What are the health effects of nuclear radiation?
This includes:
- the probability of inducing a fatal cancer;
- the chance of a non-fatal cancer occurring;
- the chance of severe hereditary effects; and,
- the length of life loss if the harm occurs (ICRP 103).
What are the long - term effects of radiation exposure?
- Increased, looser bowel movements
- Infertility (For patients in their childbearing years who wish to have children one day, there are options to preserve fertility prior to treatment.)
- Reduction in bladder capacity
- Vaginal dryness
What are the effects of a nuclear bomb?
The effects of nuclear weapons
- Blast. The expansion of intensely hot gases at extremely high pressures in a nuclear fireball generates a shock wave that expands outward at high velocity.
- Thermal radiation. ...
- Initial radiation. ...
How does radiation therapy effect the body?
- Radiation cystitis. If the radiation damages the lining of the bladder, radiation cystitis can be a long-term problem that causes blood in the urine or pain when passing urine.
- Urinary incontinence. ...
- Fistulas. ...
How Long Does Nuclear radiation stay in your body?
Our bodies eventually turn over these tissues, but it takes three months to reduce the amount of caesium in our muscles by half, so the long-term exposure to beta and gamma radiation increases the chances of cancer developing in those tissues.
What are 5 harmful effects of radiation?
Here are a few common health effects or harmful effects of radiation on the human body.Hair. Loss of hair fall occurs when exposure to radiation is higher than 200 rems.Heart and Brain. Intense exposure to radiation from 1000 to 5000 rems will affect the functioning of the heart. ... Thyroid. ... Blood System. ... Reproductive Tract.
What are the 4 major effect of radiation on human body?
At very high doses, radiation can impair the functioning of tissues and organs and produce acute effects such as nausea and vomiting, skin redness, hair loss, radiation burns, acute radiation syndrome or even death.
What should you do if exposed to nuclear radiation?
Stay inside. Close and lock all windows and doors. Go to the basement or the middle of the building. Radioactive material settles on the outside of buildings; so the best thing to do is stay as far away from the walls and roof of the building as you can.
What are the 2 most common side effects of radiation?
Early and late effects of radiation therapy The most common early side effects are fatigue (feeling tired) and skin changes. Other early side effects usually are related to the area being treated, such as hair loss and mouth problems when radiation treatment is given to this area.
Which organ is most affected by radiation?
The most radiation-sensitive organs include the hematopoietic system [4], the gastrointestinal (GI) system [5], skin [6, 7], vascular system [8, 9], reproductive system, and brain [10–12].
What is the most harmful radiation to humans?
Gamma raysGamma rays are the most harmful external hazard. Beta particles can partially penetrate skin, causing “beta burns”. Alpha particles cannot penetrate intact skin. Gamma and x-rays can pass through a person damaging cells in their path.
What diseases can you get from nuclear radiation?
At lower doses, ionizing radiation can cause health effects such as cardiovascular disease and cataracts, as well as cancer. It causes cancer primarily because it damages DNA, which can lead to cancer-causing gene mutations.
What are 3 harmful effects of radiation?
How Radiation Affects Your Body. Radiation can damage the DNA in our cells. High doses of radiation can cause Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) or Cutaneous Radiation Injuries (CRI). High doses of radiation could also lead to cancer later in life.
What are the 3 types of harmful radiation?
Alpha particles are the most harmful internal hazard as compared with gamma rays and beta particles. Radioactive materials that emit alpha and beta particles are most harmful when swallowed, inhaled, absorbed, or injected. Gamma rays are the most harmful external hazard.
What are the 2 types of radiation damage?
Non-Ionizing and Ionizing Radiation Ionizing radiation has so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms, a process known as ionization. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things, so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes.
What is most affected by radiation?
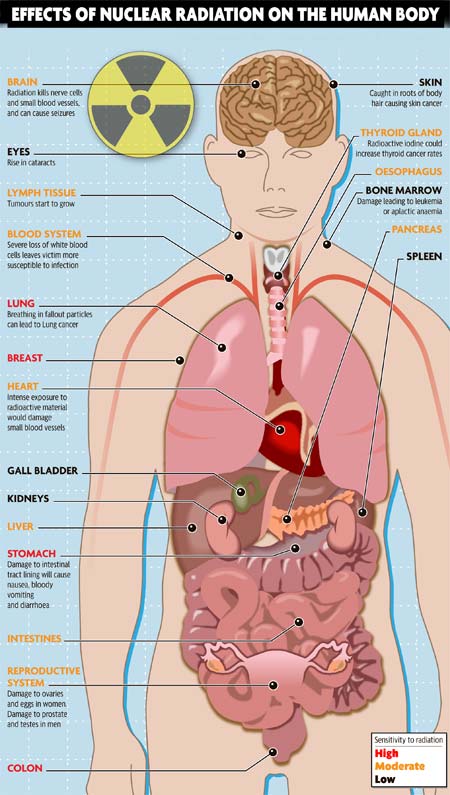
Lymphocytes (white blood cells) and cells which produce blood are constantly regenerating, and are, therefore, the most sensitive. Reproductive and gastrointestinal cells are not regenerating as quickly and are less sensitive. The nerve and muscle cells are the slowest to regenerate and are the least sensitive cells.
How does radiation affect the human body?
Brain. Nerve cells (neurons) and brain blood vessels can die, leading to seizures. Eyes. Radiation exposure increases the risk of cataracts.
How does radiation affect cells?
We are all exposed to radiation every day. High doses tend to flat-out kill cells, while lower doses tend to alter the genetic code ( DNA) of cells. If enough cells in an organ are killed, organ failure can result. Lower Doses of Radiation.
How much radiation does the average human get?
(Oddly enough, bananas and brazil nuts clock in as the most radioactive foods.) The average human is exposed to about three millisieverts of radiation per year, mostly from cosmic radiation and medical procedures.
What is the effect of ionizing radiation on cells?
While cells are damaged by free radicals all the time, they normally repair themselves, keeping the body healthy.
What happens when cells are exposed to radiation?
When cells — and what lies within them — get exposed to radiation, components of DNA and critical proteins within the cell get all jazzed up (ionized), meaning that the electrons with our atoms get kicked out, causing the DNA strands to break and the proteins to cramp up (denature).
How long does it take to die from radiation?
It's nearly impossible to predict the threshold of exactly how much radiation you would need to be exposed to in order to die, but according to the US Nuclear Regulatory Commission, "It is believed that 50 percent of a population would die within 30 days after receiving a dose of between 3500-5000 mSv (3.5-5 Sieverts) to the whole body, over a period ranging from a few minutes to a few hours."
What organs die in pregnancy?
Reproductive organs. Rapidly dividing cells (eggs and sperm) in the ovaries and testes can die, leading to sterility.
How quickly can radiation kill you?
As the radiation dose gets higher (many sieverts) this can kill you very quickly, in a matter of hours if the dose is high enough.". "It works exactly the same as lower doses of radiation but on a mass scale and when enough cells die that can cause problems", says Crossley.
What is the difference between gamma and neutron radiation?
Neutron radiation — consisting of free neutrons which are released during fission but not usually through radioactive decay. Gamma or x-rays, which are electromagnetic radiation similar to light, but with much more energy. Find out more about radiation in our Bernie's Basics: It's radioactive man. ^ to top.
What are the products of radioactive fission?
Plutonium and uranium produce a range of radioactive fission products including variations of iodine, caesium, strontium and noble gases such as argon and xenon.
What are the two types of ionizing radiation?
Types of ionising radiation include: Alpha particles — two protons and two neutrons bound together like a helium nucleus — are large particles that can do lots of damage, but only over short distances. Beta particles — are electrons, which can travel longer distances in air and tissue than alpha particles.
What happens when neutrons are smashed into an atom?
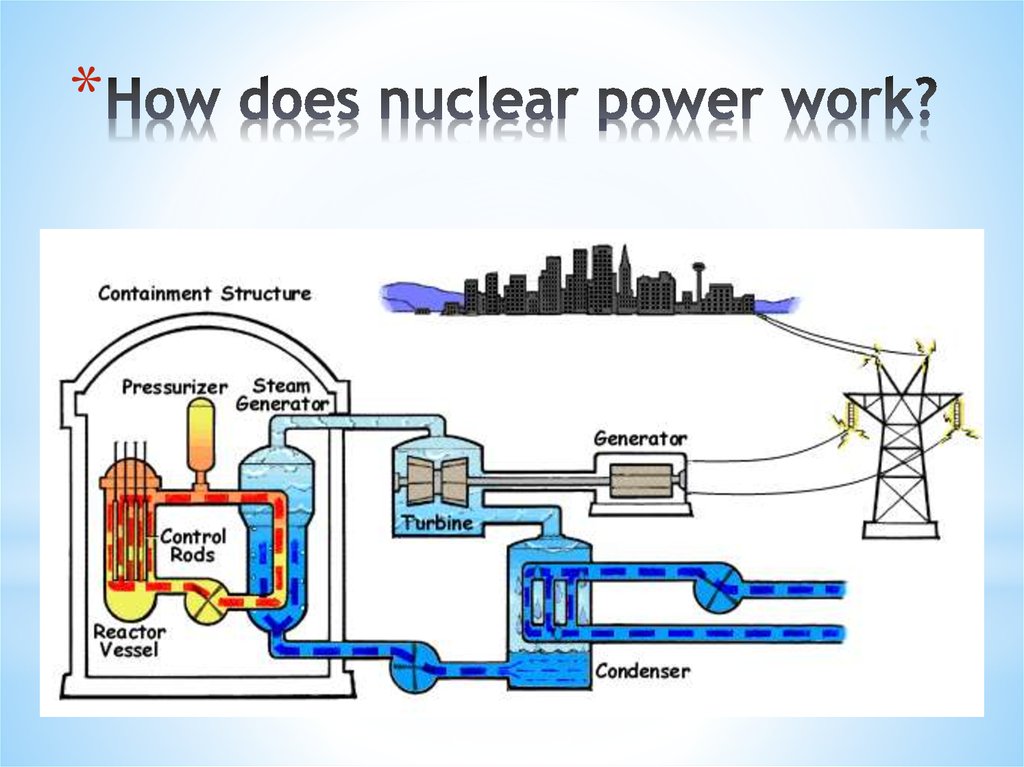
In a reactor when neutrons are smashed into an atom, the atom releases neutrons which then hit other atoms in a chain reaction (find out how nuclear reactors work).
How many ways can you be exposed to radiation?
According to Crossley, there are two ways you can be exposed to radiation.
Is radiation harmful to humans?
The amount of radiation harmful to people depends on which chemical element, and how much of it they are exposed to, says Steven Crossley, a radiation physicist at Sir Charles Gairdner Hospital in Western Australia. Different variations of elements, known as isotopes, decay by different methods and give off different types of radiation, ...
How long has radiation been studied?
minus. Related Pages. Scientists have been studying the effects of radiation for over 100 years; so we know quite a bit about how radiation interacts with living tissue, and its effect on the body. Because we can measure radiation and because we understand its health effects, we can work safely around it.
What is the medical term for high doses of radiation?
High doses of radiation can cause Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS) or Cutaneous Radiation Injuries (CRI).
Which group is more sensitive to radiation?
Children and young adults are more sensitive to the effects of radiation.
Is radiation poisonous?
It’s All About the Dose! As with other types of toxins, “the dose makes the poison”. We receive low doses of radiation from our natural environment every day. We know that radiation at high doses can cause cancer, could harm fetuses, and can even lead to death. Learn more about dose and health effects of radiation.
How does nuclear radiation affect living cells?
Atomic bombs and nuclear reactors all emit ionizing radiation which affects living cells by damaging their genetic material (DNA). Fortunately, our body cells are effective in repairing such damage. However, if the body isn’t sufficient enough to guard itself against this radiation then the cells may die or cause them to mutate in ways that eventually lead to cancer. Exposure to nuclear radiation can also result in skin burns, acute radiation syndrome, and long term cardiovascular disease.
What is Nuclear Radiation?
This is a form of radiation energy emitted by radioactive decay which can appear as high-speed particles. There are several types of radiations; beta, alpha, gamma, and x-ray. The beta exhibit itself in the form of electrons, alpha is made of two protons and two neutrons while gamma and x-ray appear as waves.
What happens to thyroid if it is exposed to radiation?
Thyroid: As a result of radiation malfunctions, radioactive iodine is released to the atmosphere. Thyroid happens to be the most sensitive part to this radiation . The radioactive iodine is absorbed by the thyroid leading to thyroid cancer. Since radioactive iodine has a high affinity for the thyroid, specialists are taking this advantage and attracting this radiation for therapeutically uses and to treat thyroid cancer.
How many rads are needed for radiation sickness?
This condition is commonly called radiation sickness. It takes more than 75 rad (0.75 grays) to cause acute radiation syndrome which is very high radiation exposure.
What causes brain cells to die?
Brain: Overexposure to nuclear radiation causes nerve cells and brain blood vessels to die leading to seizures.
How long does it take for a mammogram to emit radiation?
A mammogram emits radiation that’s equal to seven days of normal exposure to radiation.
How much radiation is needed to cause acute radiation syndrome?
Imagine getting radiation from 18,000 chest x-rays distributed over your entire body in a short period of time. This is how much radiation is required to cause acute radiation syndrome no wonder it can easily lead to death. Cases of acute radiation syndrome are rare and come from extreme events such as nuclear explosions or accidental rupture of a highly radioactive source.
What are the effects of radiation exposure?
It can also result in long-term health effects such as cancer and cardiovascular disease. Exposure to low levels of radiation encountered in the environment does not cause immediate health effects, but is a minor contributor to our overall cancer risk.
How does ionizing radiation affect cells?
Ionizing radiation Ionizing radiation Radiation with so much energy it can knock electrons out of atoms. Ionizing radiation can affect the atoms in living things, so it poses a health risk by damaging tissue and DNA in genes. has sufficient energy to affect the atoms in living cells and thereby damage their genetic material (DNA). Fortunately, the cells in our bodies are extremely efficient at repairing this damage. However, if the damage is not repaired correctly, a cell may die or eventually become cancerous. Related information in Spanish (Información relacionada en español).
What is the term for radiation sickness?
This is known as acute radiation syndrome, commonly known as “radiation sickness.”. It takes a very high radiation exposure to cause acute radiation syndrome —more than 0.75 gray gray A gray is the international unit used to measure absorbed dose (the amount of radiation absorbed by an object or person).
What is radiation risk?
Radiation risk may refer to all excess cancers caused by radiation exposure (incidence risk) or only excess fatal cancers (mortality risk). Risk may be expressed as a percent, a fraction, or a decimal value. For example, a 1% excess risk of cancer incidence is the same as a 1 in a hundred (1/100) risk or a risk of 0.01. of cancer over a lifetime.
What are radioactive forms of elements?
The risk from exposure to a particular radionuclide radionuclide Radioactive forms of elements are called radionuclides. Radium-226, Cesium-137, and Strontium-90 are examples of radionuclides. depends on: The energy of the radiation it emits. The type of radiation ( alpha, beta, gamma, x-rays ).
What is acute radiation syndrome?
Acute radiation syndrome is rare, and comes from extreme events like a nuclear explosion or accidental handling or rupture of a highly radioactive source. View CDC Fact Sheet: Acute Radiation Syndrome (ARS). Learn about protecting yourself from radiation. Learn about radiation sources and doses. Top of Page.
What is the type of radiation?
The type of radiation ( alpha, beta, gamma, x- rays ). Its activity (how often it emits radiation). Whether exposure is external or internal: External exposure is when the radioactive source is outside of your body. X-rays and gamma rays can pass through your body, depositing energy as they go.
How does nuclear radiation affect the reproductive system?
Nuclear radiation effects during WAR. The effects of nuclear radiation also include problems with the reproductive system. The cells in the system will not be able to replicate fast and can be damaged if the exposure is 200 rem or higher. Some people may not be able to have children because of the high exposure.
What is Nuclear Radiation?
Nuclear Radiation definition is when photons are emitted when a reaction occurs related to the nucleus located within an atom, nuclear radiation is produced.
How long does radiation affect the immune system?
This can cause problems with the immune system when it comes to fight infections. Some of the symptoms may last for up to ten years and this can lead to more serious problems such as lymphoma and leukemia.
What happens if you are exposed to 200 rems of radiation?
Those who are exposed to 200 rems or more of radiation may have nuclear radiation effects such as the loss of hair or hair that clumps together. There are times when the brain can be damaged but this happens only at an exposure that is higher than 5000 rems.
What does higher exposure mean?
Higher exposure means more damage, biologically. Radiation Effects on Human.
Can electrons penetrate the air?
An electron is released. It can be penetrated into the air and can be penetrated into a person’s skin causing damage. Gamma and X Radiation can easily penetrate radiation that is electromagnetic. This type can also get into the air and can also damage a person’s skin, causing harm not just to the skin but other part as well.
Does potassium iodide damage thyroid?
The iodine can do severe damage to the thyroid but this issue can be treated or decreased with the consumption of potassium iodide. If a person is exposed to anywhere from 1000 to 5000 rems of radiation, this can damage the vessels that carry blood throughout the body.
