What are the symptoms of atelectasis?
What are the symptoms of atelectasis?
- Breathing difficulty
- Low-grade fever
- Wheezing
- Increased heart rate
- Coughing
- Chest pain
- Bluish discoloration of skin and lips
What is treatment for atelectasis?
Treatments include:
- Aerosolized respiratory treatments to open the airway
- Positioning the body on the unaffected side to allow the lung to re-expand
- Removing obstructions by bronchoscopy
- Breathing exercises (incentive spirometry)
- Clap, or percussion, on the chest to loosen mucus
- Tilting the body (postural drainage) so that the head is lower than the chest to drain mucus
What are nursing interventions for atelectasis?
nursing interventions for atelectasis Nursing measures to prevent atelectasis include frequent turning, early mobilization, and strategies to expand the lungs and to manage secretions. Voluntary deep-breathing maneuvers. incentive spirometer & deep breathing the goal for atelectasis
What does mild atelectasis mean?
Mild atelectasis is typically the result of inhaling large amounts of air (hyperinflation) or by lying down when you exhale (apnea). These changes in posture can cause your diaphragm to contract, which can lead to mild atelectasis. Treatment for mild atelectasis
Why does atelectasis occur in pulmonary embolism?
Surfactant reduces surface tension and keeps the alveoli open. In conditions where there is loss of surfactant, the alveoli collapse and become atelectatic. In ARDS this occurs diffusely to both lungs. In pulmonary embolism due to loss of blood flow and lack of CO2, the integrity of surfactant gets impaired.
Can blood clots cause atelectasis?
1. Blood clot may occur following an episode of massive hemoptysis and may result in partial or complete atelectasis of lung.
Can a pulmonary embolism cause a collapsed lung?
A medium sized clot may cause breathing problems and chest pain. In more severe cases, the lung might collapse. PE can lead to heart failure and can be fatal.
What is the most common cause of atelectasis?
Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive). General anesthesia is a common cause of atelectasis. It changes your regular pattern of breathing and affects the exchange of lung gases, which can cause the air sacs (alveoli) to deflate.
What is the pathophysiology of atelectasis?
Atelectasis describes the loss of lung volume due to the collapse of lung tissue. It can be classified according to the pathophysiologic mechanism (eg, compressive atelectasis), the amount of lung involved (eg, lobar, segmental, or subsegmental atelectasis), or the location (ie, specific lobe or segment location).
What is the difference between atelectasis and pneumothorax?
A collapsed lung happens when air enters the pleural space, the area between the lung and the chest wall. If it is a total collapse, it is called pneumothorax. If only part of the lung is affected, it is called atelectasis.
What happens when a blood clot goes to your lungs?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) can cause a lack of blood flow that leads to lung tissue damage. It can cause low blood oxygen levels that can damage other organs in the body, too. A PE, particularly a large PE or many clots, can quickly cause serious life-threatening problems and, even death.
What are the complications of pulmonary embolism?
Complications of pulmonary embolism include the following:Sudden cardiac death.Obstructive shock.Pulseless electrical activity.Atrial or ventricular arrhythmias.Secondary pulmonary arterial hypertension.Cor pulmonale.Severe hypoxemia.Right-to-left intracardiac shunt.More items...•
Why do you cough up blood with pulmonary embolism?
PE can lead to further blood clots, obstructions, and smaller infarcts — or areas where tissue has died from a lack of oxygen. The increased pressure or lack of oxygen can damage your lung tissue, causing bleeding. This can appear as blood in your sputum.
What are the 3 types of atelectasis?
The term atelectasis can also be used to describe the collapse of a previously inflated lung, either partially or fully, because of specific respiratory disorders. There are three major types of atelectasis: adhesive, compressive, and obstructive.
What lung sounds do you hear with atelectasis?
ATELECTATIC crackles, as the name would suggest, are heard when a portion of the lung is collapsed and airless. They are relatively quiet, end-inspiratory crackles....They often result from:atelectasis,congestive heart failure (CHF), or.pulmonary fibrosis.
What is resorption atelectasis and when is it likely to occur?
Obstructive atelectasis is often referred to as resorptive atelectasis and occurs when alveolar air gets absorbed distal to an obstructive lesion. The obstruction either partially or completely inhibits ventilation to the area. Perfusion to the area is maintained; however, so gas uptake into the blood continues.
What does atelectasis mean on a CT scan?
Atelectasis refers to either incomplete expansion of the lungs or the collapse of previously inflated lungs, which produces areas of relatively airless pulmonary parenchyma.
What can cause a partially collapsed lung?
Collapsed lung can be caused by an injury to the lung. Injuries can include a gunshot or knife wound to the chest, rib fracture, or certain medical procedures. In some cases, a collapsed lung is caused by air blisters (blebs) that break open, sending air into the space around the lung.
Can mild atelectasis go away?
Mild atelectasis may go away without treatment. Sometimes, medications are used to loosen and thin mucus. If the condition is due to a blockage, surgery or other treatments may be needed.
How long does it take for atelectasis to heal?
The condition typically develops after a person goes under general anesthetic, or if they have a condition that impacts the lungs or structures and organs surrounding them. Most people recover from atelectasis with proper treatment within 24 hours.
Where does pulmonary embolism occur?
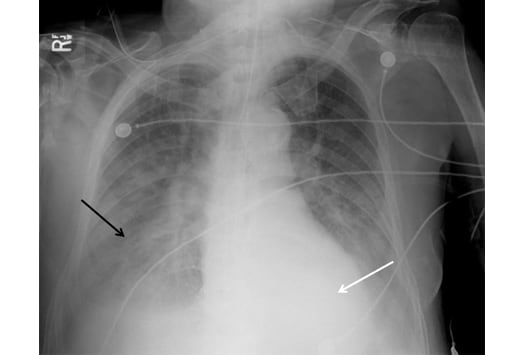
Pulmonary embolism occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets wedged into an artery in your lungs. These blood clots most commonly come from the deep veins of your legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT).
How to get rid of pulmonary embolism?
Elevating your legs when possible and during the night also can be very effective. Raise the bottom of your bed 4 to 6 inches (10 to 15 cm) with blocks or books. Physical activity. Moving as soon as possible after surgery can help prevent pulmonary embolism and hasten recovery overall.
What is PE in a lung?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) occurs when a blood clot gets lodged in an artery in the lung, blocking blood flow to part of the lung. Blood clots most often start in the legs and travel up through the right side of the heart and into the lungs. This is called DVT. However, PE sometimes can occur without any evidence of DVT.
What is it called when you have multiple clots in your lungs?
The portions of lung served by each blocked artery are robbed of blood and may die. This is known as pulmonary infarction. This makes it more difficult for your lungs to provide oxygen to the rest of your body.
What is the best treatment for pulmonary embolism?
For this reason, most hospitals are aggressive about taking measures to prevent blood clots, including: Blood thinners (anticoagulants).
What are the symptoms of pulmonary embolism?
Other signs and symptoms that can occur with pulmonary embolism include: Rapid or irregular heartbeat. Lightheadedness or dizziness. Excessive sweating. Fever. Leg pain or swelling, or both, usually in the calf caused by a deep vein thrombosis.
Can pulmonary embolism cause high blood pressure?
Pulmonary embolism can also lead to pulmonary hypertension, a condition in which the blood pressure in your lungs and in the right side of the heart is too high. When you have obstructions in the arteries inside your lungs, your heart must work harder to push blood through those vessels, which increases blood pressure and eventually weakens your heart.
What is a pulmonary embolism?
A pulmonary embolism (PE) is a blood clot that develops in a blood vessel in the body (often in the leg). It then travels to a lung artery where it suddenly blocks blood flow.
How is pulmonary embolism diagnosed?
Pulmonary embolism (PE) is often difficult to diagnose because the symptoms of PE are a lot like those of many other conditions and diseases.
What is the circulatory system?
The heart, arteries, capillaries, and veins make up the body's circulatory system. Blood is pumped with great force from the heart into the arteries. From there blood flows into the capillaries (tiny blood vessels in the tissues). Blood returns to the heart through the veins. As it moves through the veins back to the heart, blood flow slows. Sometimes this slower blood flow may lead to clot formation.
Why is PE so difficult to diagnose?
PE is often difficult to diagnose because the signs and symptoms of PE are a lot like those of many other conditions and diseases. Imaging tests and blood tests are used to look for a PE.
Why is it important to treat PE?
An important aspect of treating a PE is preventive treatment to prevent formation of additional embolisms.
Can you get anticoagulation for PE?
Rarely used, this is surgery done to remove a PE. It is generally done only in severe cases when your PE is very large, you can't get anticoagulation and/or thrombolytic therapy due to other medical problems or you haven't responded well to those treatments, or your condition is unstable.
Can a PE cause death?
A PE, particularly a large PE or many clots, can quickly cause serious life-threatening problems and, even death.
Why does atelectasis occur after heart surgery?
A mucus plug is a buildup of mucus in your airways. It commonly occurs during and after surgery because you can't cough.
What causes nonobstructive atelectasis?
Possible causes of nonobstructive atelectasis include: Injury. Chest trauma — from a fall or car accident, for example — can cause you to avoid taking deep breaths (due to the pain), which can result in compression of your lungs. Pleural effusion.
How to prevent atelectasis in children?
Prevention. Atelectasis in children is often caused by a blockage in the airway. To decrease atelectasis risk, keep small objects out of reach of children. In adults, atelectasis most commonly occurs after major surgery. If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk.
What is the most common respiratory complication after surgery?
Atelectasis is one of the most common breathing (respiratory) complications after surgery. It's also a possible complication of other respiratory problems, including cystic fibrosis, lung tumors, chest injuries, fluid in the lung and respiratory weakness. You may develop atelectasis if you breathe in a foreign object.
What is the term for a complete collapse of the lung?
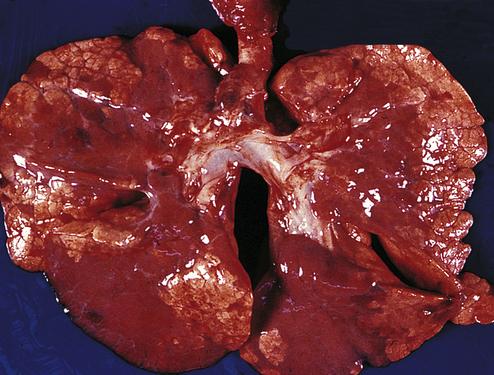
Atelectasis (at-uh-LEK-tuh-sis) is a complete or partial collapse of the entire lung or area (lobe) of the lung. It occurs when the tiny air sacs (alveoli) within the lung become deflated or possibly filled with alveolar fluid.
How to reduce the risk of atelectasis?
Some research suggests that certain breathing exercises and muscle training may lower the risk of atelectasis after certain surgeries. By Mayo Clinic Staff.
Where does atelectasis occur?
Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive).
What Is Atelectasis?
Atelectasis is a lung condition that happens when your airways or the tiny sacs at the end of them don’t expand the way they should when you breathe.
What are the two types of atelectasis?
Types of Atelectasis. The two main types of atelectasis are obstructive (also called resorptive) and nonobstructive. Obstructive atelectasis happens when something physically blocks your airway. Types of nonobstructive atelectasis include: Relaxation or compressive.
What is the fluid that lines the alveoli called?
Adhesive. The fluid that lines the alveoli in your lungs has a material in it called pulmonary surfactant. It helps your lungs in several ways, including keeping the alveoli stable and able to work. If there's a problem with this material (like if your body doesn’t make enough of it), the alveoli can collapse. When that happens, it's called adhesive atelectasis. It can be caused by serious lung problems such as respiratory distress syndrome or a bruised lung (pulmonary contusion).
What happens when you breathe in and out?
When you breathe in and out, your lungs inflate and deflate like balloons. But if your airways get blocked or something puts pressure on your lungs, they might not inflate the way they should. Doctors call that condition atelectasis. It can be life-threatening in small children or people who have another lung problem.
Why do my lungs have scars?
This scarring can happen because of certain serious lung conditions like sarcoidosis. Replacement. This is when your alveoli are filled by a tumor.
What is the name of the tube that separates the airways in the lungs?
When you breathe in, air flows into your windpipe, or trachea. The trachea splits into two channels called bronchi, and each bronchus goes to a lung. Inside your lungs, those airways divide again and again into smaller tubes called bronchioles. At the end of the smallest bronchioles are tiny sacs called alveoli.
What happens when air builds up in the lungs?
But if fluid or air builds up and separates them, your lungs can pull inward, and your alveoli can lose air. Depending on where this happens in your lung, it's either relaxation or compressive atelectasis. Adhesive. The fluid that lines the alveoli in your lungs has a material in it called pulmonary surfactant.
Why does atelectasis occur after heart surgery?from mayoclinic.org
A mucus plug is a buildup of mucus in your airways. It commonly occurs during and after surgery because you can't cough.
Where does atelectasis occur?from mayoclinic.org
Atelectasis occurs from a blocked airway (obstructive) or pressure from outside the lung (nonobstructive).
How to prevent atelectasis in children?from mayoclinic.org
Prevention. Atelectasis in children is often caused by a blockage in the airway. To decrease atelectasis risk, keep small objects out of reach of children. In adults, atelectasis most commonly occurs after major surgery. If you're scheduled for surgery, talk with your doctor about strategies to reduce your risk.
What is pulmonary embolism?from epainassist.com
Pulmonary embolism is a pathology with a high incidence in our environment. The deleterious, hemodynamic changes that develop once the embolism has been established, determine the serious and acute complications that this event frames. Advertisement.
What causes a lung to collapse?from mayoclinic.org
Air leaks into the space between your lungs and chest wall, indirectly causing some or all of a lung to collapse. Scarring of lung tissue. Scarring could be caused by injury, lung disease or surgery. Tumor. A large tumor can press against and deflate the lung, as opposed to blocking the air passages.
What is the term for the buildup of fluid between the tissues that line the lungs and the inside of the chest?from mayoclinic.org
Pleural effusion. This condition involves the buildup of fluid between the tissues (pleura) that line the lungs and the inside of the chest wall.
Can atelectasis be distal?from epainassist.com
Atelectasis can develop in areas distal to embolic obstruction and with subsequent dissolution or with distal migration of the embolic material ; there is reperfusion of these pulmonary areas. The reversal of post-embolic hypoxemia with positive pressure ventilation supports the belief in this theory. Atelectasis can have many causes.
What is atelectasis in pulmonary opacification?
Types and mechanisms of pulmonary atelectasis. Atelectasis is one of the most commonly encountered abnormalities in chest radiology and remains a daily diagnostic challenge. At times atelectasis can be overlooked, particularly when pulmonary opacification is minimal or absent, and at other times it might be interpreted as being some other form o ….
What is atelectasis in radiology?
Atelectasis is one of the most commonly encountered abnormalities in chest radiology and remains a daily diagnostic challenge. At times atelectasis can be overlooked, particularly when pulmonary opacification is minimal or absent, and at other times it might be interpreted as being some other form o ….
What are the signs of atelectasis?
Indirect signs of atelectasis are pulmonary opacification; elevation of the diaphragm; shift of the trachea, heart, and mediastinum; displacement of the hilus; compensatory hyperexpansion of the surrounding lung; approximation of the ribs; and shifting granulomas.
What is the diagnosis of atelectatic pneumonia?
The diagnosis of atelectatic pneumonia should be based upon the presence of clinical signs and symptoms of pneumonia coupled with the identification of pathogenic bacteria in sputum, tracheal aspirates, or protected bronchoalveolar lavage or bronchial brush specimens rather than on the radiographic identification of atelectasis alone.
What are the different types of atelectasis?
For descriptive purposes, atelectasis can be divided into the following types: segmental, lobar, or whole lung; subsegmental; platelike, linear, or discoid; round; and generalized or diffuse. Resorption atelectasis is caused by resorption of alveolar air distal to obstructing lesions of the airways; adhesive atelectasis stems from surfactant ...
Is atelectasis a chest abnormality?
Atelectasis is one of the most commonly encountered abnormalities in chest radiology and remains a daily diagnostic challenge. At times atelectasis can be overlooked, particularly when pulmonary opacification is minimal or absent, and at other times it might be interpreted as being some other form of intrathoracic pathology, particularly pneumonia. ...
What causes a pleural effusion?
Some patients with ascites have diaphragmatic defects that allow ascites fluid to flow into the chest, causing a pleural effusion termed a hydrothorax.
Why is pulmonary angiography rarely performed?
Pulmonary angiography is rarely performed to diagnose HPS because of the procedure’s invasiveness and risk. It is reserved for complex patients to look for large arteriovenous malformations, which may be amenable to coiling/embolization.
Why is pulmonary function testing nonspecific?
Pulmonary function testing typically demonstrates a reduced diffusing capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO) because of the longer distances needed for gas exchange and hemoglobin binding between alveoli and dilated pulmonary capillaries. However, this finding is nonspecific. In the absence of other lung disease or diaphragmatic elevation from ascites, patients with HPS have normal measured airflow and normal lung volumes.

Overview
Symptoms
- Pulmonary embolism symptoms can vary greatly, depending on how much of your lung is involved, the size of the clots, and whether you have underlying lung or heart disease. Common signs and symptoms include: 1. Shortness of breath.This symptom typically appears suddenly and always gets worse with exertion. 2. Chest pain.You may feel like you're having a heart attack…
Causes
- Pulmonary embolism occurs when a clump of material, most often a blood clot, gets wedged into an artery in your lungs. These blood clots most commonly come from the deep veins of your legs, a condition known as deep vein thrombosis (DVT). In many cases, multiple clots are involved in pulmonary embolism. The portions of lung served by each blocked artery are robbed of blood an…
Risk Factors
- Although anyone can develop blood clots and subsequent pulmonary embolism, certain factors can increase your risk.
Complications
- Pulmonary embolism can be life-threatening. About one-third of people with undiagnosed and untreated pulmonary embolism don't survive. When the condition is diagnosed and treated promptly, however, that number drops dramatically. Pulmonary embolism can also lead to pulmonary hypertension, a condition in which the blood pressure in your lungs and in the right si…
Prevention
- Preventing clots in the deep veins in your legs (deep vein thrombosis) will help prevent pulmonary embolism. For this reason, most hospitals are aggressive about taking measures to prevent blood clots, including: 1. Blood thinners (anticoagulants).These medications are often given to people at risk of clots before and after an operation — as well as to people admitted to the hospital with m…