What is the pathway of oxygen poor blood through the heart?
. Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the heart's right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
How does oxygen travel around the body?
The lungs, blood, heart and blood vessels work together to carry oxygen around the body. Air first enters the body through the nose or mouth and then goes into the larynx, trachea and the lungs, explains the NRPT.
How does the blood flow through the heart?
How Does the Blood Flow Through Your Heart 1 Right Side. Blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through... 2 Left Side. Blood flows from your left atrium into your left ventricle through the open mitral valve. 3 Blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve,... 4 Blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve,...
What is the pathway of oxygen and carbon dioxide through the body?
Oxygen and carbon dioxide travels to and from tiny air sacs in the lungs, through the walls of the capillaries, into the blood. Blood leaves the heart through the pulmonic valve, into the pulmonary artery and to the lungs. Blood leaves the heart through the aortic valve, into the aorta and to the body.
What is the piping of the heart that feeds it?
The coronary arteries are the piping of the heart that feeds it, much like the plumbing of a house that brings water to different places of use. Read more: coronary arteries. . Any reduction in the oxygen supply can have serious and sometimes irreversible consequences for the heart.
What is the posterior interventricular artery?
In one person out of ten, the posterior interventricular artery is a branch of the circumflex coronary artery on the left side of the heart. Blood is composed of red cells, white cells, platelets and plasma.
Why is the intima important?
The intima thus helps keep the artery at a larger size where necessary.
What is the name given to the pain caused by the lack of oxygen in the heart felt on exertion?
Heart medications affect these factors. In the case of certain diseases, like angina . Angina, is the name given to the pain caused by the lack of oxygen in the heart felt on exertion, relieved by rest and reproducible to a similar effort. Read more: angina.
Which artery follows the contour of the heart?
The right coronary artery follows the contour of the heart on the right and, in nine people out of ten, descends behind the heart towards the apex. It follows the posterior groove where the right ventricle meets the left ventricle. This part of the artery is called the posterior interventricular artery.
How to determine oxygen needs?
In the heart, oxygen needs are determined by: 1 The adequate filling of the left ventricle; it must be neither too empty nor too full 2 The left ventricle’s resistance to emptying its contents into the aorta 3 The strength of its contractions 4 The heart rate
What are the arteries that branch out from it called?
The arteries that branch out from it are called the diagonal branches.
What are the small blood vessels that connect the arteries and veins?
Capillaries. These are small, thin blood vessels that connect the arteries and the veins. Their thin walls allow oxygen, nutrients, carbon dioxide, and other waste products to pass to and from our organ's cells.
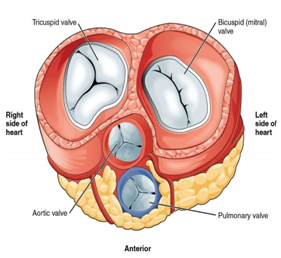
How do heart valves work?
The heart valves work the same way as one-way valves in the plumbing of your home. They prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction . Each valve has a set of flaps, called leaflets or cusps. The mitral valve has two leaflets; the others have three.
How many types of blood vessels are there?
There are three main types of blood vessels:
What is the heart?
Your heart is a key part of your cardiovascular system, which also includes all your blood vessels that carry blood from the heart to the body and then back to the heart.
What is the name of the muscle that divides the heart?
It is divided into the left and right side by a muscular wall called the septum. The right and left sides of the heart are further divided into two top chambers called the atria, which receive blood from the veins, and two bottom chambers called ventricles, which pump blood into the arteries.
How does the heart work?
How the Heart Works. The heart is an amazing organ. It pumps oxygen and nutrient-rich blood throughout your body to sustain life. This fist-sized powerhouse beats (expands and contracts) 100,000 times per day, pumping five or six quarts of blood each minute, or about 2,000 gallons per day.
What is the blood vessel that takes blood back to the heart?
Veins. These are blood vessels that take blood back to the heart; this blood has lower oxygen content and is rich in waste products that are to be excreted or removed from the body. Veins become larger and larger as they get closer to the heart.
Pathway of Blood Through the Heart
In this educational lesson, we learn about the blood flow order through the human heart in 14 easy steps, from the superior and inferior vena cava to the atria and ventricles.
14 Steps of Blood Flow Through the Heart
In summary from the video, in 14 steps, blood flows through the heart in the following order: 1) body –> 2) inferior/superior vena cava –> 3) right atrium –> 4) tricuspid valve –> 5) right ventricle –> 6) pulmonary arteries –> 7) lungs –> 8) pulmonary veins –> 9) left atrium –> 10) mitral or bicuspid valve –> 11) left ventricle –> 12) aortic valve –> 13) aorta –> 14) body..
Summary: What are the 14 steps of blood flow through the heart?
Blood flows through the heart in the following order: 1) body –> 2) inferior/superior vena cava –> 3) right atrium –> 4) tricuspid valve –> 5) right ventricle –> 6) pulmonary arteries –> 7) lungs –> 8) pulmonary veins –> 9) left atrium –> 10) mitral or bicuspid valve –> 11) left ventricle –> 12) aortic valve –> 13) aorta –> 14) body.
Why is oxygen transported in the blood?
Only a small amount of oxygen is transported in the plasma of the blood because oxygen does not dissolve easily in water. The rest of the oxygen is transported after combining with the hemoglobin in red blood cells. The NRPT notes that the heart is a vital organ for moving oxygen around the body, and it pumps approximately 70 times each minute.
How does oxygen travel through the body?
Follow Us: Oxygen is transported throughout the body via the cardiovascular system, according to the National Register of Personal Trainers, or NRPT. The lungs, blood, heart and blood vessels work together to carry oxygen around the body. Air first enters the body through the nose or mouth and then goes into the larynx, trachea and the lungs, ...
Where does oxygen enter the body?
Air first enters the body through the nose or mouth and then goes into the larynx, trachea and the lungs , explains the NRPT. Air passes through bronchial tubes in the lungs until it reaches the alveoli, tiny air sacs in the lungs where the exchange of oxygen and carbon dioxide takes place. The alveoli enable the oxygen to be transferred into the blood. Once it is in the blood, transportation of oxygen around the body begins. Only a small amount of oxygen is transported in the plasma of the blood because oxygen does not dissolve easily in water. The rest of the oxygen is transported after combining with the hemoglobin in red blood cells.
Why does the heart need to beat?
It needs to beat continuously to push the oxygen and nutrients that the body needs. The heart works with the arteries, the network of blood vessels that weave between all parts of the body, to accomplish this. Blood passes through the arteries, which are elastic and expand when the heart pumps blood. Oxygen is thus pushed into organs as the blood ...
Which part of the body is pushed into by oxygen?
Blood passes through the arteries, which are elastic and expand when the heart pumps blood. Oxygen is thus pushed into organs as the blood flows. The muscles in the arteries' walls contract when the heart relaxes to push the blood. ADVERTISEMENT.
Heart valves
Heart valves control the flow of blood so that it moves in the right direction. The valves prevent blood from flowing backward.
Adding oxygen to blood
Oxygen-poor blood from the body enters your heart through two large veins called the superior and inferior vena cava. The blood enters the heart's right atrium and is pumped to your right ventricle, which in turn pumps the blood to your lungs.
What is oxygen extraction?
Oxygen extraction considers the amount of oxygen in arterial blood that is sent to metabolically active tissue, and the amount of oxygen in venous blood being returned to the heart. The difference in arterial oxygen content and venous oxygen content determines the amount of oxygen that was used by the tissue. ...
What is the difference between VO2 and VO2?
Oxygen consumption, abbreviated VO2, is a measure of the volume of oxygen used by the body. VO2, as described by Dr. Benjamin Levine, is based on the Fick equation, which says oxygen consumption is dependent on the product of oxygen delivery and extraction. Oxygen extraction considers the amount of oxygen in arterial blood that is sent to metabolically active tissue, and the amount of oxygen in venous blood being returned to the heart. The difference in arterial oxygen content and venous oxygen content determines the amount of oxygen that was used by the tissue. Oxygen delivery, on the other hand, is a measure of cardiac function, specifically of cardiac output. Cardiac output determines the amount of blood pumped from the heart every beat. Cardiac output is the product of heart rate and stroke volume, or the amount of blood pumped per beat.
What is VO2 in medical terms?
Oxygen consumption, abbreviated VO2, is a measure of the volume of oxygen used by the body. VO2, as described by Dr. Benjamin Levine, is based on the Fick equation, which says oxygen consumption is dependent on the product of oxygen delivery and extraction. Oxygen extraction considers the amount of oxygen in arterial blood ...
Why does the heart rate increase when you exercise?
Naturally, as the body moves from rest to exercise, the heart rate begins to steadily increase. This cardiovascular response allows for faster oxygen delivery to the working tissue, such as skeletal muscle, which allows for an increase in oxygen consumption.
Why does oxygen consumption decrease?
Diseases of the cardiovascular system tend to cause a decrease in oxygen consumption that limits an individual's ability to engage in physical activity. The nature of heart failure, for example, prevents the heart from adequately increasing heart rate. Without the increase in heart rate, oxygen delivery, and therefore oxygen consumption, is limited.
What is the determining factor of oxygen consumption?
Heart rate is a determining factor of oxygen consumption. The cardiovascular and respiratory systems are linked in such a way that one cannot function without the other. These two systems work together to allow metabolism to occur in all systems throughout the body by delivering oxygen and removing wastes. Video of the Day.
What is oxygen delivery?
Oxygen delivery, on the other hand, is a measure of cardiac function, specifically of cardiac output. Cardiac output determines the amount of blood pumped from the heart every beat. Cardiac output is the product of heart rate and stroke volume, or the amount of blood pumped per beat.
What does the heart look like and how does it work?
It starts beating about 22 days after conception and continuously pumps oxygenated red blood cells and nutrient-rich blood and other compounds like platelets throughout your body to sustain the life of your organs.
How can you prevent heart attacks and strokes?
According to the American Heart Association, no matter what age you are, your heart can benefit from a healthy diet and adequate physical activity. Tthere are numerous specific suggestions about how you can decrease your risk for heart disease. For example:
What is the valve that prevents backflow of blood?
When blood leaves each chamber of the heart, it passes through a valve that is designed to prevent backflow of blood. There are four heart valves within the heart: Mitral valve between the left atrium and left ventricle. Tricuspid valve between the right atrium and right ventricle.
What are the two parts of the heart that work sequentially?
Normal heart anatomy and physiology. Normal heart anatomy and physiology need the atria and ventricles to work sequentially, contracting and relaxing to pump blood out of the heart and then to let the chambers refill.
Which artery supplies the left ventricle with blood?
The circumflex artery supplies blood to the left atrium, side and back of the left ventricle, and the left anterior descending artery supplies the front and bottom of the left ventricle and the front of the septum with blood. These arteries and their branches supply all parts of the heart muscle with blood.
How do heart valves work?
How the heart valves work. The heart valves work the same way as one-way valves in the plumbing of your home. They prevent blood from flowing in the wrong direction. Each valve has a set of flaps, called leaflets or cusps. The mitral valve has two leaflets; the others have three.
Where does blood enter the heart?
Blood enters the heart through two large veins, the inferior and superior vena cava, emptying oxygen-poor blood from the body into the right atrium of the heart. As the atrium contracts, blood flows from your right atrium into your right ventricle through the open tricuspid valve.