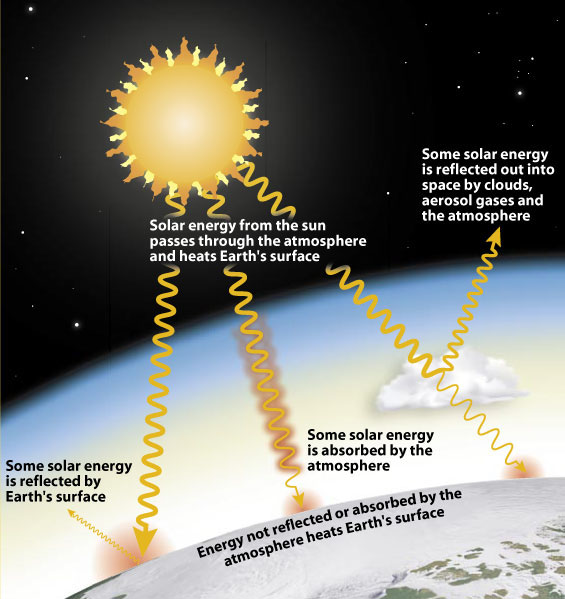
On Earth, however, molecules in the atmosphere absorb the sun’s energy as it arrives, spreading that warmth across the planet. The molecules also trap reflected energy from the surface, preventing the night side of the planet from becoming too cold. The atmosphere serves as a protective shield against radiation and cosmic rays.
How can you improve the atmosphere at work?
“Integrating plants in the work environment not only beautifies the environment but has been proven to reduce absenteeism, reduce stress, lower blood pressure, increase positive feelings, lower noise levels, decrease room temperature and lower humidity,” says Burton Ways. Be a good communicator.
How does the atmosphere help support life on Earth?
The atmosphere supports life on Earth by protecting it from dangerous electromagnetic radiation, by creating and controlling weather and climate and by providing the gases that plants and animals need to breathe. The atmosphere is composed of the troposphere, the tropopause, the stratosphere, the mesosphere and the ionosphere.
How to create a good atmosphere at work?
How to Create An Effective Team Environment
- The Team Environment Is Key. The answer is simple: the environment. ...
- Set Realistic Goals and Expectations. Let’s say the team has been assembled and awaits your instructions. ...
- Support Team Spirit. ...
- Invest In Team Skills. ...
- Show That You Care. ...
- Listen and Respect the Ideas of Others. ...
- Let the process begin! ...
How do humans help the atmosphere?
Summary
- The atmosphere is made of gases that are essential for photosynthesis and respiration, among other life activities.
- The atmosphere is a crucial part of the water cycle. It is an important reservoir for water and the source of precipitation.
- The atmosphere moderates Earth's temperature because greenhouse gases absorb heat.

How does our atmosphere stay in place?
The Short Answer: Earth's gravity is strong enough to hold onto its atmosphere and keep it from drifting into space.
What 3 things does the atmosphere do?
Not only does it contain the oxygen we need to live, but it also protects us from harmful ultraviolet solar radiation. It creates the pressure without which liquid water couldn't exist on our planet's surface. And it warms our planet and keeps temperatures habitable for our living Earth.
Does gravity hold the atmosphere?
Our atmosphere is a mixture of gases that surround Earth. It is kept in place by the pull of Earth's gravity. If Earth was a much smaller planet, like Mercury or Pluto, its gravity would be to weak to hold a large atmosphere.
Can life exist without an atmosphere?
All unprotected plant and animal life on the Earth's surface would die. We can't survive long in a vacuum, which is what we'd have if the atmosphere suddenly vanished. It would be much like being "spaced' or shot out of an airlock, except the initial temperature would be higher. Eardrums would pop.
What will happen if there is no atmosphere on Earth?
In the absence of atmosphere, there would be no life, no rains, no winds, no fires and also no ozone layer that would be used as a protection layer against harmful radiations. The earth was becoming like a moon that had temperatures ranging from −190∘C to 110∘C.
How does Earth's atmosphere not get sucked into space?
The lower the altitude, the higher the air pressure; thus, as you move higher, the air pressure decreases. In fact, at the upper limits of the atmosphere, the air pressure reduces to basically nil. And since there's no real air pressure to speak of up there, then there is no force pushing the air into the empty space.
Why there is no air in space?
Space doesn't have air because there is no gravity to hold it in empty space. air is present at gravitational places like planets. If there is a large amount of gases somewhere, they themselves form gas clouds or nebulae by their own gravity.
Why did Mars lose its atmosphere?
The solar wind stripped away most of the Martian atmosphere in only a few hundred million years after the planet lost its magnetic field. This process was quick because the Sun rotated much faster in its youth, which made the solar wind more energetic.
What are 5 things the atmosphere does for us?
Terms in this set (5) protects us from the sun. protects from metors. gives us oxygen and protein. allows us to stay alive.
What are things in the atmosphere?
We live at the bottom of an invisible ocean called the atmosphere, a layer of gases surrounding our planet. Nitrogen and oxygen account for 99 percent of the gases in dry air, with argon, carbon dioxide, helium, neon, and other gases making up minute portions.
What is the importance of the atmosphere?
The atmosphere is an important part of what makes Earth livable. It blocks some of the Sun's dangerous rays from reaching Earth. It traps heat, making Earth a comfortable temperature. And the oxygen within our atmosphere is essential for life.
How does atmosphere help us Class 3?
Atmosphere has an important role to play in cloud formation and precipitation of rain. Ozone layer present in the stratosphere prevents harmful radiations of the Sun to enter earth surface. Atmosphere exerts pressure on us, known as atmospheric pressure. Atmospheric pressure decreases as we go higher altitudes.
Why is the atmosphere important?
Besides providing us with something to breathe, it shields us from most of the harmful ultraviolet (UV) radiation coming from the Sun, warms the surface of our planet by about 33° C (59° F) via the greenhouse effect, and largely prevents extreme differences between daytime and nighttime temperatures. The other planets in our solar system also have an atmosphere, but none of them have the same ratio of gases and layered structure as Earth's atmosphere.
How does the atmosphere change?
The atmosphere grows thinner (less dense and lower in pressure) as one moves upward from Earth's surface. It gradually gives way to the vacuum of outer space. There is no precise "top" of the atmosphere. Air becomes so thin at altitudes between 100 and 120 km (62-75 miles) up that for many purposes that range of heights can be considered the boundary between the atmosphere and space. However, there are very thin but measurable traces of atmospheric gases hundreds of kilometers/miles above Earth's surface.
What are the different layers of the atmosphere?
There are several different regions or layers in Earth's atmosphere. Each has characteristic temperatures, pressures, and phenomena. We live in the troposphere , the lowest layer, where most clouds are found and almost all weather occurs. Some jet aircraft fly in the next higher layer, the stratosphere, which contains the jet streams and the ozone layer. Temperatures reacj their lowest in the mesosphere, because the there are almost no air molecules there to absorb heat energy. The sky also changes from blue to black in the mesosphere, because there are so few molecules for light to refract off of there. And fartherst from the surface we have the thermosphere , which is the widest layer of the atmosphere and absorbs much of the harmful radiation that reaches Earth from th Sun. The exosphere represents the transition from Earth's atmosphere to space.
What are the gases in the atmosphere?
Gases in Earth's Atmosphere. Nitrogen and oxygen are by far the most common; dry air is composed of about 78% nitrogen (N 2) and about 21% oxygen (O 2 ). Argon, carbon dioxide (CO 2), and many other gases are also present in much lower amounts; each makes up less than 1% of the atmosphere's mixture of gases. The atmosphere also includes water vapor.
What is the average amount of water vapor in the atmosphere?
The atmosphere also includes water vapor. The amount of water vapor present varies a lot, but on average is around 1%. There are also many small particles - solids and liquids - "floating" in the atmosphere.
Which layer of the atmosphere absorbs the most harmful radiation?
And fartherst from the surface we have the thermosphere , which is the widest layer of the atmosphere and absorbs much of the harmful radiation that reaches Earth from th Sun. The exosphere represents the transition from Earth's atmosphere to space.
Which planets have a thinner atmosphere?
The smaller, rocky planets - Earth, Venus and Mars - have much thinner atmospheres hovering above their solid surfaces. The atmospheres on moons in our solar sytem are typically quite thin. Saturn's moon Titan is an exception - air pressure at the surface of Titan is higher than on Earth!
What is the atmosphere?
The atmosphere is a an envelope of gasses that surround the earth or another planet.
Which layer of the atmosphere is responsible for transmitting radio waves?
Ionosphere- Overlaps other atmospheric layers above the earth. The ionized layer affects the transmittance and radio waves.
How far does the thermosphere extend?
Thermosphere- Extends from abot 56 miles to between 311 to 621. Temperature is very hot, don't use a thermometer to take the temperature. You need to look at the motion and speed of the gases. It can be up to thousands of degrees.
Where is the Stratosphere located?
Stratosphere-Found from about 7 to 30 miles from the earth's surface. Contains the ozone layer, which absorbs the most harmful radiation of the sun.
Which planet has the only gas that makes up air?
Earth is the only planet that actually has the combination of gas that makes up air. Even though the term atmosphere really means "sphere of air" earth is the only planet that has this.
What changes the condition closest to the Sun?
Intense solar radiation changed the condition's closest to the sun.
How does the atmosphere help plants?
Many plants also depend on insects and birds to carry their pollen and their seeds to make it possible for them to reproduce. This leads to another thing which the atmosphere does for us. It makes flight possible. Birds and insects could not fly without the air to support them. Without the air, humans would not be able to fly either. The movements of air over the wing of a bird or an airplane creates an upward lift which makes flight possible. Without the lift provided by the air, an airplane would never get off the ground and neither would a bird or a bee.
How does the atmosphere affect weather?
Wind, rain, and snow depend on the atmosphere. The atmosphere provides cool breezes on a hot day and rain to make the trees and flowers grow. Plants could not grow and animals could not survive without water. Rain provides the water we all need and the atmosphere provides the rain. The air evaporates the water from the oceans and carries it over the land in the form of clouds and then deposits that water where it is needed. The water flows into our streams and rivers and out into the ocean where the cycle is repeated. Without the atmosphere, the water could not reach the farmer's fields to grow our food. Very complex weather patterns including trade-winds and jet streams are part of the atmospheric circulation of the air that distributes heat around the earth. Weather is a function of our atmosphere.
Why is the atmosphere important for plants?
The atmosphere is also very important for plants because it contains a small amount of carbon dioxide. Plants use the carbon dioxide (CO2) along with sunshine to carry out a process called photosynthesis. In this process the plants convert the sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients from the ground into energy for them to grow and oxygen for us to breathe. Without enough carbon dioxide in the air, plants can't survive. Also the atmosphere helps plants to grow in another way. Many plants depend on the air to carry pollen from one plant to another in order to create the seeds that are needed to grow new plants. And many of those plants depend on the air to carry the seeds and scatter them around to spread the plants to new areas. Flowers and trees and plants that give us food to eat depend on our atmosphere for their life.
Why do people grow plants in greenhouses?
In a greenhouse people grow plants under the protection of glass or plastic which lets the light come through for the plants to grow, while protecting the plants from cold. In this way people are able to grow plants even in cold weather because the plants stay warm inside the greenhouse. That's the way the atmosphere protects us.
Why do plants need oxygen?
In this process the plants convert the sunlight, carbon dioxide, and nutrients from the ground into energy for them to grow and oxygen for us to breathe. Without enough carbon dioxide in the air, plants can't survive. Also the atmosphere helps plants to grow in another way.
What is the purpose of the atmosphere shield?
A RADIATION SHIELD. The atmosphere of Earth protects us and all living things on the earth from dangerous radiation from the sun. In addition to the light we see, the sun also gives off ultraviolet radiation. Much of it is filtered out by the atmosphere.
Why is ultraviolet radiation important?
Ultraviolet radiation can destroy living cells causing harm to our skin and leading to skin cancer. The sun's rays are important for us. They provide light and heat but they also contain dangerous rays that can harm us. The atmosphere helps to protect us.
What is the atmosphere of Earth?
What is Earth’s atmosphere? Earth’s atmosphere is similar to a jacket for our planet. It surrounds our planet, keeps us warm, gives us oxygen to breathe, and it is where our weather happens. Earth’s atmosphere has six layers: the troposphere, the stratosphere, the mesosphere, the thermosphere, the ionosphere, and the exosphere.
Why is the Earth a jacket?
A jacket for the planet. Earth is a great planet to live on because it has a wonderful atmosphere around it. This jacket of gases does a lot for us. It keeps us warm, it gives us oxygen to breathe, and it’s where our weather happens. The atmosphere surrounds our planet like the peel of an orange. But it’s not the same everywhere.
Is the atmosphere the same everywhere?
The atmosphere surrounds our planet like the peel of an orange. But it’s not the same everywhere. It has different layers with different qualities.
Why does the Earth's atmosphere move so fast?
Molecules in our atmosphere are constantly moving, spurred on by energizing sunlight. Some move quickly enough to escape the grip of Earth’s gravity. The escape velocity for planet Earth is a little over 11 kilometers per second – about 25 thousand miles an hour. If Earth were much less massive – say, as massive as Mars – gravity’s grip would be weaker. That’s one reason why Mars lost most of its original atmosphere.
Why did Mars lose its atmosphere?
If Earth were much less massive – say, as massive as Mars – gravity’s grip would be weaker. That’s one reason why Mars lost most of its original atmosphere. In the vicinity of our heavier Earth, where gravity is stronger than on Mars, not all particles are equally likely to escape.
What is the force that keeps us anchored to Earth?
The answer is gravity – the same force that keeps us anchored to Earth.
Is the atmosphere escaping to space?
So, thanks to gravity, although some of Earth’s atmosphere is escaping to space, most is staying here.
Is the atmosphere good for Earth?
Still, all in all, Earth’s atmosphere is here to stay. And that’s a good thing because our atmosphere protects life on Earth in many ways. It absorbs harmful ultraviolet radiation from the sun, helps keep Earth’s surface warm via the greenhouse effect, and reduces temperature extremes between day and night. Yay atmosphere! It keeps Earth livable.
Why is the atmosphere important?
The atmosphere is vital for all life on the planet, not only humans, and for reasons other than supplying gases needed for respiration and photosynthesis. Winds also transport water into the interiors of large areas of land, which would otherwise rapidly become parched desert.
How does the troposphere respond to the atmosphere?
A Perfect Planet emphasises how different elements of our environment are interconnected. The atmosphere responds to varying heating by sunlight, driving movement. These motions in the troposphere are what we experience as wind. The oceans supply water vapour, which absorbs and releases heat, forms clouds and scatters sunlight. The patterns of continents, oceans and sea ice at the surface determine the heating that drives the troposphere from below. Volcanic activity has outgassed the atmosphere itself from the body of the forming planet and continues to supply many trace gases and small particulates to the mix. Variations in volcanic output are connected to sometimes huge climate changes. Life has modified the composition of the atmosphere, resulting in the present range of gases, which is very different to the carbon dioxide-dominated atmospheres of Venus and Mars. Now humans are leaving our own mark in pollutants and greenhouse gases.
What is the altitude of the Meteosat 11?
Earth viewed by Meteosat-11 on 10 February 2019. Meteosat-11 is a geostationary satellite that orbits at an altitude of over 36,000 km above the equator, with a period of one day. It therefore hovers above a point on the Earth's surface, close to longitude = 0 degrees, latitude = 0 degrees.
What determines the heating of the troposphere?
The patterns of continents, oceans and sea ice at the surface determine the heating that drives the troposphere from below. Volcanic activity has outgassed the atmosphere itself from the body of the forming planet and continues to supply many trace gases and small particulates to the mix.
What is the atmosphere above the troposphere called?
The atmosphere above the troposphere is called the stratosphere and appears a clear, blue colour in the image. In the stratosphere the temperature begins to rise again with increasing height. In contrast to the troposphere, the stratosphere is very stable, or stratified, as implied by the name.
How much less is the atmosphere than the ocean?
The mass of the atmosphere is about 250 times less than that of the oceans and accounts for less than one millionth of the total mass of the planet. The atmospheric pressure and density of air decrease exponentially with height above the surface.
Why do we need oxygen?
A basic necessity for humans is to breathe oxygen at a sufficient pressure for our respiratory system to work. Complex, multicellular life on Earth needs an atmosphere for either respiration or photosynthesis. Even aquatic species rely on dissolved oxygen from the air.
How does the atmosphere work?
There are different types of layers in the atmosphere, and they do different things, mainly they prevent the harmful rays of the sun from reaching the earth and gives the opportunities to live on earth. You’ll read about them down below. Why nuclear weapons should be banned.
What is the atmosphere?
What is Atmosphere. Our earth is surrounded by different types of colorless gases, odorless, tasteless, and compressible, and this is known as the atmosphere. Due to the seasonal movement, the atmosphere is considered to be the most dynamic among the major atmospherical factors.
How much of the atmosphere is around the Earth?
About 99 percent of the total mass of the atmosphere is at an altitude of 32 kilometers from our land. Most changes and atmospherical phenomena also occur there. And due to the force of gravity, there is an atmosphere around our earth.
Where does the atmosphere end?
There are five major layers, the first is the troposphere in which we live, and the last is the ecosphere where our satellites are working, the ecosphere is about 10,000 kilometers above from the surface of our planet, and there our atmosphere does end.
Which layer of the atmosphere is the most affected by volcanic eruptions?
There are different types of layers in our atmosphere but we live in the Troposphere layer, In this layer, all the weather takes place such as snow and rain, which about 8 kilometers thick layer. However, when a volcanic eruption, so the material from the eruption pushes through the troposphere and then enters the stratosphere.
What protects the Earth from the sun?
The ozone layer protects our earth from the ultraviolet rays of the sun, which are harmful to living organisms.
What gases formed the atmosphere?
About 4.6 billion years ago, when our Earth began to cool, volcanoes released the types of gases that formed our Earth’s atmosphere, at that time there was methane gas, hydrogen sulfide, and 200 times more carbon dioxide than today’s atmosphere.