What is osmotic pressure and why is it important?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop water from diffusing through a membrane by osmosis. It is determined by the concentration of the solute. Water diffuses into the area of higher concentration from the area of lower concentration. When the concentration of the substances in the two areas in contact is different, the substances will diffuse until the concentration is uniform throughout.
What does it mean to have high osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is a measure of the concentration of solutions. It does not cause actual, physical pressure. High osmotic pressure in the blood will cause water to be taken out of the cells. The kidneys usually maintain osmotic pressure under very tight control, so elevated osmotic pressure usually is abnormal.
What is meant by osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure that needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of water across a semipermeable membrane. Osmotic pressure can also be explained as the pressure necessary to nullify osmosis.
What does osmotic pressure cause?
osmotic pressure. noun. Osmotic pressure is the force caused by a solution passing through a semi permeable surface by osmosis, which is equal to the force required to resist the solution from passing back through the surface. An example of osmotic pressure is the process to filter water.

Is osmosis and osmotic pressure same?
The least pressure required to apply to a solution in order to stop the flow of solvent molecules across a semipermeable membrane is known as osmotic pressure (osmosis). It is a colligative property that is regulated by the concentration of solute particles in the solution.
Does osmosis require osmotic pressure?
1.2 Osmosis Osmosis is a special type of diffusion, namely the diffusion of water across a semipermeable membrane. Water readily crosses a membrane down its potential gradient from high to low potential (Fig. 19.3) [4]. Osmotic pressure is the force required to prevent water movement across the semipermeable membrane.
How does pressure influence osmosis?
Factors Affecting the Rate of Osmosis Pressure – The more the pressure, the faster the molecules will move for they are being pushed faster across a low concentration.
What does osmotic pressure relate to?
What is Osmotic Pressure? Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution.
What happens when osmotic pressure increases?
loss of electrolytes (salt), the osmotic pressure of the extracellular fluids becomes higher than in the cells. Since water passes from a region of lower to a region of higher osmotic pressure, water flows out of the cells into the extracellular fluid, tending to lower its osmotic pressure and increase…
What is required for osmosis to occur?
Therefore, for osmosis to occur, the membrane must be permeable to water, but impermeable to the solute, and the concentration of the solute must be different on the two sides of the membrane.
Why is osmosis and understanding osmotic pressure important?
Osmosis. Osmotic pressure is of vital importance in biology since the cell membrane is selective against many of the solutes present in living organisms. When a cell is put in a hypertonic solution, water escapes the cell and flows into the surrounding solution, causing the cell to shrink and lose its turgidity.
What happens when osmotic pressure decreases?
Decreased intravascular osmotic pressure most commonly results from decreased concentrations of plasma proteins, particularly albumin. Hypoalbuminemia reduces the intravascular colloidal osmotic pressure, resulting in increased fluid filtration and decreased absorption and culminating in edema.
What will happen if there is no osmotic pressure?
Either the cell will rupture or else it will swell to a point where the pressure exerted on the membrane exceeds the pressure of the water trying to enter the cell.
Which pressure stops osmosis?
Osmotic equilibrium and osmotic pressure One way to stop osmosis is to raise the hydrostatic pressure on the solution side of the membrane. This pressure squeezes the solvent molecules closer together, raising their escaping tendency from the phase.
What is osmotic pressure in simple terms?
Osmotic pressure is the minimum pressure which needs to be applied to a solution to prevent the inward flow of its pure solvent across a semipermeable membrane. It is also defined as the measure of the tendency of a solution to take in a pure solvent by osmosis.
What does a higher osmotic pressure mean?
If a membrane is present, water will flow to the area with the highest concentration of solute. Osmotic pressure is the pressure created by water moving across a membrane due to osmosis. The more water moving across the membrane, the higher the osmotic pressure.
Which pressure stops osmosis?
Osmotic equilibrium and osmotic pressure One way to stop osmosis is to raise the hydrostatic pressure on the solution side of the membrane. This pressure squeezes the solvent molecules closer together, raising their escaping tendency from the phase.
What is difference between osmosis and diffusion?
Osmosis only allows solvent molecules to move freely, but diffusion allows both solvent and solute molecules to move freely. 4. Osmosis happens when molecules move from higher to lower concentrations, but diffusion happens when it is reversed.
How long does osmosis continue what is osmotic pressure?
This diffusion of water through the membrane—osmosis—will continue until the concentration gradient of water goes to zero or until the hydrostatic pressure of the water balances the osmotic pressure.
How is osmotic pressure of a solution related to its concentration?
The osmotic pressure of a solution is the pressure difference needed to stop the flow of solvent across a semipermeable membrane. The osmotic pressure of a solution is proportional to the molar concentration of the solute particles in solution.
What does osmotic pressure depend on?
The temperature and the initial concentration of the solute affect osmotic pressure. It is interesting to note that it is independent of what is di...
What happens when food’s osmotic pressure increases?
When a food’s osmotic pressure is increased by drying it or adding sugars or salts, the amount of water available to the bacterial cell is reduced....
Why does osmotic pressure depend on temperature?
The extra pressure that must be applied to the solution’s surface in order to prevent pure solvent osmosis. The osmotic pressure always increases a...
What is the difference between Oncotic pressure and osmotic pressure?
Osmotic pressure is the pressure required to stop the net movement of water across a permeable membrane that divides the solvent and solution, wher...
What happens when osmotic pressure and temperature are same?
When osmotic pressure and temperature are both equal, an equivalent volume of solution contains a same number of moles of solute.
Osmosis
The phenomenon of osmosis was studied for the first time by Abbe Nollet in 1748. Let us consider an aqueous solution of sugar placed in an inverted thistle funnel having a semi-permeable membrane such as animal bladder or parchment paper, attached to its bottom. The thistle funnel is lowered into a beaker containing water.
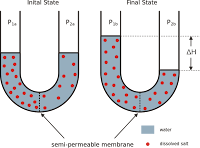
Osmotic Pressure
To understand the concept of osmotic pressure, consider an apparatus shown in the figure. It consists of a vessel divided into two compartments by a semi-permeable membrane. These two compartments are fitted with water-tight frictionless pistons. Let us take solution in one compartment and pure solvent in the other compartment.
What is the meaning of osmosis pressure?
Osmotic Pressure Definition. Osmotic pressure can be thought of as the pressure that would be required to stop water from diffusing through a barrier by osmosis. In other words, it refers to how hard the water would “push” to get through the barrier in order to diffuse to the other side. Osmotic pressure is determined by solute concentration – ...
How is osmotic pressure determined?
Osmotic pressure is determined by solute concentration – water will “try harder” to diffuse into an area with a high concentration of a solute, such as a salt, than into an area with a low concentration. In reality of course, osmotic pressure is not a “desire” of water to move, but rather an extension of the natural law ...
Why do organisms use osmotic pressure?
Some organisms, such as plants that use osmotic pressure to move water, have taken advantage of this principle. But it can also threaten the health of cells and organisms when there is too much or too little water in the extracellular environment compared to the inside of the cell.
Why can't solutes move in osmosis?
So in the case of osmosis, the solutes cannot move because they cannot pass through the membrane. However, the water can move, and it does – passing through the membrane to an area with higher solute concentration. This can cause the total volume of water on each side of the membrane to change: the side of the membrane with more solutes may end up ...
What does hypertonic mean in science?
In scientific terms, they are “ hypertonic ” – which means “the concentration of solute is too high.”. Plants can also demonstrate the power of osmotic pressure as they grow. You may have seen plants springing up through asphalt, or tree roots growing through bricks or concrete.
What happens if you have too much water in your cell?
This can cause the total volume of water on each side of the membrane to change: the side of the membrane with more solutes may end up with much more water. This can lead to problems for cells, such as bursting (if too much water moves into the cell ), or becoming dehydrate (if too much water moves out).
What pressure is used to push water through plants?
This, too, is made possible by osmotic pressure: as plants grow, their cells draw in more water. The slow but inexorable pressure of water moving through the plant cell ’s membranes can actually push through asphalt!
What is osmosis pressure?
Understanding Osmotic Pressure – What is Osmosis? The term ‘osmosis’ refers to the movement of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from a region where the solute concentration is low to a region where the solute concentration is high. Eventually, an equilibrium is established between the two sides of the semipermeable membrane ...
What is the purpose of measuring osmotic pressure?
The measurement of osmotic pressure can also be used to determine molecular weights of compounds. Another important application of osmotic pressure is in the desalination and purification of seawater, which involves the process of reverse osmosis.
What is the process of moving a solvent from the solution side to the solvent side?
This process is called reverse osmosis (click the hyperlink to learn more about it!).
What is the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a?
Osmotic pressure can be defined as the minimum pressure that must be applied to a solution to halt the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane (osmosis). It is a colligative property and is dependent on the concentration of solute particles in the solution. Osmotic pressure can be calculated with the help of the following formula:
Which side of the solution does the solvent pass through?
In the illustration provided above, it can be observed that the solvent molecules tend to pass through the semipermeable membrane into the solution side until the osmotic pressure (of the solution) is applied to the solution side.
What is the osmotic pressure of 1M salt?
The osmotic pressure of the 1M salt solution is 49.26 atmospheres at a temperature of 27 o C.
What is the molar concentration of potassium chloride in a solution?
Therefore, the molar concentration of potassium chloride in the solution is 1.015 M.
How does osmosis work?
Osmosis is simply the flow of solvent molecules through a semipermeable membrane from higher solventconcentration to lower solvent concentration. Be careful: higher solvent concentration implies lower soluteconcentration. All mass transport properties occur from higher concentration to lower concentration (of the molecules that move). The semipermeable membrane has pores in it that are large enough to allow solvent molecules (often water) to pass through, but small enough to prevent passage of solute molecules (such as sugar, ions, etc). The presence of solute molecules on one side of the membrane causes fewer water molecules on the solute side to approach (and cross) the membrane from that side. Thus, water will flow toward the solute faster than it flows away from the solute. For example, take a sugar solution that is placed in a bag that is then placed in pure water. Osmosis causes the bag to enlarge as water flows inside the bag.
How to prevent osmosis?
Osmosis can be prevented by applying an external pressure to the solution (as opposed to solvent-only) side of the membrane. The pressure required to prevent osmosis is called osmostic pressure. For reasonably dilute solutions, the osmotic pressure is related to the concentration of soluteby the following equation:
What happens if you inject water into a patient?
If pure water is injected into a patient, the solutes present in the patient's cells would cause the water to rush into the cells, causing them to swell, and possibly burst. On the other hand, if the solution is too concentrated, the patient would become even more dehydrated, as the water would rush out of the patient's cells.
What is the ideal gas constant?
In the above equation, R is the ideal gas constant, 0.08206 L·atm / mol·K; T is the temperature (in Kelvin); and cis the concentration, in molarity. This equation is amazingly similar to the Ideal Gas Equation, where P is replaced by P, and n/V is replaced by c.
When the osmotic pressure of the solution outside the blood cells is higher than the osmotic?
When the osmotic pressure of the solution outside the blood cells higher than the osmotic pressure inside the red blood cells, the solution is hypertonic. The water inside the blood cells exits the cells in an attempt to equalize the osmotic pressure, causing the cells to shrink or create.
What is the difference between osmotic pressure and tonicity?
Both are scientific terms pertaining to pressure. Osmotic pressure is the pressure of a solution against a semipermeable membrane to prevent water from flowing inward across the membrane . Tonicity is the measure of this pressure. If the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane is equal, then there is no tendency for water ...
What happens if the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane is equal?
If the concentration of solutes on both sides of the membrane is equal, then there is no tendency for water to move across the membrane and no osmotic pressure. The solutions are isotonic with respect to each other. Usually, there is a higher concentration of solutes on one side of the membrane than the other.
What happens when you have sugar solution on one side of a semipermeable membrane and pure water on the other?
If you have a sugar solution on one side of a semipermeable membrane and pure water on the other side of the membrane, there will always be pressure on the water side of the membrane to try to dilute the sugar solution. Does this mean all of the water will flow into the sugar solution?
What is diffusion versus osmosis?
Diffusion Versus Osmosis. Diffusion is the movement of particles from a region of higher concentration to one of lower concentration. For example, if you add sugar to water, the sugar will diffuse throughout the water until the concentration of sugar in the water is constant throughout the solution.
When the osmotic pressure outside the red blood cells is the same as the pressure inside the cells, the?
When the osmotic pressure outside the red blood cells is the same as the pressure inside the cells, the solution is isotonic with respect to the cytoplasm. This is the usual condition of red blood cells in plasma.
Does water move through the membrane during osmosis?
However, the particles may be too large to cross a semipermeable membrane separating regions of a solution, so water moves across the membrane.