weight of a solute can be obtained by plotting osmotic pressure divided by c versus concentration and extrapolating the data back to c=0.
How is osmotic pressure related to mass?
Osmotic pressure is inversely proportional to gram molecular weight.
What factors affect osmotic pressure?
The factors affecting the rate of osmosis include:Pressure.Temperature.Surface Area.Water Potential.Concentration gradient.
How can molar mass of a substance be determined from the measurement of osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is directly proportional to the molarity of the substance at a given temperature. Different methods are used like Barkley and Hartley's method in order to determine the molecular mass using osmotic pressure. ∴π= W /m× 1/V ×S.T⟶ From this equation molar mass can be determined.
How do you find molar mass from osmotic pressure?
0:4210:58Now what we need to do is plug in everything that we have into this equation. And our goal is toMoreNow what we need to do is plug in everything that we have into this equation. And our goal is to solve for the molarity of the solution molarity is defined as moles of solute per liters of solution.
What has higher osmotic pressure?
The solution which has higher osmotic pressure than some other solution is known as Hypertonic solution.
What causes osmotic pressure to increase or decrease?
Increasing the osmotic pressure of a food through drying or by the addition of sugars or salts leads to the reduction of water available to the bacterial cell. The major reaction toward an osmotic upshift is the efflux of water from the microorganisms into the external environment.
How is osmotic pressure dependent on the number of moles of a solute?
If w2 grams of solute, of molar mass, M2 is present in the solution, then n2 = w2 / M2 and we can write, in a dilute aqueous solution molarity is equal to molality. c = m when p = 1 and solution is dilute. The osmotic pressure will increase with an increase in molality of the solution at a given temperature.
How do you increase the osmotic pressure of a solution?
What is osmotic pressure? Medium. ... The osmotic pressure of a solution is directly proportional to. Hard. ... The osmotic pressure of a solution may be increased by. Hard. ... A millimolar solution of potassium ferricyanide is 70% dissociated at 27∘C. ... Osmotic pressure of a solution is 0.0821 atm at temperature of 300 K .
How is osmotic pressure determined?
Osmotic pressure is determined by solute concentration – water will “try harder” to diffuse into an area with a high concentration of a solute, such as a salt, than into an area with a low concentration. In reality of course, osmotic pressure is not a “desire” of water to move, but rather an extension of the natural law ...
Why do organisms use osmotic pressure?
Some organisms, such as plants that use osmotic pressure to move water, have taken advantage of this principle. But it can also threaten the health of cells and organisms when there is too much or too little water in the extracellular environment compared to the inside of the cell.
What is the meaning of osmosis pressure?
Osmotic Pressure Definition. Osmotic pressure can be thought of as the pressure that would be required to stop water from diffusing through a barrier by osmosis. In other words, it refers to how hard the water would “push” to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side. Osmotic pressure is determined by solute concentration – ...
Why can't solutes move in osmosis?
So in the case of osmosis, the solutes cannot move because they cannot pass through the membrane. However, the water can move, and it does – passing through the membrane to an area with higher solute concentration. This can cause the total volume of water on each side of the membrane to change: the side of the membrane with more solutes may end up ...
What happens if you have too much water in your cell?
This can cause the total volume of water on each side of the membrane to change: the side of the membrane with more solutes may end up with much more water. This can lead to problems for cells, such as bursting (if too much water moves into the cell ), or becoming dehydrate (if too much water moves out).
What is the molar concentration of a solute?
M is the molar concentration of the solute. Molar concentration refers to the actual number of atoms, ions, or molecules of the solute. This is important because it is the number of particles that determine how the particles interact in osmosis – not the volume or weight.
When the concentrations of substances are different in two areas and the areas have contact with each other, what causes the substances
When the concentrations of substances are different in two areas and the areas have contact with each other, the random motion of particles will cause the substances to diffuse until the solution is uniform throughout the whole area. Osmosis is the particular diffusion of water through a semi-permeable membrane.
What is osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the basis of filtering (" reverse osmosis "), a process commonly used in water purification. The water to be purified is placed in a chamber and put under an amount of pressure greater than the osmotic pressure exerted by the water and the solutes dissolved in it.
What is potential osmotic pressure?
Potential osmotic pressure is the maximum osmotic pressure that could develop in a solution if it were separated from its pure solvent by a semipermeable membrane. Osmosis occurs when two solutions containing different concentrations of solute are separated by a selectively permeable membrane.
What is the minimum pressure needed to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis.
What is the role of osmotic pressure in the homeostasis of an organism?
Osmotic pressure is an important factor affecting cells. Osmoregulation is the homeostasis mechanism of an organism to reach balance in osmotic pressure . Hypertonicity is the presence of a solution that causes cells to shrink. Hypotonicity is the presence of a solution that causes cells to swell.
What happens to the solvent molecules in a hypotonic solution?
When a substance is placed in a hypotonic solution, the solvent molecules will move into the cell, and the cell becomes turgid or undergoes deplasmolysis.
What is the condition for the chemical potential of a solvent?
Consider the system at the point when it has reached equilibrium. The condition for this is that the chemical potential of the solvent (since only it is free to flow toward equilibrium) on both sides of the membrane is equal. The compartment containing the pure solvent has a chemical potential of.
What happens when a cell is in a hypotonic environment?
When a biological cell is in a hypotonic environment, the cell interior accumulates water, water flows across the cell membrane into the cell, causing it to expand. In plant cells, the cell wall restricts the expansion, resulting in pressure on the cell wall from within called turgor pressure.
What is osmosis pressure?
Understanding Osmotic Pressure – What is Osmosis? The term ‘osmosis’ refers to the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region where the solute concentration is low to a region where the solute concentration is high. Eventually, an equilibrium is established between the two sides of the semipermeable membrane ...
What is the purpose of measuring osmotic pressure?
The measurement of osmotic pressure can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds. Another important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater, which involves the process of reverse osmosis.
What is the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a
Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Osmotic pressure can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
Why is osmotic pressure important?
Osmotic pressure is especially useful in this regard, because a small amount of solute will produce a much larger change in this quantity than in the boiling point, freezing point, or vapor pressure. even a 10 –6 molar solution would have a measurable osmotic pressure.
What is the pressure required to achieve osmotic equilibrium?
The pressure required to achieve osmotic equilibrium is known as the osmotic pressure. Note that the osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop osmosis, not to sustain it. Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop osmotic flow. Caution!
What is osmotic flow?
Osmotic flow is simply diffusion of a solvent through a membrane impermeable to solute molecules. Now take two solutions of differing solvent concentration, and separate them by a semipermeable membrane. Being semipermeable, the membrane is essentially invisible to the solvent molecules, so they diffuse from the high concentration region to ...
How does an osmotic cell work?
So imagine an osmotic cell in which one side is supplied with fresh water from a river, and the other side with seawater. Osmotic flow of fresh water into the seawater side forces the latter up through a riser containing a turbine connected to a generator, thus providing a constant and fuel-less source of electricity.
How to stop osmosis?
One way to stop osmosis is to raise the hydrostatic pressure on the solution side of the membrane. This pressure squeezes the solvent molecules closer together, raising their escaping tendency from the phase. If we apply enough pressure (or let the pressure build up by osmotic flow of liquid into an enclosed region), the escaping tendency of solvent molecules from the solution will eventually rise to that of the molecules in the pure solvent, and osmotic flow will case. The pressure required to achieve osmotic equilibrium is known as the osmotic pressure. Note that the osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop osmosis, not to sustain it.
What happens when you apply enough pressure to a solution?
If we apply enough pressure (or let the pressure build up by osmotic flow of liquid into an enclosed region), the escaping tendency of solvent molecules from the solution will eventually rise to that of the molecules in the pure solvent, and osmotic flow will case.
Who discovered the equation of osmotic pressure?
The Dutch scientist Jacobus Van’t Hoff (1852-1911) was one of the giants of physical chemistry. He discovered this equation after a chance encounter with a botanist friend during a walk in a park in Amsterdam; the botanist had learned that the osmotic pressure increases by about 1/273 for each degree of temperature increase. van’t Hoff immediately grasped the analogy to the ideal gas law.
