How check DR and BDR in OSPF?
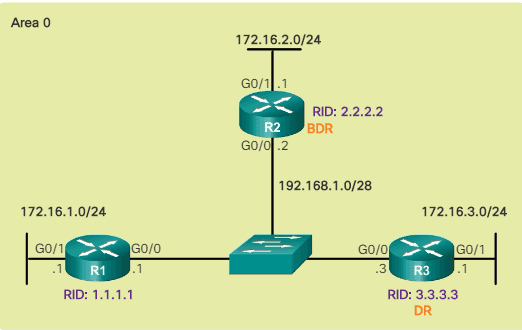
OSPF figures this out by looking at the interface type. For example, an Ethernet interface is considered a multi-access network, and a serial interface is considered a point-to-point interface. From R1 perspective, R2 is the BDR and R3 is the DR.
What is DR and BDR in OSPF?
In an OSPF broadcast network, OSPF elects one router to serve as the designated router (DR) and another router on the segment to act as the backup designated router (BDR). This minimizes the amount of repetitive information that is forwarded on the network. OSPF forwards all messages to the designated router.
How many DR and BDR are in an OSPF area?
one DRThere is only one DR and only one BDR per multiaccess-network, i.e. those that use the broadcast or nbma network types. All other OSPF routers should be capable of taking over DR or BDR duties unless explicitely configured not to. But only one of each active at any one time. If its more then you have problems!
How does OSPF choose designated router?
When the first OSPF links are active, the routing device with the highest router identifier (defined by the router-id configuration value, which is typically the IP address of the routing device, or the loopback address) is elected the designated router.
Why BDR is elected first in OSPF?
If two or more routers tie with the highest priority setting, the router sending the hello with the highest Router ID wins. Typically, the router with the second highest priority number becomes the BDR. The priority values range between 0 – 255, with a higher value increasing its chances of becoming DR or BDR.
How do you show DR and BDR?
Two rules are used to elect a DR and BDR:router with the highest OSPF priority will become a DR. By default, all routers have a priority of 1.if there is a tie, a router with the highest router ID wins the election. The router with the second highest OSPF priority or router ID will become a BDR.
What happens when Dr goes down in OSPF?
The DR is an OSPF router representing a multi-access network. And the BDR is the backup of the DR. If the DR goes down, the BDR becomes the next DR. The OSPF router that is neither the DR nor the BDR in a multi-access network is the DROTHER.
Why OSPF uses two multicast address?
OSPF uses two IP multicast addresses on broadcast and point-to-point networks: 225.0. 0.5 for all OSPF routers and 224.0. 0.6 for all DR/BDR (designated router/backup designated router) routers. Using IP multicast addresses is more efficient than using broadcast addresses.
What is the highest OSPF priority?
The OSPFv2 router assigned the highest priority becomes the designated router, and the OSPFv2 router with the second-highest priority becomes the backup router. If you set the priority to 0, the device does not participate in DR and BDR election. The no form of the command restores the default value.
How do I change DR and BDR in OSPF?
DR and BDR Selection RulesThe Priority can be set on the Router Interface using “ip ospf priority” command.The default priority is 1.A priority of 0 means you will never be elected as DR or BDR.You need to use “clear ip ospf process” before this change takes effect.
How do I show priority in OSPF?
You can verify which neighbors are the DR/BDR/DROTHER by using the show ip ospf neighbor command in privileged mode. Configures an OSPF priority on a per interface basis used to manipulate the DR/BDR election process.
Which routers will become the new DR and BDR?
Answer: Router R3 will become the DR and router R1 will become the BDR.
What is the role of a DR in OSPF?
Within OSPF, the role of the Designated Router (DR) and a Backup Designated Router (BDR) is to act as a central point for exchanging of OSPF information between multiple routers on the same, multiaccess broadcast network segment.
What is 2 way state in OSPF?
2-Way. This state designates that bi-directional communication has been established between two routers. Bi-directional means that each router has seen the other's hello packet. This state is attained when the router receiving the hello packet sees its own Router ID within the received hello packet's neighbor field.
What happens when Dr goes down in OSPF?
The DR is an OSPF router representing a multi-access network. And the BDR is the backup of the DR. If the DR goes down, the BDR becomes the next DR. The OSPF router that is neither the DR nor the BDR in a multi-access network is the DROTHER.
What is the highest OSPF priority?
The OSPFv2 router assigned the highest priority becomes the designated router, and the OSPFv2 router with the second-highest priority becomes the backup router. If you set the priority to 0, the device does not participate in DR and BDR election. The no form of the command restores the default value.
What is DR/BDR ?
DR (Designed Router)/BDR (Backup Designated Router) is a router that is chosen to efficiently synchronize LSDB on a multi-access network such as Ethernet. The DR is an OSPF router representing a multi-access network. And the BDR is the backup of the DR. If the DR goes down, the BDR becomes the next DR. The OSPF router that is neither the DR nor the BDR in a multi-access network is the DROTHER.
What is a DR/BDR router?
The DR/BDR is a router that is elected to efficiently synchronize the LSDB on a multi-access network such as Ethernet; OSPF router establishes an adjacency with the DR/BDR, exchanges LSAs, and synchronizes the LSDB.
What is the DR in 192.168.134.0/24?
In 192.168.12.0/24, R2 with high router priority is the DR; in 192.168.134.0/24, R1 with high router priority is the DR. Then, in a multiple-access network, it becomes the adjacency and synchronizes the LSDB with the DR. In a point-to-point network, the DR is not elected, but R1 and R5 are the neighbors i.e., they are the adjacency and synchronize the LSDB. Eventually, the LSDBs of all OSPF routers in R1 to R5 will be synchronized.
What is LSDB synchronization?
LSDB synchronization is ensured on a multi-access network with the DR at the center; if the DR is changed, LSDB synchronization cannot be maintained and packets can no longer be routed. So, Once a DR/BDR is determined, it is kept as unchanged as possible. Even if a router with a higher router priority is added later, the existing DR/BDR will not change. Also, when a DR goes down, the BDR becomes the new DR.
How does OSPF synchronize?
In order to achieve this synchronization, OSPF elects a DR on the multi-access network; it establishes an adjacency between the DR and the OSPF routers on the multi-access network. Each router sends its own LSA to the DR. Each router sends its own LSA to the DR, which means that all LSAs will be gathered in the DR.
What is router priority?
Router Priority and Router ID are both included in the Hello packet. The router priority is an 8-bit value set for the OSPF interface ; in decimal, the value ranges from 0 to 255. The router with the highest router priority value becomes the DR, and the next highest router becomes the BDR. And, Priority “0” means that it will not be DR/BDR.
What is the priority of R1?
In the following figure, R1’s router priority is 5, making it a DR, and R2’s router priority is 2, making it a BDR. Even if we add a new R5 with router priority 10, the DR and BDR will not change.
What is OSPF protocol?
OSPF Routing Protocol is the most used protocol in the world, especially in the world of service provider, through this hand-on-labs workbook, you will discover another aspect of OSPF which is the RFCs that stands for "Request For Comments", A Request for... view more.
What does BGP stand for?
0. Introduction:BGP stands for Border Gateway Protocol , as the name implies it is a protocol that works on our network border devices, BGP is a an application layer protocol and it does work with TCP protocol 179 to establish it's peering connection with nei... view more.
What is the new DR on R4?
The above output of Router R4 shows that new DR is Router R1 since it has got highest priority of 255.
What does R4 output show?
Router R4 output of “ show ip ospf neighbor ” shows that R1 as the DRother.
What does 0 priority mean?
A priority of 0 means you will never be elected as DR or BDR.
Does OSPF come up at the same time?
It is assumed that all OSPF configured Routers come up at same time, the output on R1 and R4 will be as per snapshot below –
What is a BDR in OSPF?
Within OSPF, the role of the Designated Router (DR) and a Backup Designated Router (BDR) is to act as a central point for exchanging of OSPF information between multiple routers on the same, multiaccess broadcast network segment.
What is the default priority for routers?
There are two rules used to determine who is elected: Priority - Router with the highest wins the election. The default priority is 1. This is configured on a per-interface level. Router ID - If there is a tie, the highest router ID wins the election.
Does OSPF have DR/BDR?
Note: OSPF does not elect DR/BDR roles upon point-to-point links, i.e. two directly connected routers. You can find further details on the different OSPF network types at : https://www.ccexpert.us/ospf-network/different-network-types-and-ospf.html.
What is the purpose of OSPF and BDR?
The goal of DR and BDR is to reduce the complexity of the multi-access network from a link state database point-of-view.
How can we influence the election of DR and BDR?
We can influence the election of DR and BDR by configuring explicit Router ID or OSPF priority on the routers.
What is a router that is not elected a DR or a BDR?
A router that is not elected a DR or a BDR is called a DROTHER. The router with the Highest OSPF Priority value will become the DR. In the event that the priorities are the same (Default priority is 1 for all routers), the Router ID becomes the tie breaker.
What does state mean on OSPF router?
The “State” shows that this router has established a “ FULL ” OSPF relationship with the neighbor router. This is the normal state for an OSPF router.
What is the neighbor ID on a router?
The Neighbor ID is the Router ID of the neighbor router. The Router ID is the highest IP address of the device or the highest IP address among loopback addresses (if one is configured) on the Cisco router or can be configured manually by “ router-id a.b.c.d ” command under the OSPF process.
What is a BDR router?
So, if two or more routers are connected on a broadcast network (e.g an Ethernet LAN) and are configured for OSPF, they must select a DR (Designated Router) and a BDR (Backup Designated Router).
What is OSPF routing?
The OSPF (Open Short Path First) dynamic routing protocol is probably the most popular and most used IGP routing protocol in TCP/IP networks. Because OSPF is supported by all networking vendors, it does not have the restrictions of proprietary protocols like Cisco EIGRP for example (in terms of multi-vendor environments etc).
What is a DR and BDR?
DR and BDR serve as the central point for exchanging OSPF routing information. Each non-DR or non-BDR router will exchange routing information only with the DR and BDR, instead of exchanging updates with every router on the network segment.
How to influence DR and BDR election?
You can influence the DR and BDR election process by manually configuring the OSPF priority. This is done by using the ip ospf priority VALUE command interface command.
What is router priority?
By default, all routers have a priority of 1. if there is a tie, a router with the highest router ID wins the election. The router with the second highest OSPF priority or router ID will become a BDR. To better understand the concept, consider the following example.
Which routers are OSPF?
All routers are running OSPF. Routers R1 and R2 have been elected as DR and BDR because they have the highest and the second highest router ID (100.0.0.0 and 90.0.0.0 respectively). If, for example, R3’s directly connected subnet fails, R3 informs R1 and R2 (the DR and BDR for the segment) of the network change (step 1).
Can OSPF routers be DR?
Based on the network type, OSPF router can elect one router to be a Designated Ruter (DR) and one router to be a Backup Designated Router (BDR). For example, on multiaccess broadcast networks (such as LANs) routers defaults to elect a DR and BDR.
Why was OSPF developed?
OSPF protocol was developed due to a need in the internet community to introduce a high functionality non-proprietary Internal Gateway Protocol (IGP) for the TCP/IP protocol family. The discussion of the creation of a common interoperable IGP for the Internet started in 1988 and did not get formalized until 1991. At that time the OSPF Working Group requested that OSPF be considered for advancement to Draft Internet Standard.
What is OSPF protocol?
The Open Shortest Path First (OSPF) protocol, defined in RFC 2328 , is an Interior Gateway Protocol used to distribute routing information within a single Autonomous System. This paper examines how OSPF works and how it can be used to design and build large and complicated networks.
How many databases does an ABR keep?
ABRs will keep a copy of the database for all areas they service. If a router is connected to five areas for example, it will have to keep a list of five different databases. The number of areas per ABR is a number that is dependent on many factors, including type of area (normal, stub, NSSA), ABR CPU power, number of routes per area, and number of external routes per area. For this reason, a specific number of areas per ABR cannot be recommended. Of course, it's better not to overload an ABR when you can always spread the areas over other routers. The following diagram shows the difference between one ABR holding five different databases (including area 0) and two ABRs holding three databases each. Again, these are just guidelines, the more areas you configure per ABR the lower performance you get. In some cases, the lower performance can be tolerated.
What is flooding in OSPF?
As previously mentioned, OSPF uses flooding to exchange link-state updates between routers. Any change in routing information is flooded to all routers in the network. Areas are introduced to put a boundary on the explosion of link-state updates. Flooding and calculation of the Dijkstra algorithm on a router is limited to changes within an area. All routers within an area have the exact link-state database. Routers that belong to multiple areas, and connect these areas to the backbone area are called area border routers (ABR). ABRs must therefore maintain information describing the backbone areas and other attached areas.
How is BDR election done?
DR and BDR election is done via the Hello protocol. Hello packets are exchanged via IP multicast packets (Appendix B) on each segment. The router with the highest OSPF priority on a segment will become the DR for that segment. The same process is repeated for the BDR. In case of a tie, the router with the highest RID will win. The default for the interface OSPF priority is one. Remember that the DR and BDR concepts are per multiaccess segment. Setting the ospf priority on an interface is done using the ip ospf priority <value> interface command.
How does OSPF point to point work?
Administrators do not have to worry about having multiple subnets for each point-to-point link. The cloud is configured as one subnet. This should work well for people who are migrating into the point-to-point concept with no change in IP addressing on the cloud. Also, they would not have to worry about DRs and neighbor statements. OSPF point-to-multipoint works by exchanging additional link-state updates that contain a number of information elements that describe connectivity to the neighboring routers.
What is an ABR router?
A router that has interfaces in multiple areas is called an area border router (ABR). Routers that act as gateways (redistribution)between OSPF and other routing protocols (IGRP, EIGRP, IS-IS, RIP, BGP, Static) or other instances of the OSPF routing process are called autonomous system boundary router (ASBR).
What to do if routers do not elect the correct DR and BDR after setting the OSPF priorities?
Note: If the routers do not elect the correct DR and BDR after setting the OSPF priorities try restarting Packet Tracer.
How to monitor DR and BDR election?
You can monitor the DR and BDR election process with a debug command. On RA and RB, enter the following command.
What to do if show ip ospf neighbor command does not return RB as the?
Note: if the show ip ospf neighbor command does not return RB as the DR and RA as the BDR, turn off debugging on RA and RB with the undebug all command and retry steps 4 and 5.
What does it mean when a router shows FULL/DROTHER?
Use the appropriate command on each router to examine the current DR and BDR. If a router shows FULL/DROTHER it means that the router is not a DR or a BDR.
How to disable debugging in RA?
Enter the command undebug all on RA and RB to disable debugging.
How long does a packet tracer stay amber?
When you first open the file in Packet Tracer, you may notice that the link lights for the switch are amber. These link lights will stay amber for 50 seconds while the STP protocol on the switch makes sure that one of the routers is not another switch.
What does the red font color on the instructor's copy mean?
Instructor Note: Red font color or green highlights indicate text that appears in the instructor copy only.
