
The release of norepinephrine from the synaptic vesicles is regulated by both stimulatory and inhibitory substances, including presynaptic α-adrenergic and β-adrenergic receptors. After release, norepinephrine binds to adrenergic receptors on target cells.
What receptors does norepinephrine act on?
What receptors do norepinephrine act on? Norepinephrine can then go on to bind three main receptors: alpha1 (alpha-1), alpha-2, and beta receptors. These receptors classify as G-protein coupled receptors with either inhibitory or excitatory effects and different binding affinities to norepinephrine.
What secretes norepinephrine adrenergic fibers?
Adrenergic neurons secrete norepinephrine and are found in both the central and autonomic nervous system.Within autonomic fibers, adrenergic neurons are exclusively found in postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system.
Does norepinephrine increase SVR?
The hemodynamic effects of norepinephrine are dominated by A1Rmediated vasoconstriction and increased SVR, while B1R activation provides just enough inotropy to maintain CO. Increasing doses of norepinephrine may increase CO in some patients due to B1R activation, augmentation of venous return, and improved fluid responsiveness.
Is norepinephrine an emergency hormone?
The researchers concluded from the three-year study that meditation blocks the effect on the body of norepinephrine, an "emergency hormone" secreted in response to stress.
See more
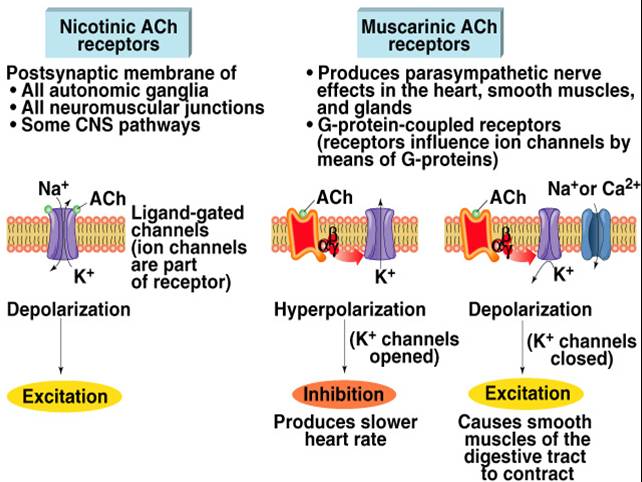
What happens when norepinephrine binds to beta adrenergic receptors?
Norepinephrine binding activates β-adrenergic receptors present on the basolateral membranes of salivary acinar cells. This results in activation of a G-protein that activates adenylate cyclase, which carries out the conversion of ATP to cAMP.
What happens when norepinephrine binds to alpha adrenergic receptors?
Alpha2 receptors also exist presynaptically associated with nerve terminals. Activation of these receptors inhibits the release of norepinephrine. Norepinephrine acts at presynaptic alpha2 receptors to inhibit its own release. Norepinephrine acts at presynaptic alpha2 receptors to inhibit its own release.
Does norepinephrine bind to alpha or beta receptors?
Adrenergic drugs can also be non-selective and hence bind to a combination of adrenergic receptors. Norepinephrine binds to the alpha-1, alpha-2, and beta-1 receptors.
Do epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to the same receptors?
Both epinephrine and norepinephrine work on alpha and beta receptors. However, epinephrine has a greater effect on beta receptors compared with norepinephrine. Alpha receptors are only found in the arteries. Beta receptors are in the heart, lungs, and arteries of skeletal muscles.
What happens when norepinephrine binds to alpha-2 receptors?
Alpha-2 adrenoceptors are implicated in diverse physiological functions in the heart, and presynaptic alpha-2 receptors inhibit the release of norepinephrine and other neurotransmitters in both the central and peripheral nervous systems.
Is norepinephrine an adrenergic agonist?
Agonists at adrenergic receptors are either direct-acting or indirect-acting. Catecholamines, norepinephrine, and epinephrine are direct-acting and nonselective adrenergic agonists.
Does norepinephrine bind to b2?
Norepinephrine released from sympathetic nerve terminals binds well to α receptors, as well as to β-1 receptors in the heart. However, norepinephrine binds very poorly to β-2 receptors.
What binds to adrenergic receptors?
Adrenergic receptors (adrenoceptors) are receptors that bind adrenergic agonists such as the sympathetic neurotransmitter NE and the circulating hormone epinephrine (EPI).
How is norepinephrine regulated?
The adrenal medulla is the inner portion of the adrenal gland. It regulates and secretes both epinephrine and norepinephrine in response to stress and other imbalances in the body, such as low blood pressure.
What are two receptors that bind norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine exerts its effects by binding to α- and β-adrenergic receptors (or adrenoceptors, so named for their reaction to the adrenal hormones) in different tissues. In the blood vessels, it triggers vasoconstriction (narrowing of blood vessels), which increases blood pressure.
Which of the following is an effect of norepinephrine binding to beta 2 adrenergic receptors?
Which of the following is an effect of norepinephrine binding to beta 2 adrenergic receptors? Vasodilation; The binding of norepinephrine to the beta 2 adrenergic receptors in blood vessels causes vasodilation.
How do adrenergic receptors work?
Adrenergic receptors are cell surface glycoproteins that recognize and selectively bind the catecholamines, norepinephrine and epinephrine, which are released from sympathetic nerve endings and the adrenal medulla.
What is the function of norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine is part of the sympathetic nervous system, which manages the body’s response to stress. It is one of the fight or flight hormones, along with its close relative epinephrine [ 5 ].
What is the relationship between dopamine and norepinephrine?
Dopamine and Norepinephrine Interplay. Dopamine is the direct precursor to epinephrine and norepinephrine, and so these catecholamines have a close relationship. One enzyme, dopamine beta hydroxylase ( DBH ), converts dopamine to norepinephrine directly [ 19 ].
What is Norepinephrine?
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is a compound that functions in the human brain and body as a hormone and a neurotransmitter [ 1 ].
How to check epinephrine levels?
Doctors can check their patients’ catecholamine (epinephrine, norepinephrine, and dopamine) levels through either a blood or urine test. In catecholamine blood tests, epinephrine and norepinephrine levels are expected to be significantly higher when the patient is standing up than when he or she is lying down [ 30, 31 ].
How does epinephrine work?
They also work together to decrease activity in the digestive system.
Which receptors bind to the same receptors?
Adrenergic Receptors. Epinephrine and norepinephrine bind to the same series of adrenergic receptors, but each receptor has “ preferences ” for a certain neurotransmitter. These preferences produce the differing effects of the two compounds. The α1 receptor prefers norepinephrine. It constricts blood vessels, increases blood pressure, ...
What amino acids are used in the assembly line of norepinephrine?
The body makes norepinephrine and other catecholamines in a cascade that can start with either of two amino acids, phenylalanine and tyrosine . The assembly line looks like this [ 16, 10 ]:
Where are norepinephrine receptors located?
Alpha-1 receptors are located postsynaptically throughout the brain and have moderate concentrations in the basal ganglia (Nicholas et al. 1993 ). α-2 receptors, on the other hand, are located both postsynaptically and presynaptically as autoreceptors on the synaptic terminals of norepinephrine-containing neurons where they regulate norepinephrine release ( Nicholas et al. 1993 ). β receptors are located throughout the brain. There are significant numbers of these receptors in the globus pallidus, and they are moderately concentrated in the caudate nucleus and putamen ( Reznikoff et al. 1986 ). There is a gradient in receptor numbers in the striatum, with receptors being denser ventrally than dorsally, similar to the known serotonergic pattern of innervation ( Waeber et al. 1991 ). The beta adrenergic receptors in the caudate nucleus and putamen are decreased in Huntington's disease, suggesting that they are located on intrinsic striatal neurons ( Waeber et al. 1991 ).
What is the effect of alpha-2 adrenergic receptor?
The alpha-2 adrenergic receptor appears to activate anticonvulsant mechanisms that suppress epileptiform activity (as seen when GABA A blockade is induced in hippocampal slices). Alpha-1 adrenergic activation increases the rate of spontaneously occurring IPSPs in CA3 pyramidal neurons, an effect that appears to be due to a depolarization of interneurons. Alpha-1 activation also appears to depress excitatory synaptic transmission by presynaptic mechanisms.
What receptors are involved in the hippocampus?
Norepinephrine (NE) receptors in the hippocampus include the beta and alpha (1 and 2) receptors . NE action at the beta 1 receptor causes a decrease in the slow AHP by activation of cyclic AMP. Presumably, cAMP leads to phosphorylation of either the calcium-activated potassium channel or other effectors of this conductance, and thus reduces the activation of the conductance by calcium. This effect is associated with an increase in the rate of interictal discharges produced by disinhibition or elevations of potassium in the hippocampal slice. The beta receptor also enhances calcium currents carried by L-type channels. Overall, the actions of norepinephrine on noradrenergic beta receptors are proconvulsant.
Where do NE receptors occur?
NE receptors occur in multiple layers of the MOB and are expressed by multiple cell types, in general consistent with the pattern of NE fiber innervation (for review, see Ennis, M. et al., 2007).
Does NE affect the neocortex?
NE also has indirect effects on the neocortex. For example, noradrenergic fibers target the BF and therefore indirectly regulate cholinergic activation. In vitro, application of NE to the BF increased cortical activity [15]; in vivo, application of NE to the BF caused waking [16]. Together, these results suggest that NE signaling boosts cholinergic neuromodulation. However, cortical activation by NE is not solely an indirect consequence of upregulated cholinergic tone, since blocking noradrenergic receptors in the cortex induces a transition to slow rhythmic cortical activity in the awake animal [17].
Does sertraline affect dopamine?
Sertraline acts primarily by inhibiting serotonin reuptake and has minimal effects on norepinephrine and dopamine reuptake. It downregulates serotonin and norepinephrine receptors in the brain.
Which receptors bind catecholamines?
Alpha-1 receptors bind catecholamines including, both epinephrine and norepinephrine. In instances in which there is hypoperfusion secondary to decreased cardiac output or decreased systemic vasculature resistance, alpha-1 receptors become stimulated.
What receptors are used for alpha receptor modification?
The indication for the use of an alpha-receptor modifying medication depends on which receptor is the target: the alpha-1 receptor or the alpha-2 receptor. Further, when administering a pharmacologic agent, it can exert either agonistic or antagonistic activity on the alpha receptors. This activity reviews the various alpha receptors and examines the types of agents that can act upon these receptors to alter the physiologic response for therapeutic effect.
How is alpha-1 administered?
Administration of alpha-1 receptor agonists is done intravenously through a central line for shock. In the setting of anaphylaxis, epinephrine administration should be either intramuscular or subcutaneous, not intravenous.
What are the contraindications for alpha-2 agonists?
Contraindications for alpha-2 agonists include concurrent use of phosphodiesterase inhibitors, orthostatic hypotension, and any condition leading to autonomic instability. [28] . Monitoring. Monitoring depends on the setting of drug administration.
What are the adverse effects of alpha-2 receptor agonists?
The most common adverse effects of alpha-2 receptor agonists are sedation and fatigue.[22] The adverse effects of alpha-1 agonists include hypertension, tachycardia or other dysrhythmias, increased cardiac demand, and subcutaneous ischemia at the site of injection. [23][24] Contraindications.
What are the adverse effects of alpha 1 blockers?
With the initial administration of an alpha-1 blocker, systemic vasodilation can lead to a tachycardic response and orthostatic hypotension. [21] This same effect may also occur in the alpha-2 agonist family; however, this is generally less pronounced than in the alpha-1 blockade. The most common adverse effects of alpha-2 receptor agonists are sedation and fatigue.[22] The adverse effects of alpha-1 agonists include hypertension, tachycardia or other dysrhythmias, increased cardiac demand, and subcutaneous ischemia at the site of injection. [23][24]
What are the effects of alpha receptors?
The alpha-1 receptor is of the Gq type, resulting in activation of phospholipase C, increasing IP3 and DAG, and ultimately increasing the intracellular calcium concentrations leading to smooth muscle contraction and glycogenolysis.[19] The alpha-2 receptor acts as an allosteric inhibitor through Gi function, leading to an inhibition of adenylyl cyclase, decreasing the formation of intracellular cAMP. It also leads to a reduced amount of cytoplasmic calcium, which decreases neurotransmitter release and central vasodilation.[20] Epinephrine and norepinephrine have relatively equal affinities for both types of alpha-receptors, with other drugs used in shock having a higher selectivity for the alpha-1 receptor.
Which receptors does norepinephrine bind to?
The table below shows the efficacy of norepinephrine and epinephrine in binding to α and β receptors. Norepinephrine released from sympathetic nerve terminals binds well to α receptors, as well as to β-1 receptors in the heart. However, norepinephrine binds very poorly to β-2 receptors.
What receptors do norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to?
Norepinephrine and epinephrine bind to two main subtypes of metabotropic receptors: α and β. The α subtype can be divided into the α-1 and α-2 subtypes. The β subtype can be divided into β-1, β-2 and β-3 receptors, although β-3 receptors are less important than the other subclasses.
What happens to the sympathetic nervous system when a drug acts on the adrenergic receptors?
As a consequence of the baroreceptor reflex, a drug that acts on adrenergic receptors can precipitate changes in sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system activity that tends to offset the effects of the drug. Take, for example, the case of an α1 receptor antagonist. Although such a drug would decrease total peripheral resistance and lower blood pressure, its administration also results in reflex-mediated increases in heart rate and contractility, as shown below.
What are stretch receptors in the large arteries called?
As noted in the neural control of blood pressure lecture, stretch receptors in the large arteries called baroreceptors signal changes in blood pressure to the central nervous system. These inputs trigger the baroreceptor reflex, which attempts to return blood pressure to the previous level by altering sympathetic and parasympathetic nervous system activity. These actions are summarized in the table below:
Where does norepinephrine come from?
Norepinephrine is synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine through by a series of enzymatic steps in particular cells in the central nervous system, as well as by most postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system. Norepinephrine is released like most neurotransmitters: when an action potential invades a nerve terminal, voltage-gated calcium channels (typically N-type) open, and the entry of calcium causes fusion of the norepinephrine-containing vesicles with the membrane, thereby releasing norepinephrine into the synaptic cleft.
Does epinephrine affect heart rate?
Hence, the effects of epinephrine on the cardiovascular system are highly dose-dependent. At normal physiological concentrations, epinephrine activates β-1 and β-2 receptors, resulting in an increase in heart rate and contractility and dilation of muscle arterioles. At high concentrations, epinephrine causes vasoconstricton due to its effects on α-1 receptors.
Does epinephrine bind to receptors?
In contrast, epinephrine binds well to β-1 and β-2 receptors, and with much less efficacy to α-receptors. However, in very high concentrations (e.g., use of the EPI-pen ), epinephrine activates α-1 receptors.

Overview
Norepinephrine (NE), also called noradrenaline (NA) or noradrenalin, is an organic chemical in the catecholamine family that functions in the brain and body as both a hormone and neurotransmitter. The name "noradrenaline," derived from Latin roots meaning "at/alongside the kidneys," is more commonly used in the United Kingdom; in the United States, "norepinephrine," derived from Greek roo…
Structure
Norepinephrine is a catecholamine and a phenethylamine. Its structure differs from that of epinephrine only in that epinephrine has a methyl group attached to its nitrogen, whereas the methyl group is replaced by a hydrogen atom in norepinephrine. The prefix nor- is derived as an abbreviation of the word "normal", used to indicate a demethylated compound. Norepinephrine comprises of a cat…
Biochemical mechanisms
Norepinephrine is synthesized from the amino acid tyrosine by a series of enzymatic steps in the adrenal medulla and postganglionic neurons of the sympathetic nervous system. While the conversion of tyrosine to dopamine occurs predominantly in the cytoplasm, the conversion of dopamine to norepinephrine by dopamine β-monooxygenase occurs predominantly inside ne…
Functions
Like many other biologically active substances, norepinephrine exerts its effects by binding to and activating receptors located on the surface of cells. Two broad families of norepinephrine receptors have been identified, known as alpha and beta adrenergic receptors. Alpha receptors are divided into subtypes α1 and α2; beta receptors into subtypes β1, β2, and β3. All of these function as G protein-co…
Pharmacology
A large number of important drugs exert their effects by interacting with norepinephrine systems in the brain or body. Their uses include treatment of cardiovascular problems, shock, and a variety of psychiatric conditions. These drugs are divided into: sympathomimetic drugs which mimic or enhance at least some of the effects of norepinephrine released by the sympathetic nervous system; sympatholytic drugs, in contrast, block at least some of the effects. Both of these are lar…
Diseases and disorders
A number of important medical problems involve dysfunction of the norepinephrine system in the brain or body.
Hyperactivation of the sympathetic nervous system is not a recognized condition in itself, but it is a component of a number of conditions, as well as a possible consequence of taking sympathomimetic drugs. It causes a distinctive set of symptoms including aches and pains, rapi…
Comparative biology and evolution
Norepinephrine has been reported to exist in a wide variety of animal species, including protozoa, placozoa and cnidaria (jellyfish and related species), but not in ctenophores (comb jellies), whose nervous systems differ greatly from those of other animals. It is generally present in deuterostomes (vertebrates, etc.), but in protostomes (arthropods, molluscs, flatworms, nematodes, annelids, etc.) it is …
History
Early in the twentieth century Walter Cannon, who had popularized the idea of a sympathoadrenal system preparing the body for fight and flight, and his colleague Arturo Rosenblueth developed a theory of two sympathins, sympathin E (excitatory) and sympathin I (inhibitory), responsible for these actions. The Belgian pharmacologist Zénon Bacq as well as Canadian and US-American pharmacologists between 1934 and 1938 suggested that noradrenaline might be a sympathetic …